Overmolding Services
One thermoplastic material is molded over another material to form one part, ideal for aesthetic and functional products.
Overview: How Overmolding works?
The Basics Of Overmolding
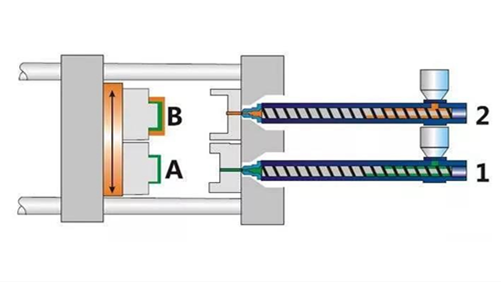
Overmolding is a process where a single part is created using two or more different materials in combination. Typically the first material, sometimes referred to as the substrate, is partially or fully covered by subsequent materials (overmold materials) during the manufacturing process.
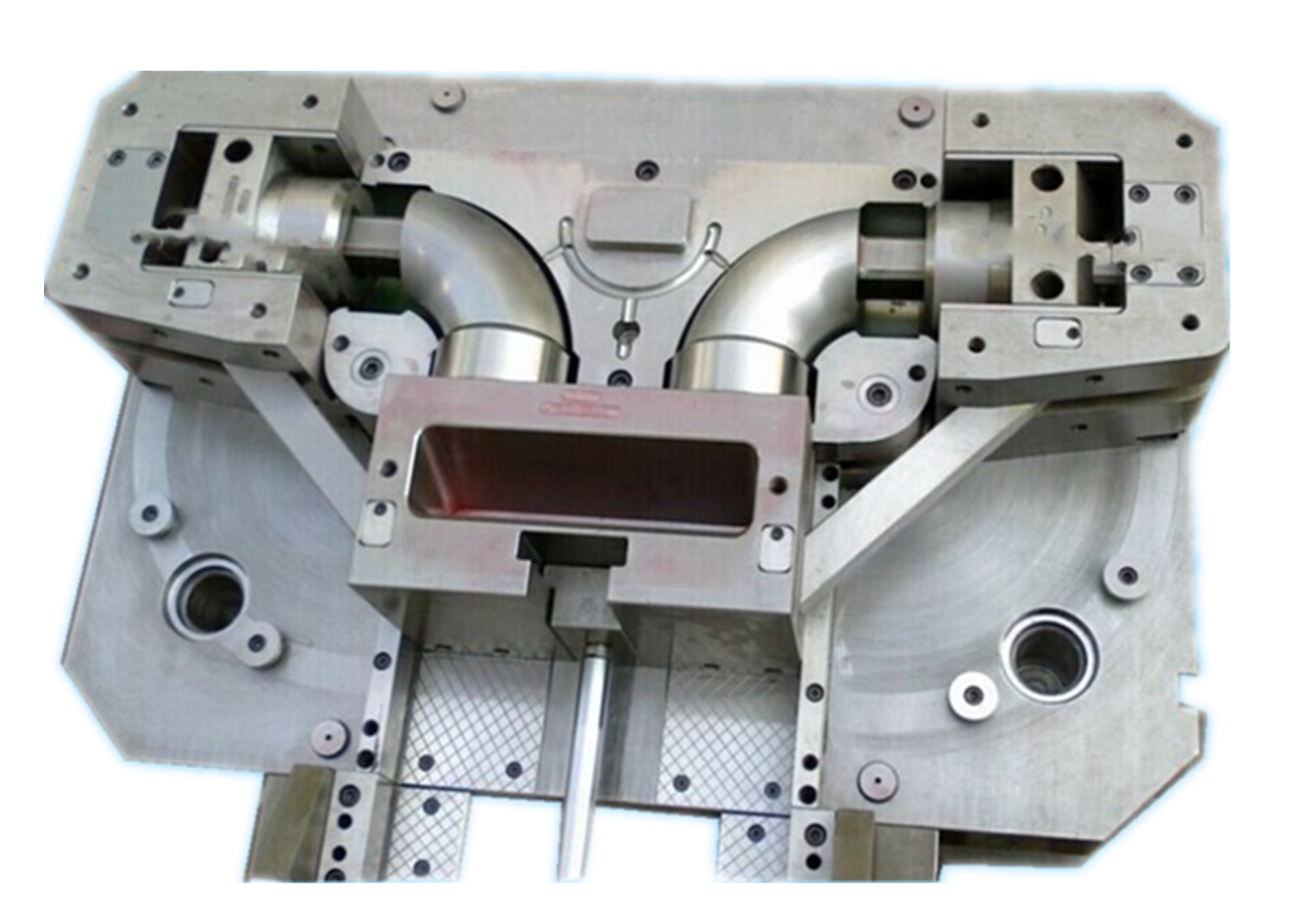
 What is the Substrate?
