- SLA 3D Printed Connectors with Gaskets Durable Resin Prototype
- SLM 3D Print Aluminum Sample with Mirror Polish Finishing
Gallery
About Project
Do you want to know how to design your metal parts for DMLS 3D printing and surface finishing? If so, you might want to check out our latest project: a polished aluminum sample strip with different stages of thickness.
DMLS stands for direct metal laser sintering, which is a 3D printing technology that uses a laser to fuse metal powder into solid parts. DMLS can produce complex and functional metal parts with high accuracy and mechanical properties.
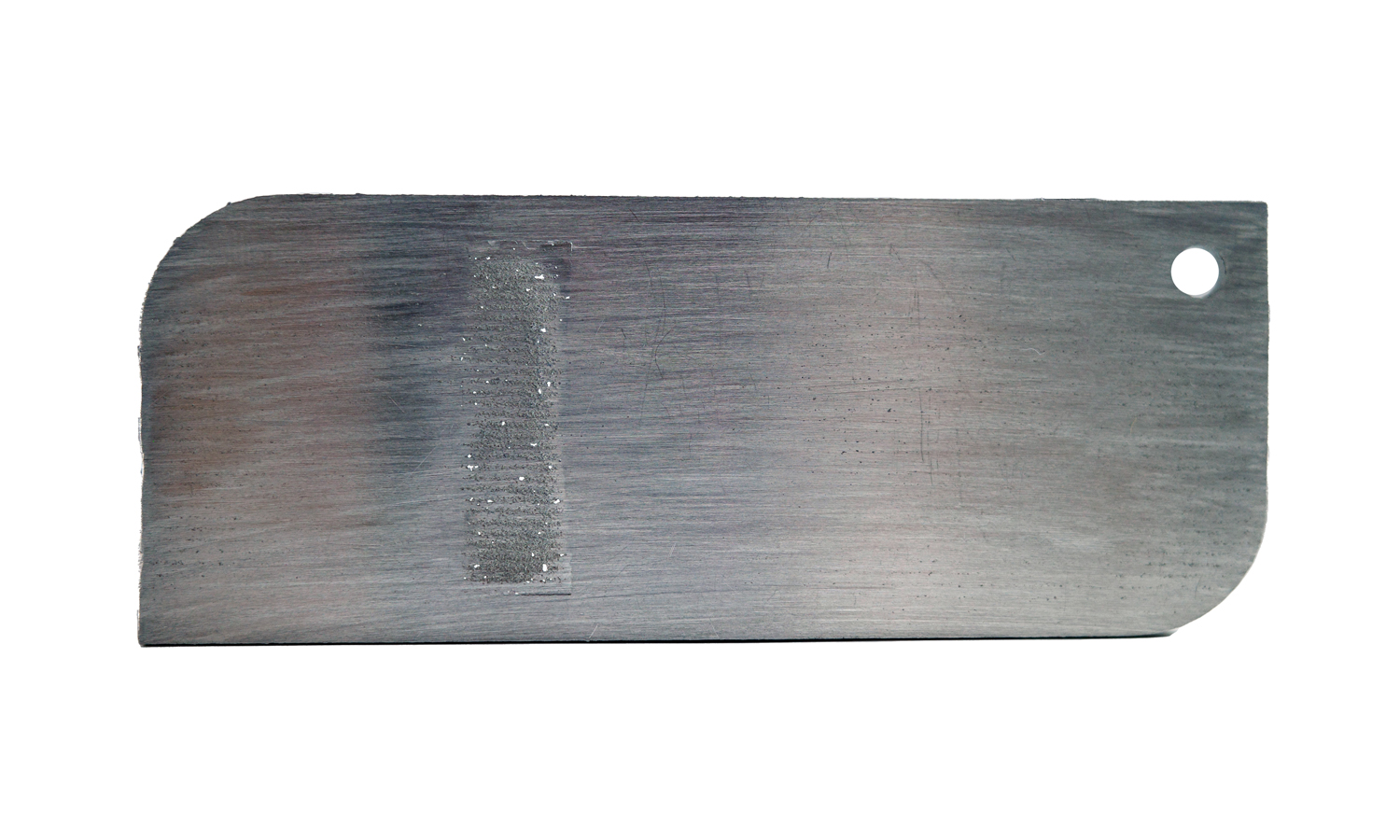
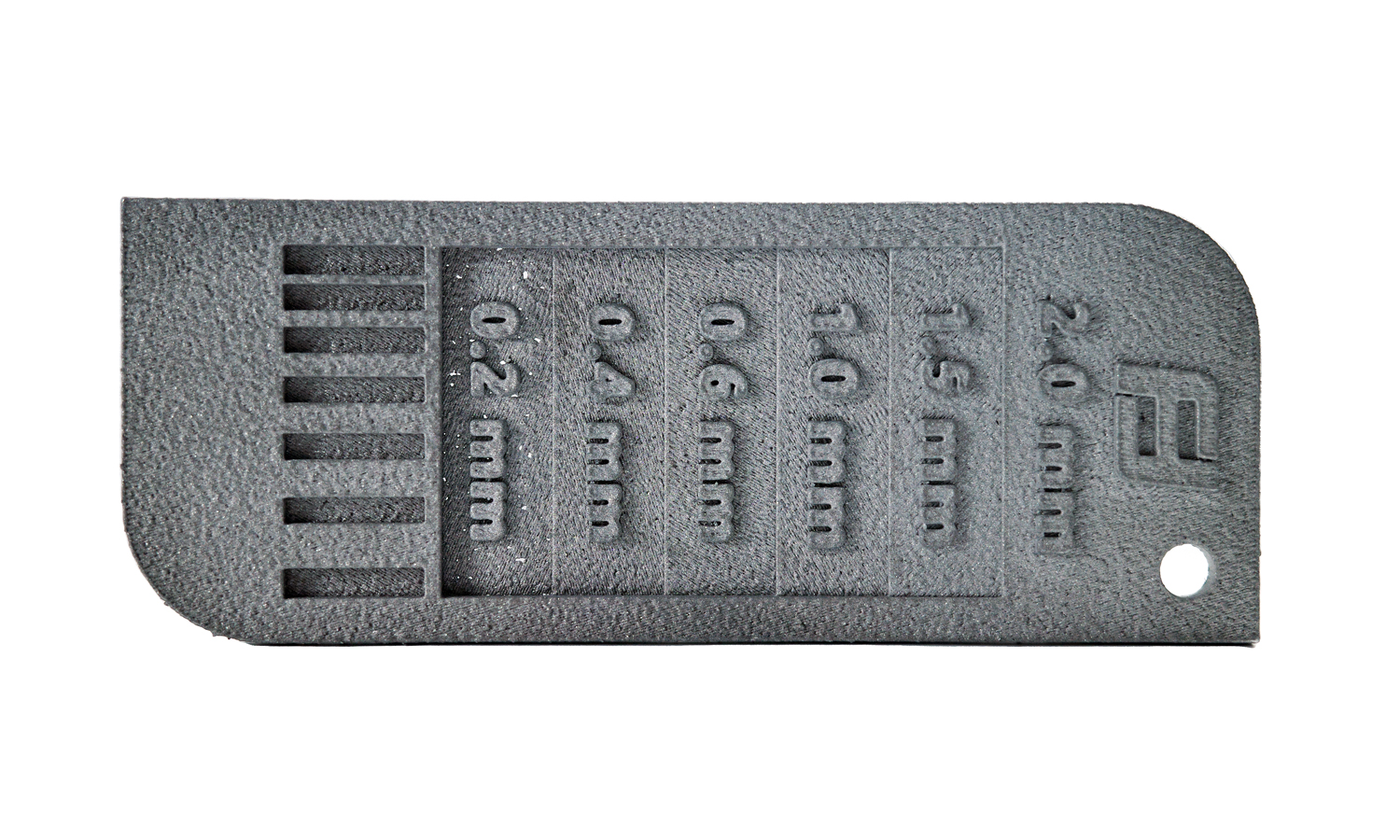
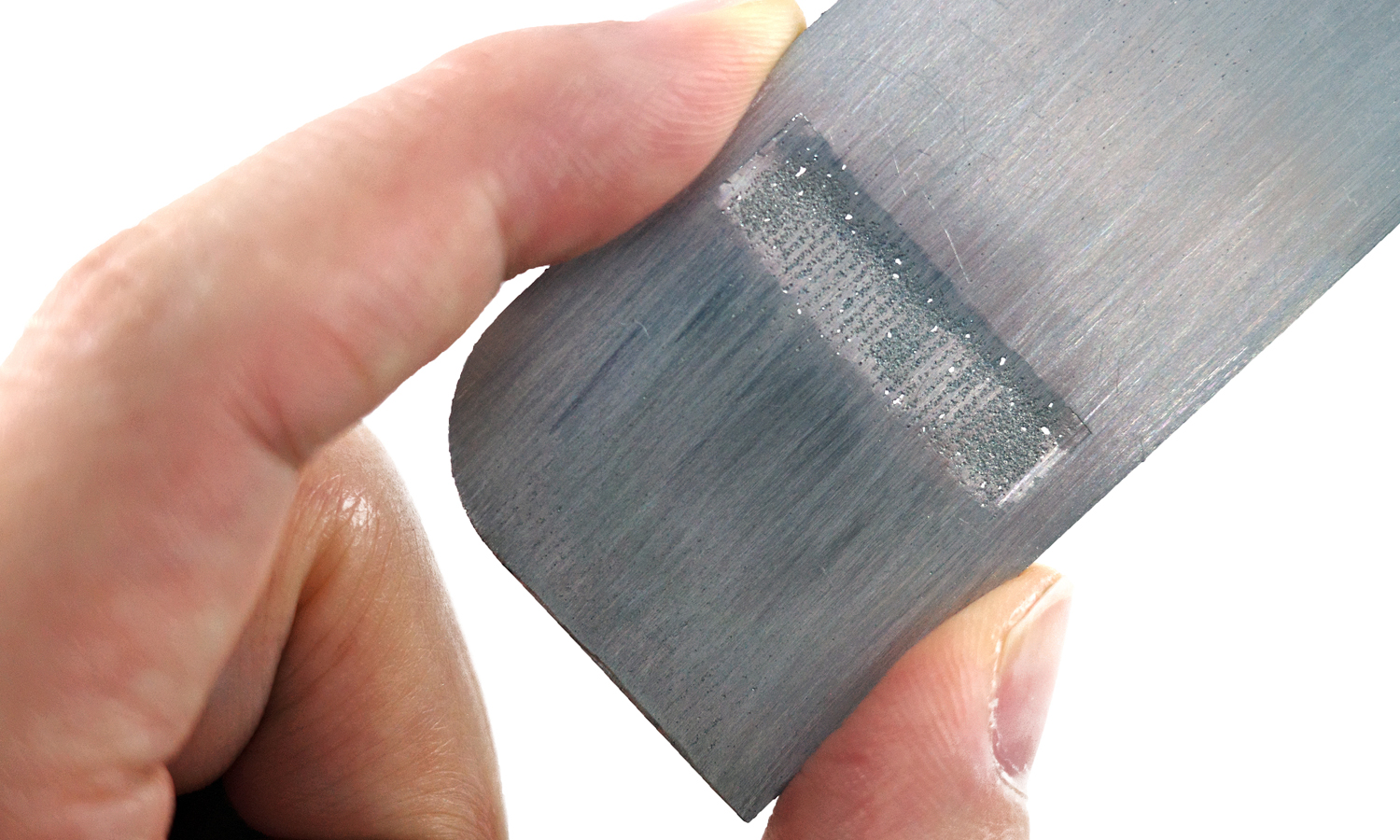
For this project, we printed an aluminum sample strip with DMLS technology. The sample strip contains stages of different thicknesses, from 0.2mm to 2mm. There are raised letters on the front noting the thickness of each stage. We polished the back of the sample strip with sandpaper and left the front as raw finishing.
The purpose of this project is to show how the printing effect and the surface finishing effect would be with different thicknesses and what is a safe thickness for both. The sample strip can be used as a design guide and a demonstration of our capabilities in 3D printing and surface finishing.
