Photocentric launches LC Opus LCD printer 3D Printer Hardware
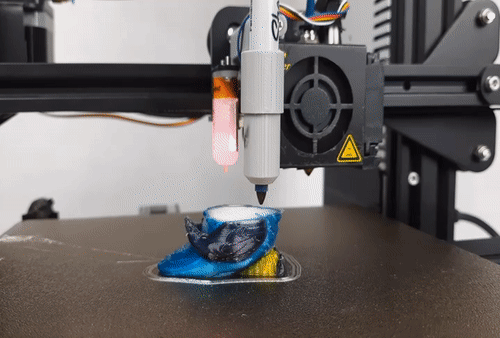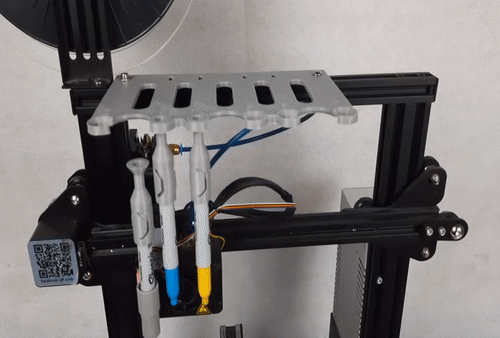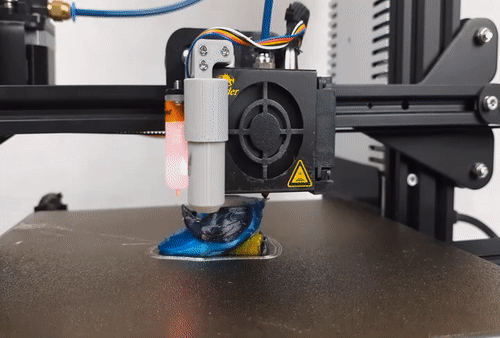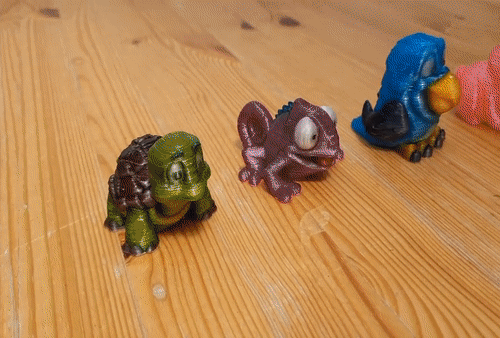
Photocentric, the inventor of LCD printing, has launched LC Opus, its quickest LCD printer yet. The rugged LC Opus is fast and accurate, delivering reliable and repeatable performance. With a unique design featuring a custom monochrome screen, the LC Opus comes pre-calibrated and ready to print out of the box. Ideal for a desktop or workbench, the machine is suited for a huge variety of applications and environments.