3D printing offers great possibilities and many varieties when it comes to printing flexible and rubber-like materials. From production parts to innovative and cool projects for hobbyists, this is something to check out. Let us take a look at the options of flexible polymers for 3D printing for the technologies available at FacFox.
Shore hardness indicators of different 3D printing materials
When it comes to flexible polymers, Shore hardness is one of the main properties to look out for.
The Shore hardness scales were created to provide a common reference point when comparing different materials. It is measured using a durometer gauge. There are different Shore hardness scales for measuring the hardness of different materials.
- The Shore OO Scale measures extremely soft materials like gels (e.g. gel insoles).
- The Shore A Scale measures a wide range of material types; from very soft and flexible to semi-rigid plastics with almost no flexibility at all.
- The Shore D Scale measures very hard rubbers, semi-rigid and rigid plastics (e.g. PVC pipe).
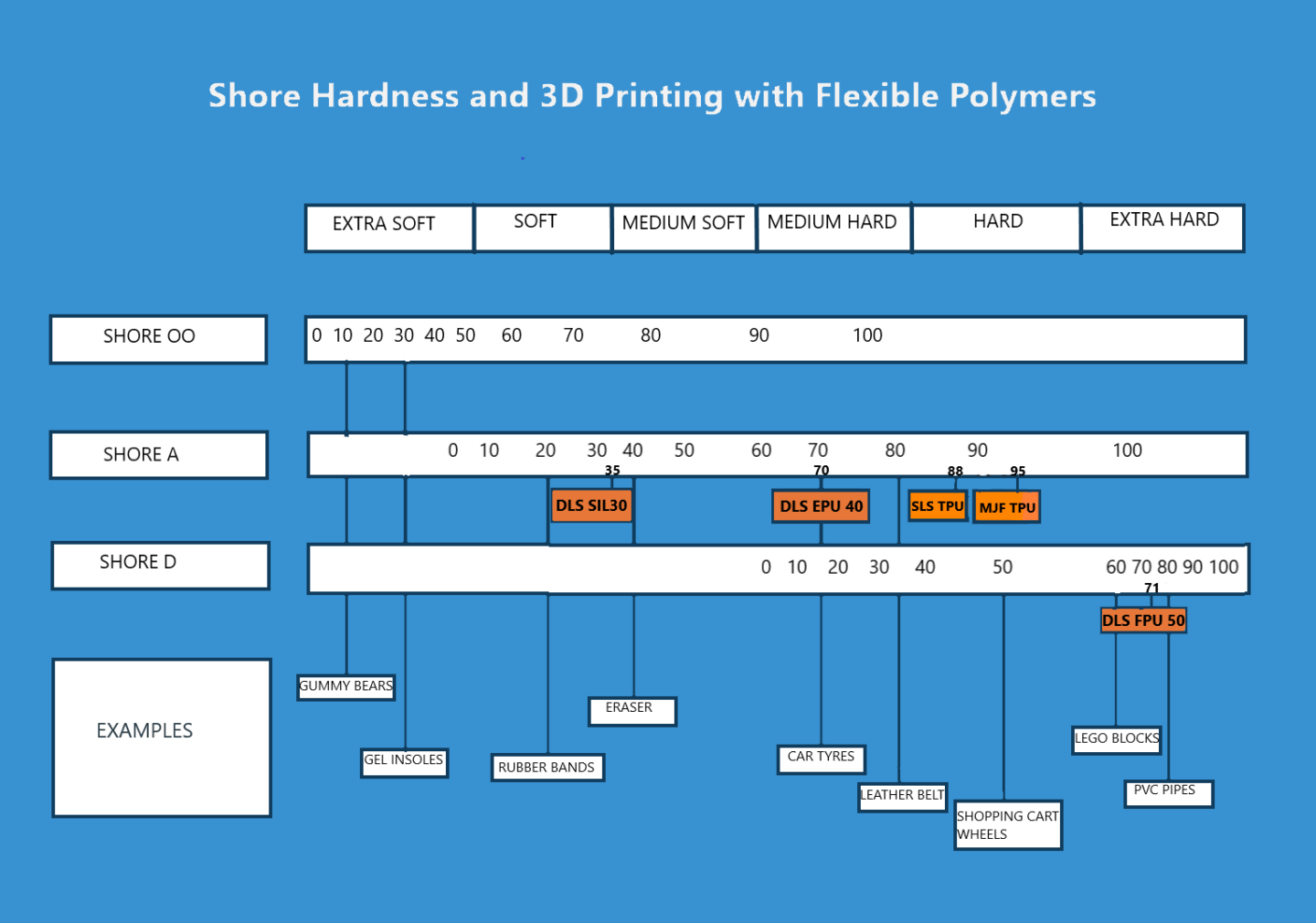 Shore hardness comparison of different flexible 3D printing options
Shore hardness comparison of different flexible 3D printing optionsAs you can see from the image, there is overlap on the different scales. For example, a material with a Shore hardness of 95A is also a Shore 50D.
Flexible polymers available at FacFox:
Different printing technologies require different polymers or resins to print. Let us see what print material each technology requires and their properties in detail

Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)
TPUs belong to Thermoplastic Elastomers category. TPEs can range from 10 Shore 00 up to 72 Shore D, spanning all three hardness scales, however, the most commonly used is the Shore A scale.
TPU Polyurethane 88/95A
Commonly known as Ultrasint™ TPU01 is a multi-purpose material for application exclusively in Multi Jet Fusion (MJF). This material is a thermoplastic urethane, with flexibility, high tear strength and offers good details. TPU 3D printing offers unique possibilities that are otherwise tough to achieve with other 3D printing materials like ABS, PLA or Nylon.