The result is a striking contrast between the two sides of the sample strip. The back side has a smooth and shiny surface, while the front side has a rough and matte surface. The back side also has irregular scratches under strong light, which add some texture and character to the metal. The front side shows the details and accuracy of DMLS printing, such as the letters and the layers. The front face has a roughness of Ra 3.2, and you can see how the laser moves and fuses the metal powder.
However, not all thicknesses are suitable for DMLS printing and surface finishing. The 0.2mm thick stage has already broken and has many tiny holes. This is because the metal powder is not fully fused at such a thin layer, resulting in weak and brittle parts.
We suggest that the minimum wall thickness of your design for DMLS 3D printing should be 0.7mm to avoid breakage or deformation. For surface finishing, such as polishing, we recommend a minimum wall thickness of 1mm to avoid damaging or warping the parts.
We are very proud of the results of this project, as it shows our expertise and experience in DMLS 3D printing and surface finishing. If you want to try out this technology for your own projects, you can contact us at FacFox, a professional online 3D printing service provider.
We offer high-quality DMLS 3D printing services with various metals and options. We also offer various surface finishing services, such as polishing, sandblasting, painting and coating.
Visit our website facfox.com or email us via facfox.com today to get a free quote and start your 3D printing journey with us!
Solution
- Step 1: A 3D model was prepared and exported into a 3D printable file format (an STL format). The model was hollowed to reduce the amount of metal powder.
- Step 2: The file was loaded into the software and the printing parameters such as layer thickness, laser power and scanning speed were set up.
- Step 3: The build chamber was filled with Aluminum powder and leveled with a recoater blade.
- Step 4: The printing process started and the laser scanned each layer according to the file.
- Step 5: The part was allowed to cool down inside the build chamber before being removed.
- Step 6: Any support structures that were needed to prevent warping or distortion during printing were broken off.
- Step 7: Excess powder that remained on the part was cleaned off using brushes or compressed air.
- Step 8: The part was heat treated to improve mechanical properties and microstructure. Then it got hand polished with fine-grit sandpaper.