ExOne introduces S-MAX Pro for industrial sand 3D printing 3D Printer Hardware
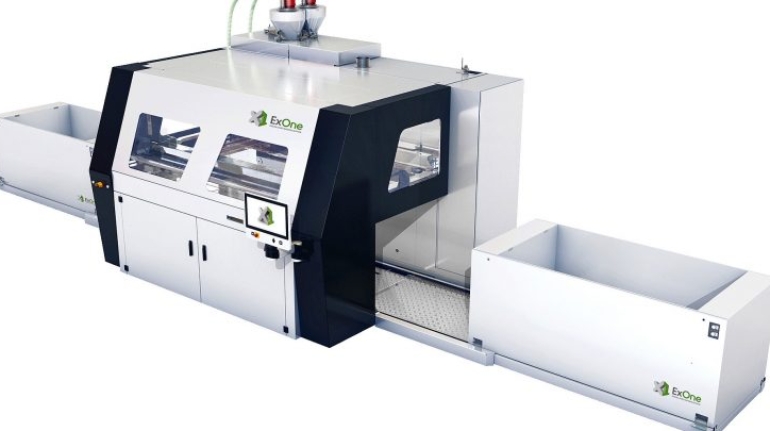
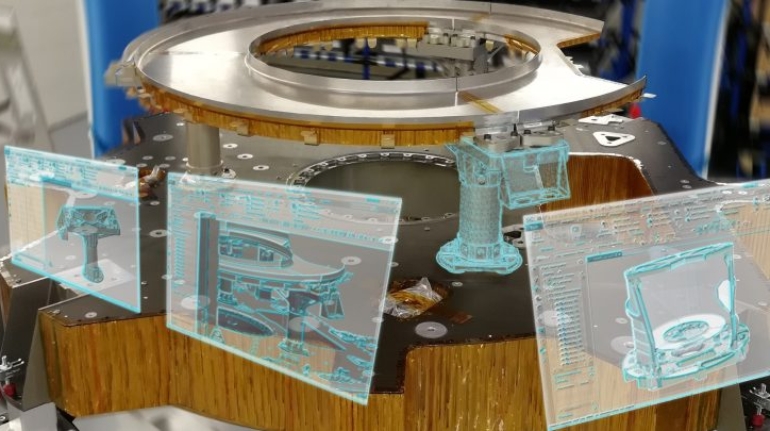
Binder jet 3D printing company ExOne has today unveiled its latest industrial sand 3D printer: the S-MAX Pro, which boasts improved print speeds, reliability and precision. In addition to the 3D printer, the company has also announced a partnership with Siemens that it says will benefit its industrial customers in the foundry, aerospace, automotive and energy markets, among others.