Combining the properties of both plastic and rubber, TPU can produce elastic, highly durable parts that can be easily bent or compressed. The material exhibits stiff rubber-like qualities – much like a skateboard wheel – allowing for a range of end-use applications. In addition, the material is easy to print, and has good UV and hydrolysis resistance. Take a look at this spec sheet for detailed properties

Technology: Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
Flex TPU/TPE like
If you require a resistant, flexible and rubbery material, Flexible TPU/TPE for Selective laser sintering (SLS) is the perfect option. With a good resilience after deformation and a high Ultraviolet (UV) stability, this elastomeric SLS TPU offers many advantages. By creating an interesting structural design, parts can be 3D printed for various applications, from automotive to footwear industries. The material gives a smooth white surface and also offers good hydrolysis resistance, great shock absorption.
Technology: Selective laser sintering (SLS)
TPU materials can be also used with FDM printing, but usually such 3D prints are of lower quality than when printed using powder-based technologies like SLS or MJF, moreover, they almost don’t differ in price.
Properties of TPU
There a few exclusive key properties of TPUs which benefits the industries
Abrasion/Scratch resistance
High abrasion and scratch resistance means durability and high aesthetic value.TPUs give excellent results compare to other thermoplastic materials when abrasion and scratch resistance are critical for an application like automotive interior parts, sports and technical parts,
UV Resistance
Apart from maintaining good mechanical properties, they also show extraordinary stability to ultraviolet radiation and thus superior color stability. For both light & dark color parts, industries can rely on TPU’s high scratch resistance & UV performance as TPUs ensure color fastness to the aesthetic parts.
High flexibility
TPUs offer high flexibility, shock absorption and rebound and are excellent choices for making footwear, sports equipment and orthopedic models. This property is very helpful when it comes to automotive interiors and air filter covers.
Other Advantages
- Good flexibility over a wide temperature range
- Excellent low-temperature and impact strength
- Robust weather and high-energy radiation resistance
- High elasticity across the entire hardness range
- Resilience to oils, greases and numerous solvents
Flexible CLIP resins
CLIP resins are a class of high quality resins used with Carbon DLS 3D printing technology. At FacFox, we offer three types of flexible CLIP resins. Check out our video overview to see how they look like:
- DLS EPU 40 (1:22)
- DLS FPU 50 (2:36)
- DLS SIL 30 (3:36)
DLS EPU 40 (Elastomeric Polyurethane):
EPU 40 is a high-performance polyurethane elastomer that is a good choice for applications where high elasticity and tear resistance are needed. Elastomeric Polyurethane CLIP Resin, due to its high performance allows excellent elastic behavior under cyclic tensile and compressive loads. You can stretch it and bend it, it takes back its original printed shape.
EPU 40 is comparable to commercial TPUs with a Shore hardness of 70A. EPU resin is rubbery, resistant, flexible and stretchable, with a layer thickness of 100 µm or 0.1 mm which are almost invisible. Parts are then very close to injection moulded models, which makes it very interesting for prototyping. Take a look at the spec sheet.
Key Features
- Highly elastic
- Tear-resistant
- Chemical and biocompatibility
Applications
- Gaskets and seals
- Shock absorbers
- Vibration isolators
DLS FPU 50 (Flexible Polyurethane)
FPU 50 is an impact, abrasion and fatigue resistant semi-rigid material that is a good choice for parts that must withstand repetitive stresses. This material can be ideal for tough enclosures, hinging mechanisms, and friction fits. FPU is comparable to polypropylene for its excellent fatigue and heat resistance. Features as thin as 0.25 mm can be 3D printed and it is not rubbery and elastic like EPU 40. Click here for the overall specs of DLS FPU 50.
Key Features
- Tough and fatigue resistant
- High tensile strength
- High impact and yield strength
Applications
- Snap fits
- Strain reliefs
- Mounts and brackets to encapsulate small electric circuits
DLS SIL 30 (Silicone)
SIL, a silicon-urethane material is comparable to commercial TPEs with a Shore A hardness of 35. CLIP technology enables 3D printing with novel classes of polymers, including complex chemistries such as polyurethane and cyanate ester-based resins. The result is a diverse and growing selection of materials reflecting common engineering requirements. Here is the spec sheet.
Key Features
- Soft-touch
- Biocompatible
- Tear-resistant
Applications:
- Wearable (Wrist bands, headphone pads)
- Medical equipment
All of these CLIP resins are suitable for long-term (>30 days) skin contact. Similarly, all can be used for short-term (<24 hours) mucosal contact except EPU 40*, which is suitable for skin contact only. Hence, they find their way into printing safe materials in the medical industry as well.
Flexible polymers cost comparison
Let’s have a cost comparison of the three resins from FacFox’s quote engine for the CAD model.
| Material | Cost per one unit | Unit cost per 10 pieces | Unit cost per 100 pieces |
| TPU Polyurethane 88/95A(MJF) | 29.95€ | 12.37€ | 11.41€ |
| Flex TPU/TPE like(SLS) | 25.84€ | 23.24€ | 21.41€ |
| EPU 40 | 212.44€ | 48.82€ | 48.82€ |
| FPU 50 | 436.53€ | 100.31€ | 100.31€ |
| SIL 30 | 632.56€ | 159.24€ | 159.24€ |
Conclusion
There are 2 main types of flexible polymers for 3D printing available on the mass market: TPUs, which can be printed with FDM, MJF and SLS 3D printers and CLIP resins (Carbon DLS). Go with the TPU materials if you’re looking for more affordable parts and with the more expensive CLIP resins if you require advanced material properties like high strength or tear resistance.
All these 3D printing options are available at FacFox, just upload your CAD files and check out the price options.