Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) is a metal additive manufacturing technique that uses a high-power laser to selectively fuse metal powder layer by layer. DMLS can create complex and precise metal parts with excellent mechanical properties and surface quality. However, depending on the application and design requirements, some DMLS parts may need additional surface finishing processes to improve their appearance, functionality or durability.
In this article, we will introduce some common surface finishing processes that can be applied to DMLS 3D printed parts, such as brushing, polishing and coating. We will also show you some examples of how different surface finishes affect the look and feel of DMLS parts made with aluminum powder.
What is DMLS 3D Printing?
DMLS 3D printing is a metal additive manufacturing technique that belongs to the powder bed fusion family. It is similar to selective laser melting (SLM), but the main difference is that in DMLS, the metal powder is not fully melted, but only sintered together. This allows for more flexibility in creating alloys and composite materials.
DMLS 3D printing can create metal parts with high strength, density and accuracy. It can also produce complex geometries and internal structures that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. DMLS 3D printing is widely used for applications such as aerospace, medical, automotive and industrial components.
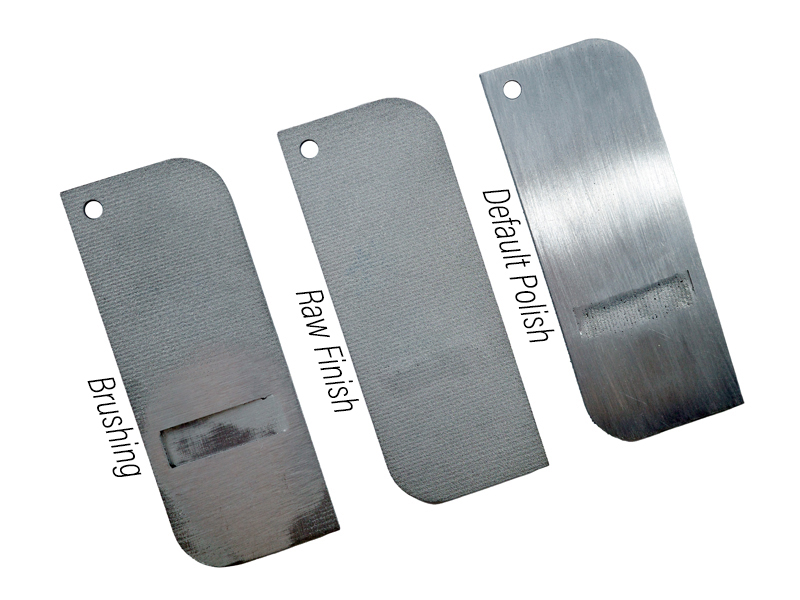
What Structures Are Suitable for Polishing?
Polishing is one of the most popular surface finishing processes for DMLS 3D printed parts, as it can greatly improve their visual appeal and quality. However, not all structures are suitable for polishing, as some may be too thin, fragile or complex to withstand the polishing force.
As a general rule of thumb, structures that are thicker than 0.6 mm can be polished without breaking or deforming. Structures that are thinner than 0.6 mm may be prone to cracking or bending during polishing. Structures that are thinner than 0.2 mm will definitely break with DMLS 3D printing. Indeed, FacFox could not guarantee that walls thinner than 0.5 mm can be printed successfully.
Therefore, when designing DMLS 3D printed parts that require polishing, it is advisable to avoid very thin or delicate features that may compromise their integrity or printability.
In addition, only flat or curved structures with a single shape are suitable for polishing. Structures that have patterns, letters, or similar features cannot be polished (for manual polishing, gaps are very difficult to polish).
What Surface Finishing Processes Can Be Applied to DMLS 3D Printed Parts?
Depending on the design specifications and intended use of the DMLS 3D printed parts, some surface finishing processes may be necessary or desirable to enhance their performance or aesthetics. Some common surface finishing processes for DMLS 3D printed parts are:
- Brushing: This process involves using a rotating brush or abrasive belt to remove the roughness and irregularities on the surface of the DMLS part. Brushing can improve the smoothness and shine of the part and reduce the visibility of layer lines and defects. Brushing can also create a uniform texture or pattern on the surface of the part.
- Polishing: This process involves using a polishing wheel, pad or cloth with a polishing compound to rub or buff the surface of the DMLS part. Polishing can further improve the smoothness and glossiness of the part, as well as remove any scratches or marks. Polishing can also create a mirror-like finish on the surface of the part.
- Coating: This process involves applying a thin layer of material on the surface of the DMLS part to protect it from corrosion, wear, abrasion or oxidation. Coating can also change the color or appearance of the part, as well as add functionality such as electrical conductivity or thermal insulation. Some common coating materials for DMLS parts are anodizing, electroplating, powder coating and painting.
