3D printing fashion is becoming more and more common in the design world, but there are many challenges surrounding it. It is not easy to adopt a technology that is widely used to manufacture solid plastic objects and produce flexible and wearable products, and many 3D printing methods are still not what you call wearability, except on the runway. Many more successful 3D printing methods involve conventional fabrics with 3D printing accents, but this has its own challenges in making 3D printed plastics firmly adhere to the fabrics. In a paper entitled “3D Printing of PLA on Textile Fabrics”, a group of researchers discussed this challenge.
In the study, a PLA model was 3D printed on eight different fabric samples that differed in fabric weight, warp density, weft density, warp linear density, and weft linear density. The researchers discovered a relationship between polymer adhesion force and warp density.
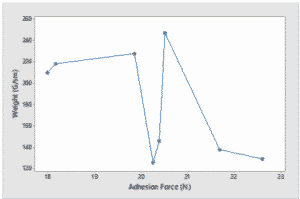
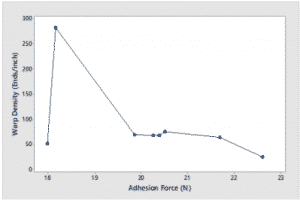
“While the relationship is not direct, there is however a general tendency for the adhesion force to increases the warp density decreases,” they explained. “This can be explained by the fact that as the warp yarns become more densely packed it becomes difficult for the polymer to surround the individual yarns. This leads to less area available for the polymer to hold on to the fabric hence reducing the adhesion force.”
As the weft density increases, the adhesion generally decreases, which may be due to the same reasons as above. The researchers also found that the warp curve density is proportional to the adhesion, but:
“While it may appear that an increase of the linear density provides more area for the polymer to hold onto the fabric, the results of the relationship between the adhesion force and the weft linear density, as shown in Fig. 6, tends to suggest otherwise.”
In short, although warp yarn density, weft yarn density, and warp yarn density have an effect on adhesion, fabric weight and thread weft yarn density have no direct effect on adhesion. Designers can use this information to find the appropriate fabric type to combine with 3D printed plastic ornaments to minimize the challenge of adhering 3D printed plastic to the fabric.
There are many advantages to using 3D printing to create fashion. If done well, combining the texture of the fabric and the polymer can produce a unique effect that is both eye-catching and wear-resistant. 3D printing can also be used to create custom clothing that other technologies cannot. However, when creating 3D printing fashion, it is important to have appropriate knowledge and skills. It is possible to sew or paste the 3D printed stress on the fabric, but printing the 3D printed stress directly on the fabric can save time, money, and consumables. Knowing the correct fabric for 3D printing can save designers more time, money and effort and enable them to create attractive wearable artwork.
The authors of the paper include Nonsikelo Sheron Mpofu, Josphat Igadwa Mwasiagi, Londiwe Nkiwane, and David Njguna.