SLM Pure CopperCu 3D printed copper leverages its superior thermal and electrical conductivity for demanding applications. Ideal for heat sinks, heat exchangers, and electrical components like inductors and bus bars, 3D printing enables complex designs and customization. Its high-temperature resistance also makes it suitable for aerospace applications. Explore the potential of this versatile material for optimized performance. Max Build Size Min Build Size 5 x 5 x 5 mm Default Layer Height 0.05 mm Optional Layer Heights 0.05 mm Tolerance ┬▒0.2% (with a lower limit of ┬▒0.2 mm) N/A Smooth ŌśģŌśģŌśģ Detail ŌśģŌśģŌśģ Accuracy ŌśģŌśģŌśģ Rigidity ŌśģŌśģŌśģ Flexibility ŌśģŌśģŌśģ Available ColorsBronze
Available Post ProcessPolish
, Sandblast
, Electroplate
Suitable For Functional prototypes and end products, Not Suitable For Large models, Additional Info3D printed copper is opening up some exciting possibilities due to copper’s excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. Here are some of the key use cases: 1. Heat Management:
2. Electrical Components:
3. Aerospace and Rocketry:
4. Medical Devices:Customized prosthetics and orthotics: 3D printing allows for the creation of personalized medical devices with complex geometries and improved fit. 5. Other Applications:
Feature
3D PrinterCustomized LCD Printer Material Spec Sheet
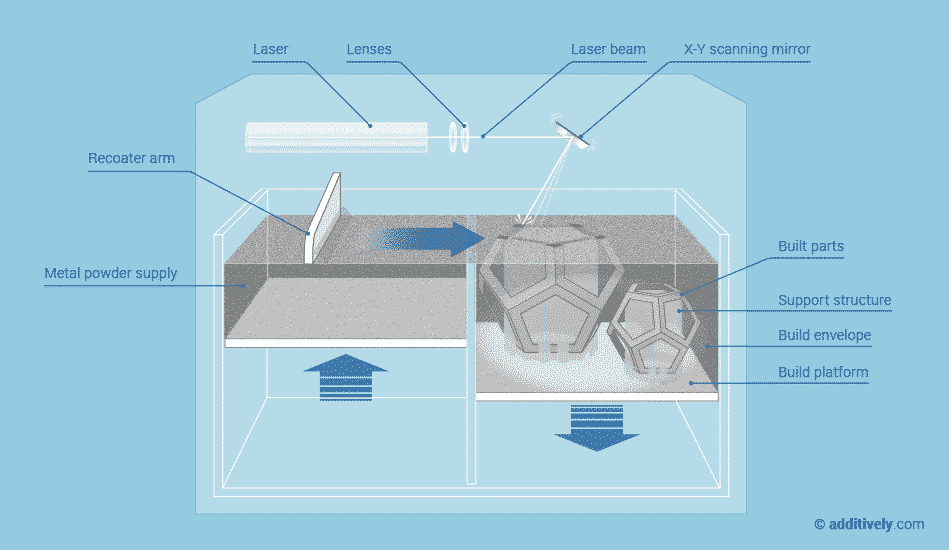
Selective Laser Melting creates objects from thin layers of powdered material by selectively melting it using a high power laser. The process takes place in a low oxygen environment in order to reduce thermal stresses and to prevent warping. Industrial metals are best used for high-tech, low-volume use cases from prototyping to creating end-use parts. Metal 3D prints are comparable to traditionally manufactured parts in terms of chemical composition, mechanical properties (static and fatigue) as well as microstructure. Once the printing is done, the extra powder that was not bound, and is not part of your design, is removed. Your part is now solid metal, and after the flutes are manually removed, it is tumbled and polished to produce a smooth finish.
|