What is the Substrate?
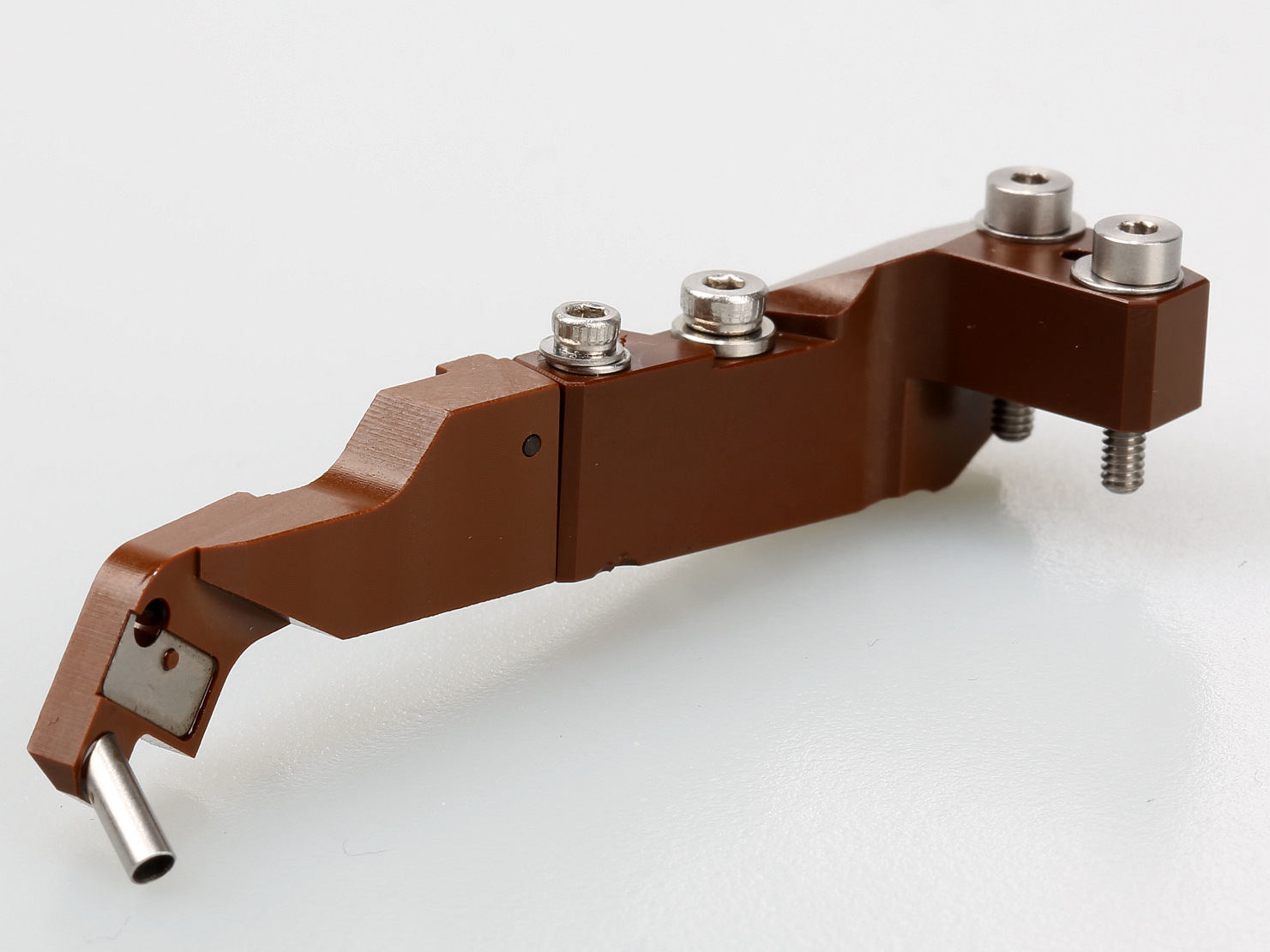
The substrate could really be anything: a machined metal part, a molded plastic part, or even an existing product like threaded inserts, screws, or electrical connectors. It is the first piece in what will eventually become a single continuous part composed of chemically bonded and often mechanically interlocked materials of separate types.
- What is the Overmolding Material?