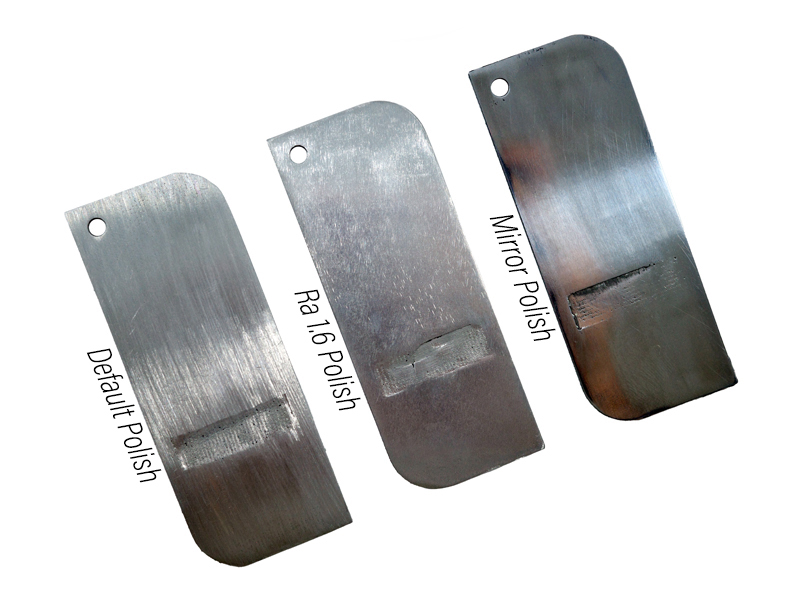

What Are The Main Types of Polishing?
There are different types of polishing that can be applied to DMLS 3D printed parts, depending on the desired level of smoothness and reflectivity. Some common types of polishing are:
- Default polishing: This is the standard polishing process that removes most of the roughness and layer lines on the surface of the DMLS part. It creates a smooth and shiny finish with a roughness average (Ra) value of about 0.8 micrometers.
- Ra 1.6 polishing: This is a more intensive polishing process that removes more material from the surface of the DMLS part. It creates a smoother and glossier finish with a Ra value of about 0.4 micrometers.
- Mirror polishing: This is the most advanced polishing process that removes the finest details and imperfections from the surface of the DMLS part. It creates a mirror-like finish with a Ra value of fewer than 0.1 micrometers.
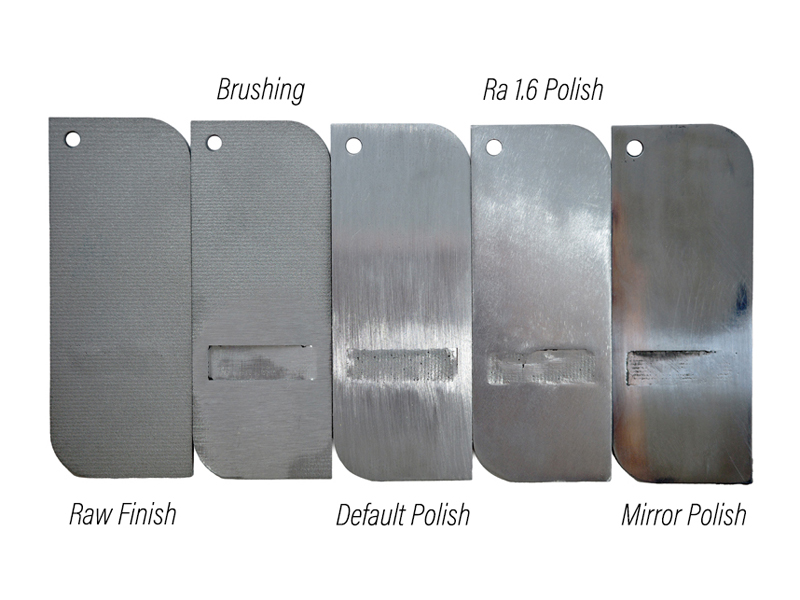
How Do Different Surface Finishes Affect the Look and Feel of DMLS Parts?
To illustrate how different surface finishes affect the look and feel of DMLS parts, we have 3D printed five pieces of sample strips with aluminum powder. Each strip has six stages of different thicknesses: 0.2 mm, 0.4 mm, 0.6 mm, 1.0 mm, 1.5 mm and 2.0 mm.
The front face of each strip has raised texts indicating the thickness of each stage. The texts are difficult to be polished so we leave the front face as a raw finish (Ra 3.2).
The back face of each strip has a different surface finish: Raw finish (Ra 3.2), Brushing, Default polishing, Ra 1.6 polishing and Mirror polishing.
