The dental industry is flourishing in developed countries since the 19 century and has been trendy for young, wealthy and educated people in developing countries. The report “Global Dental 3D Printing Market Analysis, 2014-2025” reveals that the thriving dental industry will increase by 17% averagely in the following years, and the market volume will boost from $260 in 2018 to $930 in 2025. The nature of dental care – highly customization – explains why it can be matched perfectly with 3D printing technology. Besides, additive manufacturing also offers advantages like high quality, fast lead time and low cost to the diverse sectors of this industry. In this article, we want to introduce how many ways can dentists implement 3D printing into their work and which materials are best applied in each kind of application.
Esthetic Dentistry – Orthodontics
Esthetic dentistry is generally used to improve the appearance of teeth, gums, and bite. More than 30% of people have symptoms like overbite, underbite, crossbite, spacing, crowding, etc. Orthodontics usually involves the use of braces, which includes stainless steel and porcelain brackets with adheres, clear aligners, and retainers. Steel braces are usually printed through the SLM printing technique while SLA and DLP are suitable for printing invisible transparent aligners.
High-elastic braces
- Pros: high intensity and elasticity; not easy to deform; tight and comfortable bracket.
- Technique: traditional embedding-casting and 3D wax casting.
FDM printed braces
- Pros: high intensity, elasticity, and tenacity; tight and comfortable bracket; customization; light-weighted and compact.
- Technique: FDM printing.
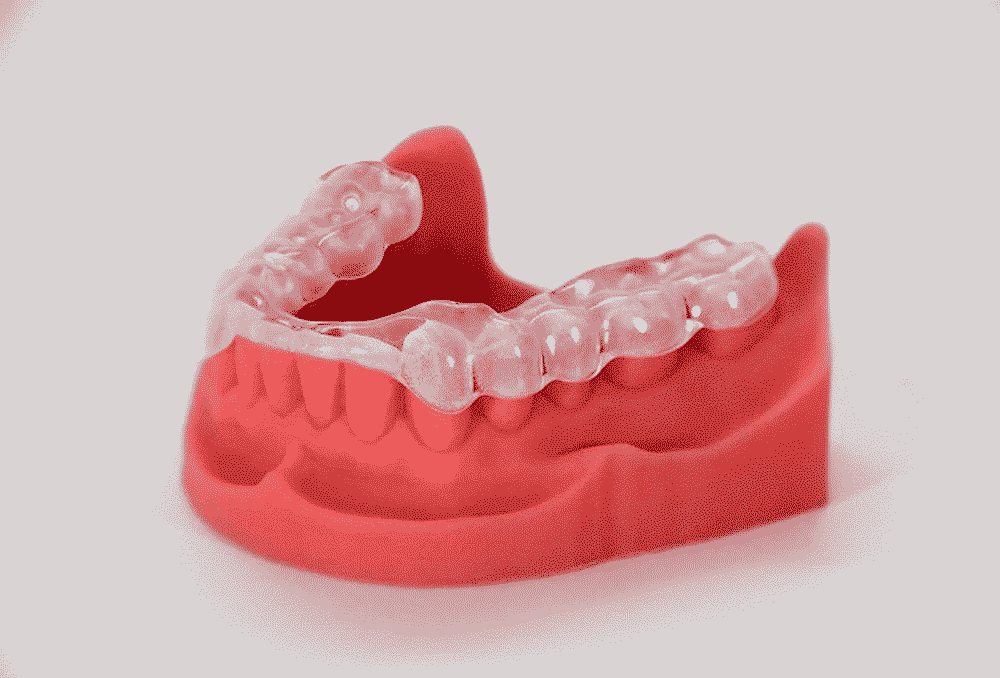
Transparent aligners and night guard
- Pros: high accuracy and precision; flexible and customized for patients; subtle and smooth surface; durable; convenient to modify the shape for patient.
- Technique: SLA / DLP printing
Prosthodontics – Dentures & Crowns & Bridges & Veneers
FDM printed porcelain dental crown
Directly build crowns layer by layer from the bottom up by heating and extruding thermoplastic metal filament.
- Pros: the inner part of the crown is compact and purified; the metal and porcelain combine perfectly; the apparent color of the crown is authentic.
- Application: any crown and bridge; applicable for the long bridge if butments are more than the missing teeth.
FDM printed titanium and porcelain crown
- Pros: light-weighted; avoid the shrinkage cavity and deformation of pure casting Ti crown; the inner part of the crown is compact and purified; the metal and porcelain combine perfectly.
- Application: any crown and bridge; applicable for the long bridge if butments are more than the missing teeth.