Overmold materials (typically plastic) start off in pellet form. These pellets are mixed with additives like colorants, foaming agents, and other fillers. Theyãre then heated to their melting point and injected into the mold tooling as a liquid. There are some limitations on what materials are suitable for overmolding. If you are overmolding a metal part with plastic, you can really use any plastic. If you are overmolding a plastic part with another plastic (or a rubber or TPE), then there can be compatibility issues. The material manufacturer typically publishes a compatibility chart for overmolding.
How Overmolding Works
We have a great video that illustrates the process and should help the reader to make sense of the explanation above. You can watch it here:
Which molding service suits you?
Features of Overmolding
Advantages
Drawbacks
Injection Molding Processes
The overmolding process is utilized for a number of reasons that vary according to the specifics of the particular project. Common materials include toothbrushes, tool handgrips (e.g. cordless drills and screw drivers), and personal care products (e.g. shampoo bottles and shaving razors).
Here are some examples of typical overmolding applications:
First a rigid plastic substrate is molded. Then another rigid plastic is molded onto or around the substrate. The plastics could differ in color and/or resin. First a rigid plastic substrate is molded. Then a soft rubber or TPE is molded onto or around the substrate. This is often used to give a soft grip area to a rigid part. First a metal substrate is machined, cast or formed. Then, the substrate is inserted into an injection molding tool and the plastic is molded onto or around the metal. This is often used to capture metal components in a plastic part. First a metal substrate is machined, cast, or formed. Then the substrate is inserted into an injection molding tool and the rubber or TPE is molded onto or around the metal. This is often used to provide a soft grip surface.Plastic Over Plastic
