3D printing offers great possibilities and many varieties when it comes to printing flexible and rubber-like materials. From production parts to innovative and cool projects for hobbyists, this is something to check out. Let us take a look at the options of flexible polymers for 3D printing for the technologies available at FacFox.
Comparison between 3 FacFox materials
| SLS TPU | DLP Flexible Resin | Polyjet Rubber | |
| Color | White | White | White/Black/Colorful |
| Hardness | Shore 92A | Shore 75A | Shore 30A-95A |
| Flexibility | ★ | ★★ | ★★★ |
| Elasticity | ★★★★ | ★★★ | ★★ |
| Durability | ★★★★★ | ★★ | ★ |
| Tear Resistance | ★★★★★ | ★★ | ★ |
| Smoothness | ★ | ★★★★ | ★★★★ |
| Accuracy | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★★★ |
| Bio-compatiblity | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Cost | ★★ | ★★ | ★★★ |
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)
TPUs belong to Thermoplastic Elastomers category. TPEs can range from 10 Shore 00 up to 72 Shore D, spanning all three hardness scales, however, the most commonly used is the Shore A scale.
Commonly known as SLS TPU (FarSoon TPU 1092A) is a multi-purpose material for application exclusively in SLS 3D printing. This material is a thermoplastic urethane, with flexibility, high tear strength and offers good details. TPU 3D printing offers unique possibilities that are otherwise tough to achieve with other 3D printing materials like ABS, PLA or Nylon.
Combining the properties of both plastic and rubber, TPU can produce elastic, highly durable parts that can be easily bent or compressed. The material exhibits stiff rubber-like qualities – much like a skateboard wheel – allowing for a range of end-use applications. In addition, the material is easy to print, and has good UV and hydrolysis resistance. Take a look at this spec sheet for detailed properties.
The molecular bonding pattern of TPU resembles the structure of classic polyurethanes. However, in this case the three-dimensional structure of the cross-linked building blocks is linear. Polymer chains are able to slide off each other. TPUs are thus fusible and can be processed like other thermoplastics. Yet, at the same time, they still possess properties of “classical” polyurethanes. This combination makes them very interesting – for laser sintering as well.
Properties of TPU
There a few exclusive key properties of TPUs which benefits the industries
Abrasion/Scratch resistance
High abrasion and scratch resistance means durability and high aesthetic value.TPUs give excellent results compare to other thermoplastic materials when abrasion and scratch resistance are critical for an application like automotive interior parts, sports and technical parts,
UV Resistance
Apart from maintaining good mechanical properties, they also show an extraordinary stability to ultraviolet radiation and thus superior color stability. For both light & dark color parts, industries can rely on TPU’s high scratch resistance & UV performance as TPUs ensure colour fastness to the aesthetic parts.
High flexibility
TPU offer high flexibility, shock absorption and rebound and are excellent choices for making footwear, sports equipment and orthopaedic models. This property is very helpful when it comes to automotive interiors and air filter covers.
Other Advantages
- Good flexibility over a wide temperature range
- Excellent low-temperature and impact strength
- Robust weather and high-energy radiation resistance
- High elasticity across the entire hardness range
- Resilience to oils, greases and numerous solvents
Key Features
- Highly elastic
- Tear resistant
- Chemical and bio compatibility
Applications
- Gaskets and seals
- Shock absorbers
- Vibration isolators
Material Datasheet
DLP Flexible Resin (Resione F39)
DLP resins is a class of rubber-like flexible resin used with SLA 3D printing technology.

F39 is a white flexible resin. It has medium tear strength and elongation at break, and the texture is similar to rubber.
This flexible resin print will harden at low temperatures (below 20°C). It is recommended that the prints be used in an environment above 25℃.
Characteristics
- Low elongation
- Medium Tear resistance
- Easy to print
Application
- Prototypes of shoes
- Wearable devices
- Cushioning parts
- Airtight parts
Material Data Sheet
Application Examples
It can produce elastic parts with high strength and high abrasive resistance for shoe and sports industry, pipes, sealings, prosthetics, and many more applications.
Characteristics
- Low wrapping tendency
- Stable sintering process
- Fully recyclable
Application
- Footwear and insoles
- Wearable devices
- Mechanical prototypes
DLP Rubber (Stratasys Agilus+Vero)
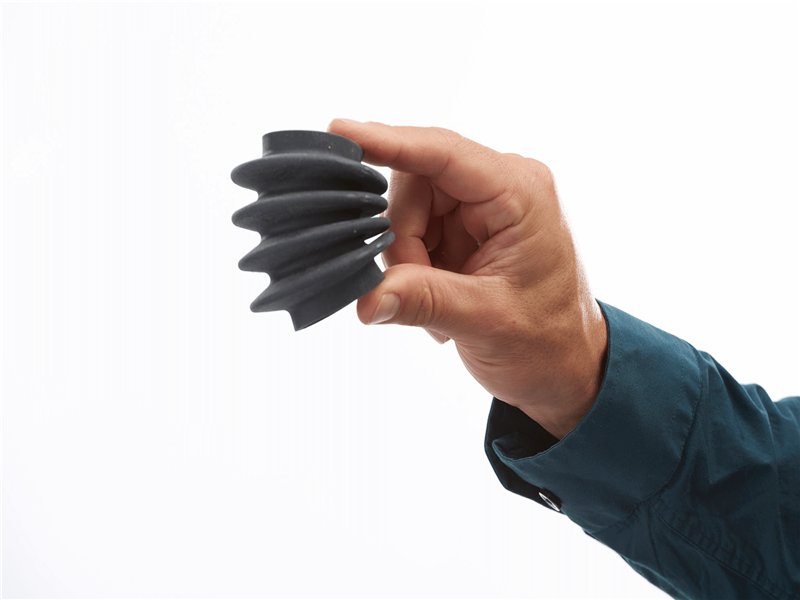

Simulate grips, rubber-like surfaces, and soft-touch components to prototypes with over-molding. Through a range of material hardness options and colors, overmolded models can be created with enhanced tactile and visual realism. The process utilizes flexible Agilus, 30-95 (Shore A), over Vero, 83-86 (Shore D), for simulation of end product feel and look.
Highlights
- Ideal for precise models, complex shapes and intricate details
- Durable and tear-resistant with smooth surface finish
- Wide range of simulated Shore A elastomers (30A – 95A)
- Black 30A is also known as “AGILUS30 BLACK (FLX9840)”
Applications
- Design validation and rapid prototyping
- Uses include realistic simulation of rubber parts, soft-touch parts, non-slip surfaces, rubber-like surrounds and over-molding, knobs, seals, gaskets, wearables, masks, covers, living hinges, jigs, fixtures and human anatomy
Material Data Sheet