Digital cutting Ti and porcelain crown
- Pros: Avoid the bubbles, fissile, carbonization, and oxidization problems in the traditional embedding-casting method; improve the combination of metal and porcelain; light-weighted, durable, and tenacious.
- Application: 6-8 crowns (cause Ti is soft) if butments are more than the missing teeth.
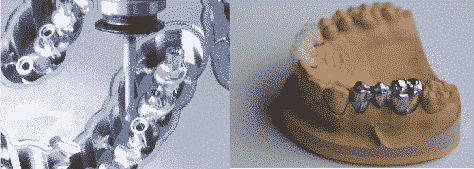
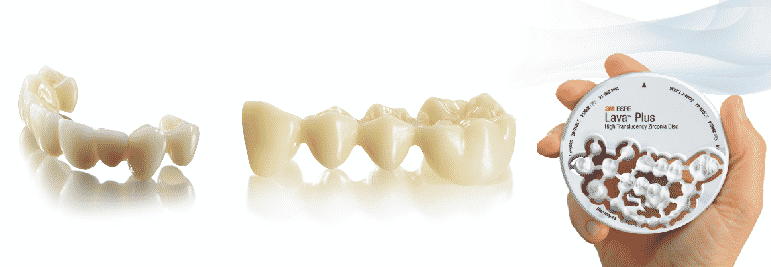
Lava frame zirconia crown
- Pros: high transmittance; the intensity reaches 1400 MPa, 3 times more than glass-ceramic; well-joint with gums; durable.
- Application: any crown and bridge; 4-crowns connecting bridge for anterior teeth and 2-crowns connecting bridge for posterior teeth.
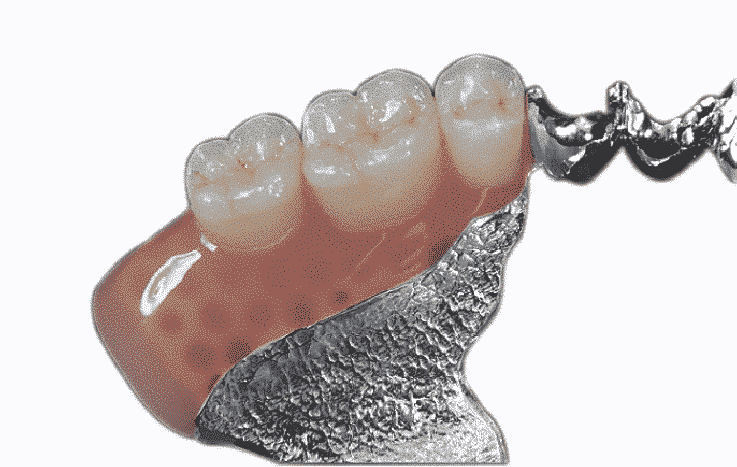
 Germany zirconia crown
Germany zirconia crown
- Pros: made by German and Japan sintering device; the intensity reaches 1200 MPa; durable and reliable.
- Application: 2-crowns connecting bridge; applicable for the long bridge if butments are more than the missing teeth.
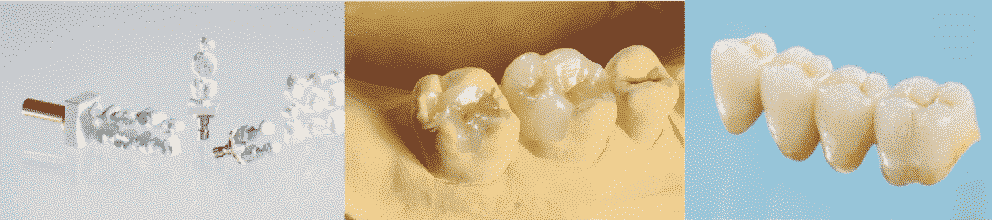
Glass-ceramic crown
- Pros: fast produced; compact and well-joint with gums.
- Application: single crown; 6 colors available.
Porcelain Veneers
- Pros: ultra-thin with only 0.2mm; fit perfectly with natural crowns; the intensity reaches 400 MPa; durable; authentic color and high transmittance.
- Application: single crown; 16 colors available.