Rubber Over Plastic
Plastic Over Metal
Rubber Over Metal
Available Materials
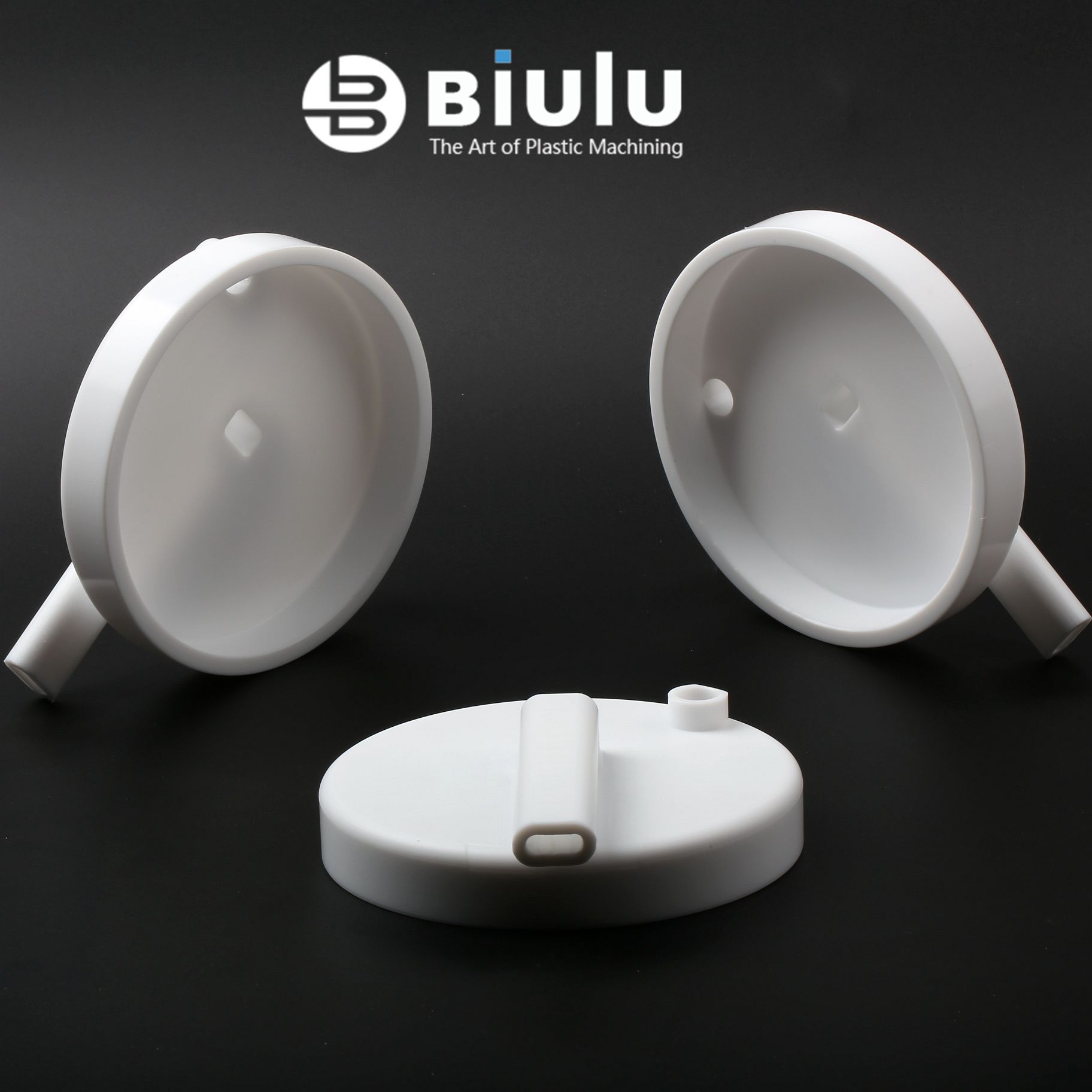
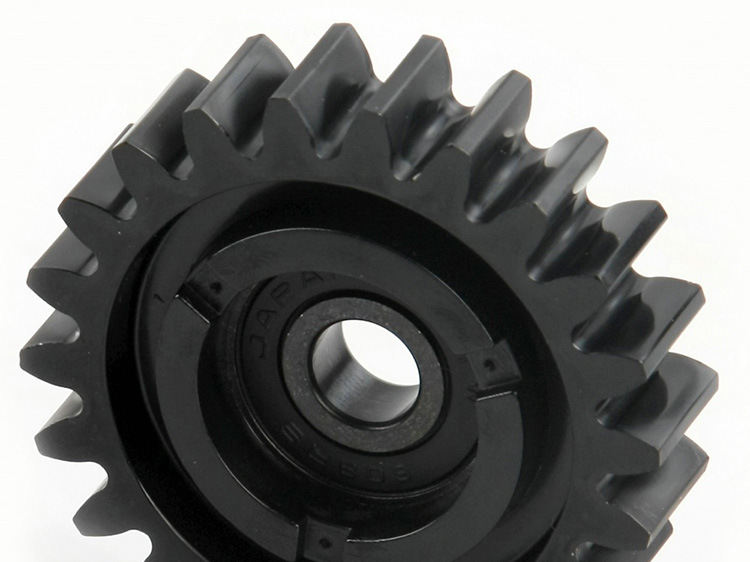
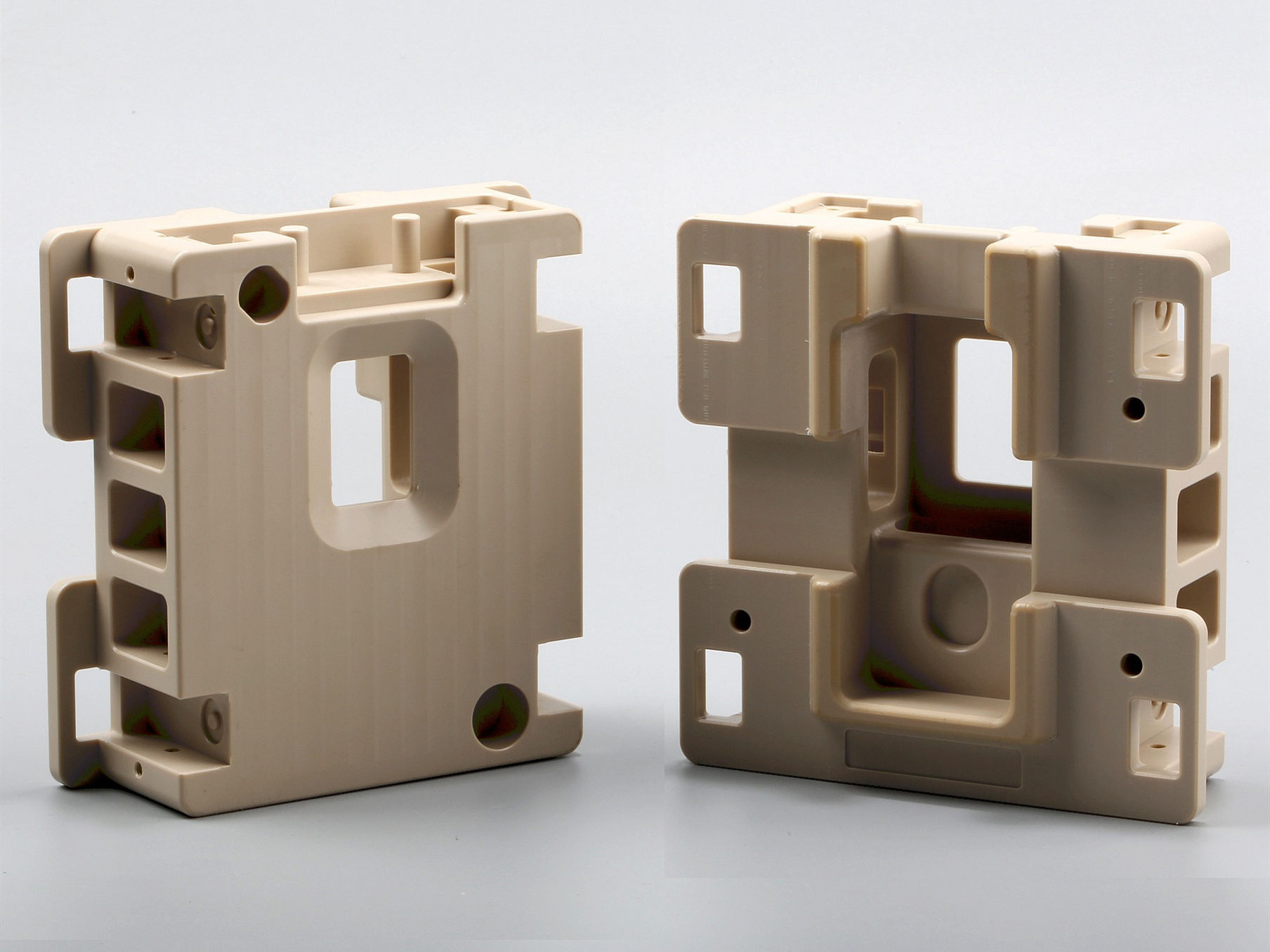
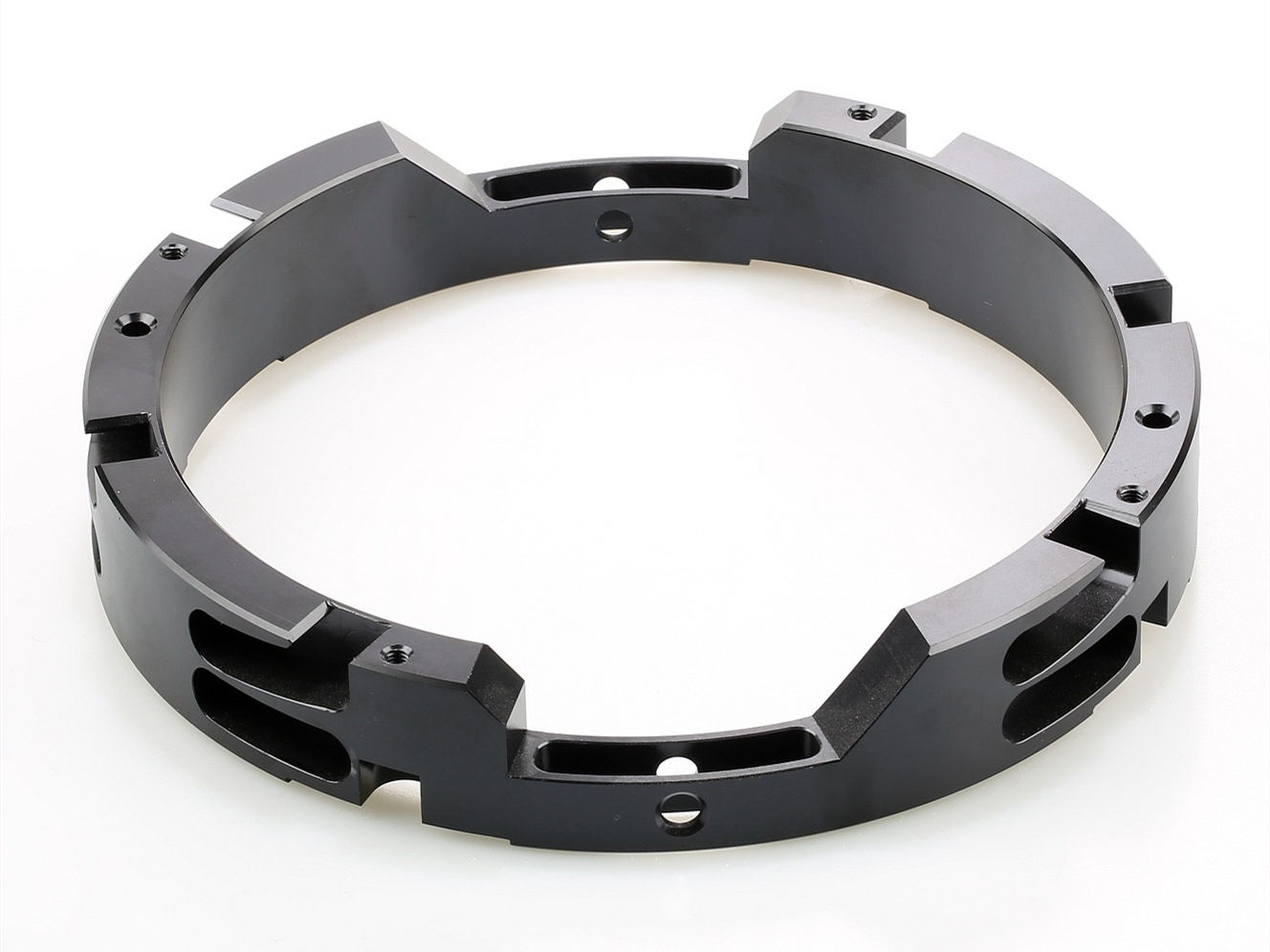
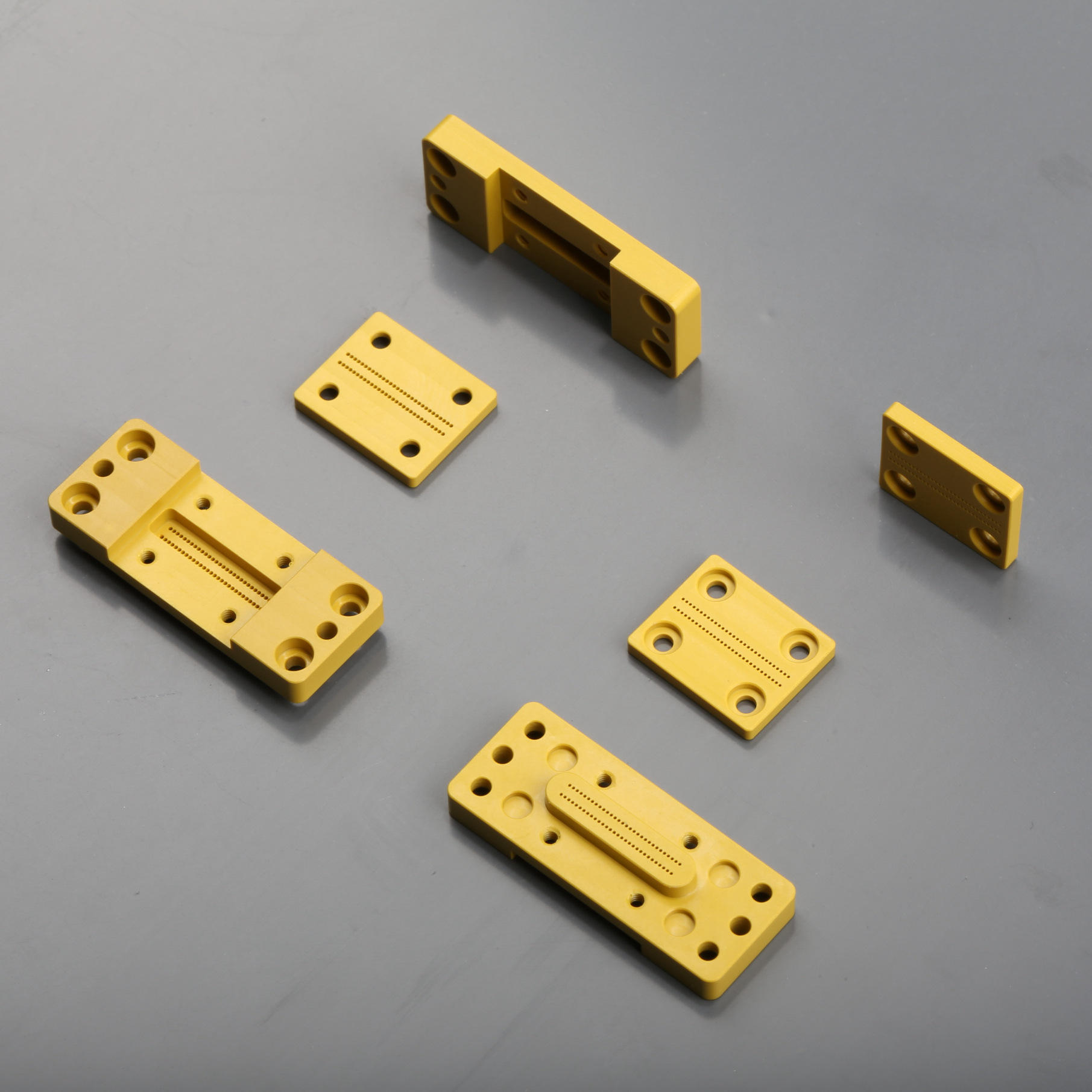
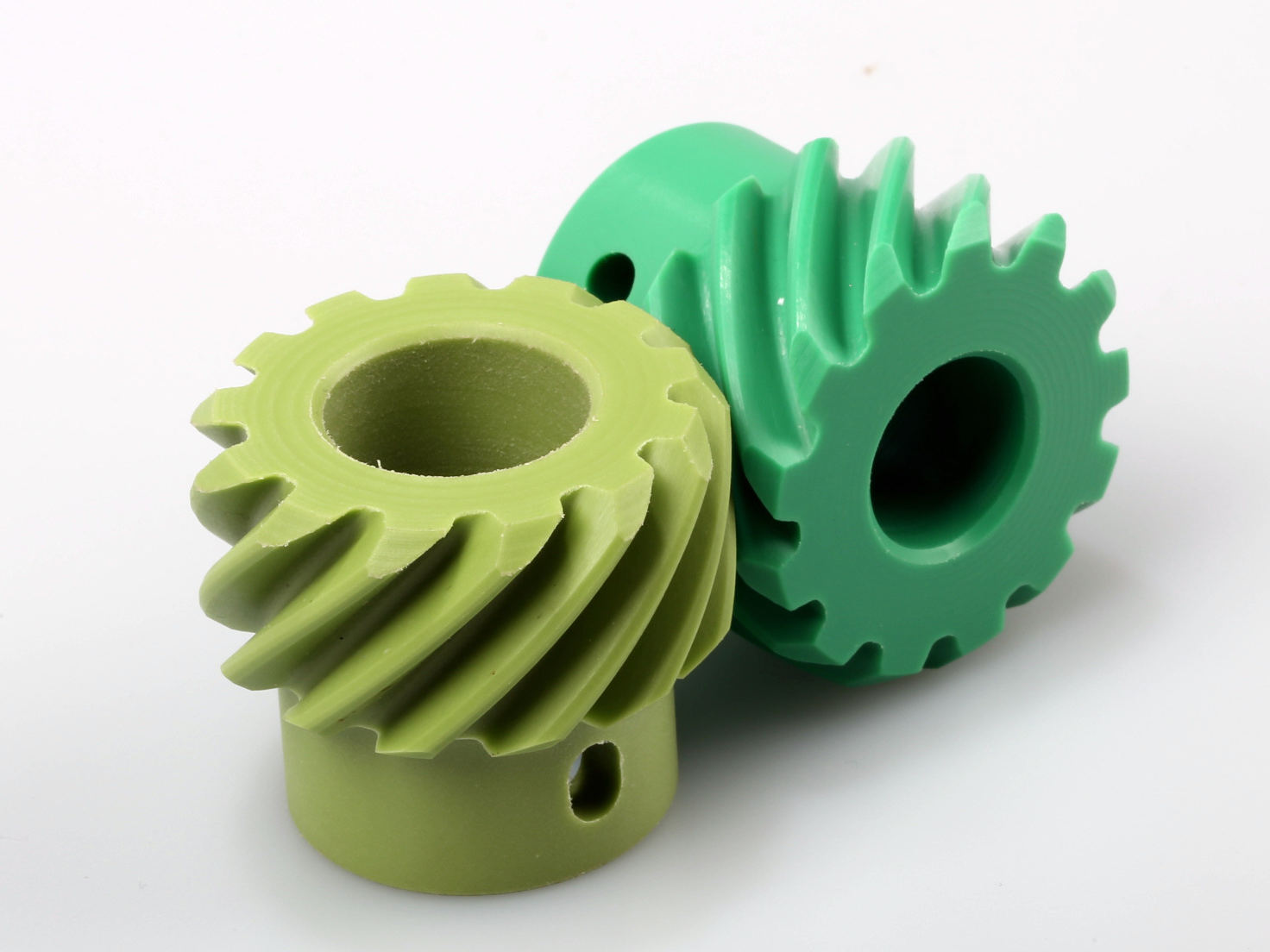
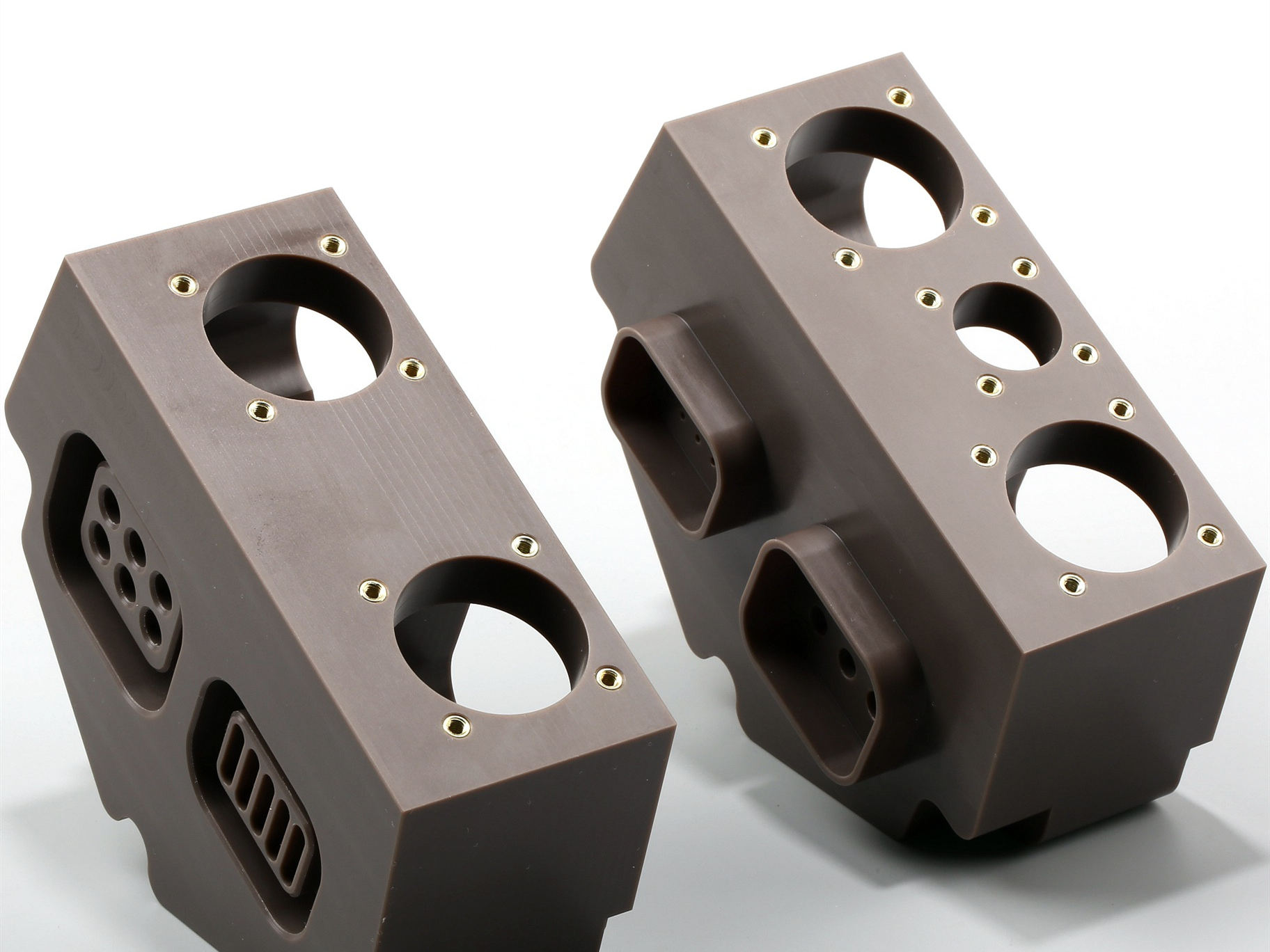






















Available Finishes
For rapid design molds, customers can receive T1 samples off a steel tool in as fast as 10 business days. Customers own the core and cavity inserts and we use factory-owned, interchangeable mold base inserts. Aluminum, S50C, P20, and NAK80 tool inserts are available as well as the Master Unit Die (MUD) quick-change system. Side actions are created with hand pick out inserts.
For production tooling, we produce stand-alone tools, ultimately owned by the customer. P20, H13, S7, NAK80, and SS420 insert steel is available as well as family & multi-cavity tools.
We will polish the mold to make the injected parts smooth enough, without obvious tooling marks.
- Sandblasting
- Surface Texturing
- Donãt see the finish you need? Submit an RFQ with ‘Suggest’ option, or make a note with your special request, weãll look into a finishing process for you.
Overmolding Applications
With rapid injection molding, we can produce parts within 1-2 weeks using material the same as requested end products, which will outperform the 3D printed or CNC machined prototypes. CNC machining can be applied to make high-quality tools from aluminum 7075-T6 for injection molding, the lifespan, depending on geometry of the design, lasts 1,000-5,000 parts. Injection molding is the best choice for mass production the end products can be made using the exact material that will eventually be produced before the mass production.Prototypes
Small Batch Production
Mass Production
Industries with Injection Molding
Resources for Overmolding