FDM is not only as useful as the small desktop computer we saw. FDM can be very large and can be sold for millions of RMB. This issue introduces several unconventional FDM filaments, hoping to help users in this field to expand their applications.
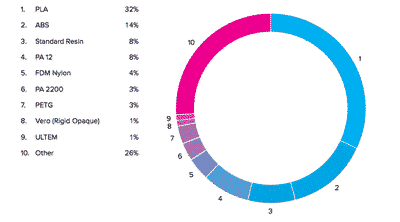
FDM filaments statistics
1.TPE / TPU flexible material
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is a soft material with sufficient toughness, which is very suitable for parts requiring rubber-like properties. It has great elasticity and can be repeatedly stretched, moved, and impacted without being worn or degraded. In commercial applications, TPU is usually used in the field of automotive parts, medical supplies, and household appliances. It can produce seals, gaskets, shoe soles, smartphone covers, wrist straps, etc., and currently, there are designers used to print clothing. However, this material is difficult to print, especially for a 3D printer that feeds at a far end, it is difficult to control the advance and retreat of the material, and it is easy to block the nozzle.
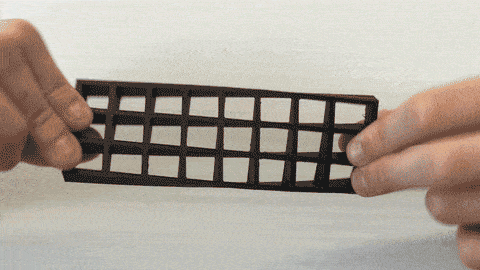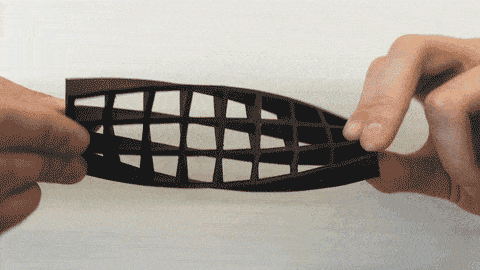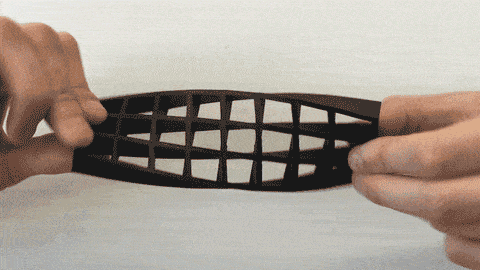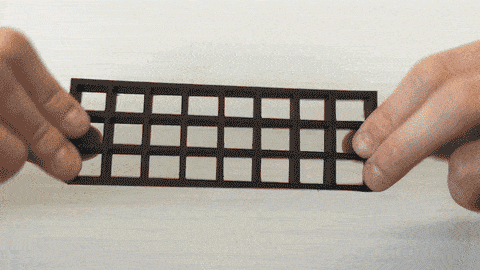
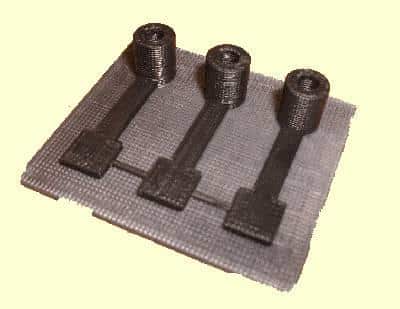
2. Carbon fiber reinforced filaments
Carbon fiber reinforced filaments is improved on the basis of high-strength PLA, nylon, and other polymers. It itself contains a large number of fine carbon fibers of varying lengths. These fibers are very small, which can pass through the extrusion nozzle of the FDM 3D printer and increase the strength and rigidity of the polymer, thereby effectively strengthening the 3D printed parts. The rigidity and strength are far more than ordinary PLA and ABS. And it also has very high melt strength, high melt viscosity, good dimensional accuracy and stability, and little odor during printing. However, the material exhibits excellent performance, and the abrasive nature of the carbon fiber in the wire may cause accelerated wear of brass, so it is recommended to use stainless steel or hardened copper alloy nozzles.

Carbon fiber reinforced materials can provide strength comparable to metals, but also very light, and have broad application prospects in industries that need to consider the ratio of weight to strength, including aerospace and automotive.
3.PEEK
PEEK is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic with high-temperature resistance, self-lubricity, chemical stability, radiation resistance, and electrical properties, as well as excellent mechanical properties. It is considered to be one of the best engineering thermoplastics in the world. PEEK can be used to manufacture demanding applications in the aerospace, automotive, oil and gas, and medical industries. In the field of biomedicine, polyether ether ketone has excellent biocompatibility. Compared with metallic implants, its elastic modulus is closer to that of human bone, and it can meet the normal physiological needs of the human body. Orthopedic implant material.

PEEK can be used as a 3D printing material to manufacture mechanical parts and orthopedic implants. However, due to the high melting point of PEEK materials, the working performance of most 3D printer nozzles is not enough to better melt PEEK materials. This problem gives PEEK 3D printing, especially FDM. 3D printing brings some difficulty.
4. Nylon filaments
Nylon has the advantages of excellent toughness, wear resistance, fatigue resistance, etc., and is widely used in the industry. FDM Nylon 12 is suitable for applications requiring high fatigue resistance, such as reusable friction-fit inserts. Nylon 6 can accurately predict the performance of durable functional prototypes and manufacturing tools that can withstand harsh production environments, and can meet the production of low-volume parts with high functional requirements.
In the aerospace and automotive fields, FDM printed nylon can be used to make tools, fixtures, and fixtures, as well as prototypes for interior panels, low-heat intake components, and radomes; in product development for consumer products, it can be used for snap panels and anti-slip durable prototype of impact components.
5. Metal texture filaments
Metal texture filament is actually a material in which PLA or ABS is mixed with metal powder. After the models are polished, you can visually feel that the models are made of bronze, brass, aluminum, or stainless steel. The printing wires mixed with these metal powders and PLA and ABS are much heavier than ordinary ABS and PLA, so the feel is not like plastic, but more like metal.
6. FDM conductive filaments
Conductive filaments can be used to make capacitive (touch) sensors, sensors, and printed circuits in wearable applications, and are widely used in electronic devices. At the same time, they can provide a high degree of freedom for the customization of actual products.
This material is often mixed with carbon powder in conventional materials such as ABS to achieve electrical conductivity. Printing circuits through FDM can be faster, safer, and cheaper than using etching and welding, and can maintain good uniformity and rate of change during the printing process. No more than 5%. However, there are few conductive filaments currently on the market.
To sum up
3D printing technology must compete with traditional manufacturing, and even FDM must compete with other technologies. Composite materials will be one of the driving forces behind the technology becoming a mainstream technology, and the problem is equipment. The great enlightenment given by the above materials is the doping and recombination of materials. When one of the several materials is mixed, unexpected performance can be obtained. Carbon fibers and PEEK, nylon, composite materials can be achieved but the strength of the metal, it can replace metal in some areas lighter than metal. Graphene is added to the TPU and processed into conductive TPU filaments, which can print flexible sensors, radio frequency shields, flexible conductive circuits, and wearable electronic products. Therefore, please do not think that FDM is too low-level, FDM is promising in the aviation and automotive fields!