Cariology and Endodontology – Implants
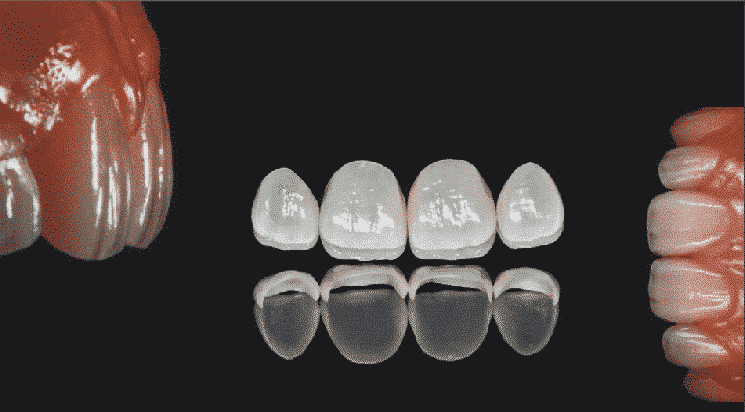
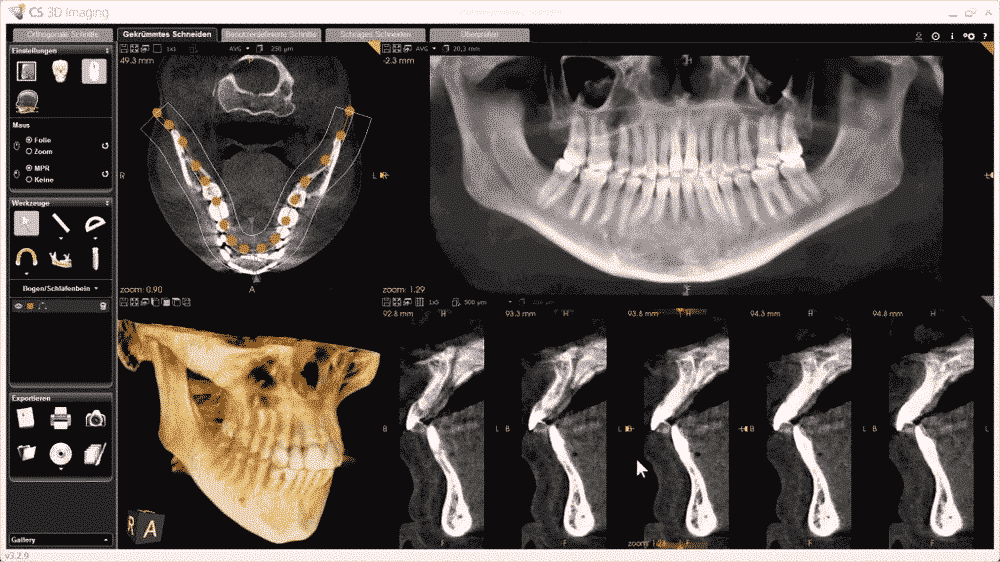
The dentists can make precise intraoral scanning and generate a 3D model of patients’ teeth. Each scanning device consists of a handheld camera to collect the data inside the mouth region and a computer system to process, analyze and visualize the intraoral structure. The abundant information generated from the cone beam scan contains the bone, bone density, soft tissue, location and nerves of the patients, and enables clinicians to virtually place an implant or test which is the best location for planting.
The traditional implanting surgery requests a long period to cover the whole process: damaged tooth removal, dental implant placement, bone growth, and healing, abutment placement, and denture placement. Patients need to visit the dentist for many times and the bone healing process may take many months. 3D printing technology enables one to print a complete false tooth including root, abutment, and crown. Thus, the entire surgery time can be shrunk to 1-2 hours. Ti and its alloy have fine biocompatible attributes and mechanic performance, hence it’s suitable to be the implant root. The material of the crown includes gold, CoCr alloy, NiCr alloy, ceramal alloy, and zirconium dioxide as well as resin.


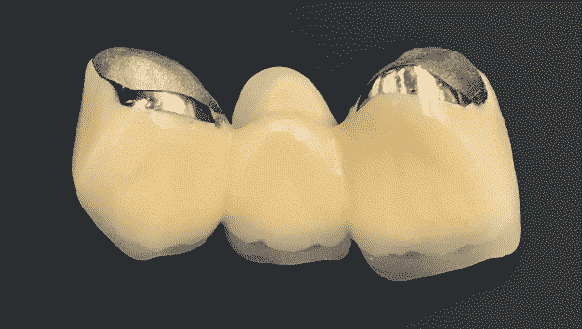
 Germany zirconia crown
Germany zirconia crown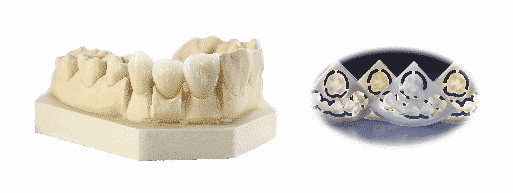

Leave A Comment