From the photos below, you can see how different surface finishes affect the appearance and quality of the DMLS parts:
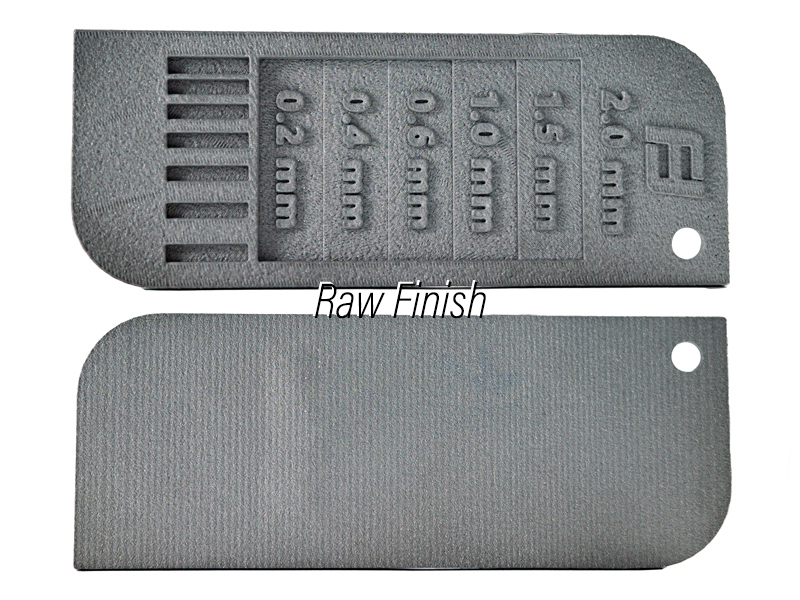
Raw finish (Ra 3.2)
This is the original surface finish of the DMLS part after printing. It has a rough and matte appearance with visible layer lines and defects. The thinnest stage (0.2 mm) has deformed and has a lump on it.

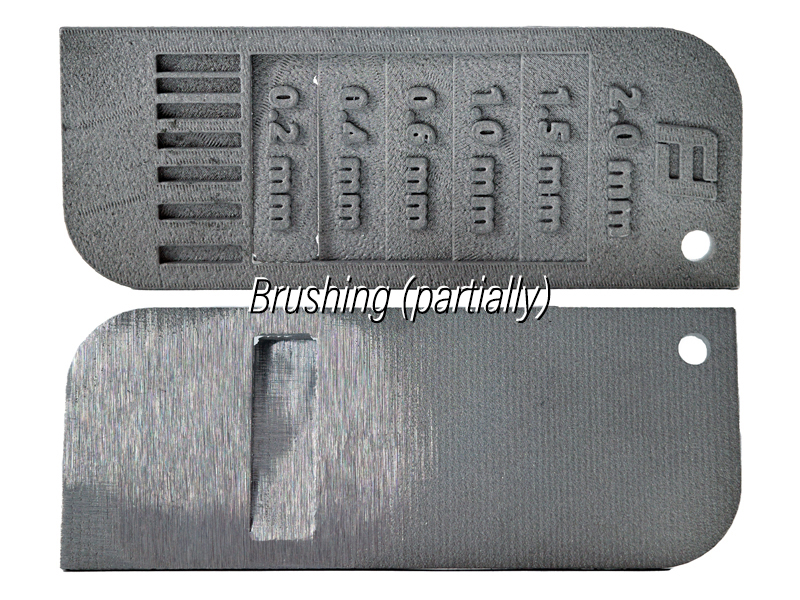
Brushing
This is the surface finish after brushing the DMLS part with a rotating brush. It has a smoother and shinier appearance with reduced layer lines and defects. The thinnest stage (0.2 mm) has broken off due to the brushing force.

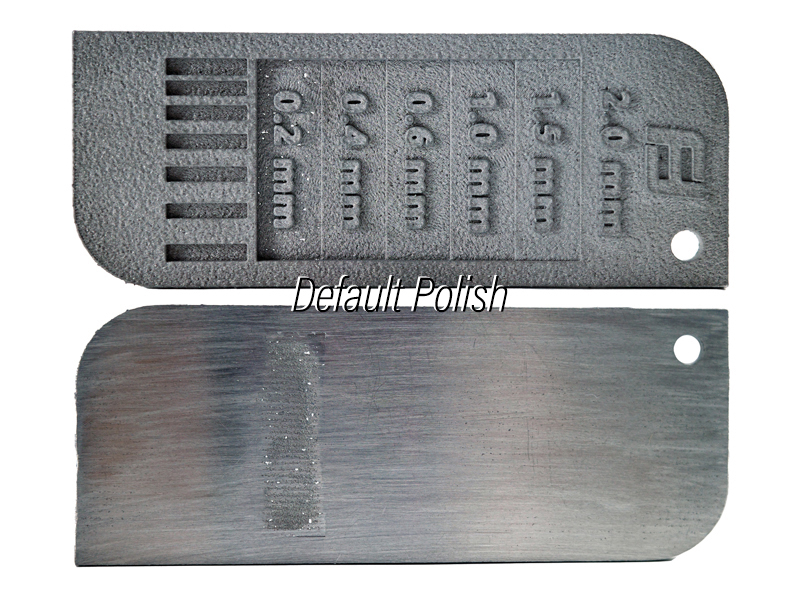
Default polishing
This is the surface finish after polishing the DMLS part with a polishing wheel and compound. It has a smoother and glossier appearance with minimal layer lines and defects. The thinnest stage (0.2 mm) has broken off due to the polishing force.

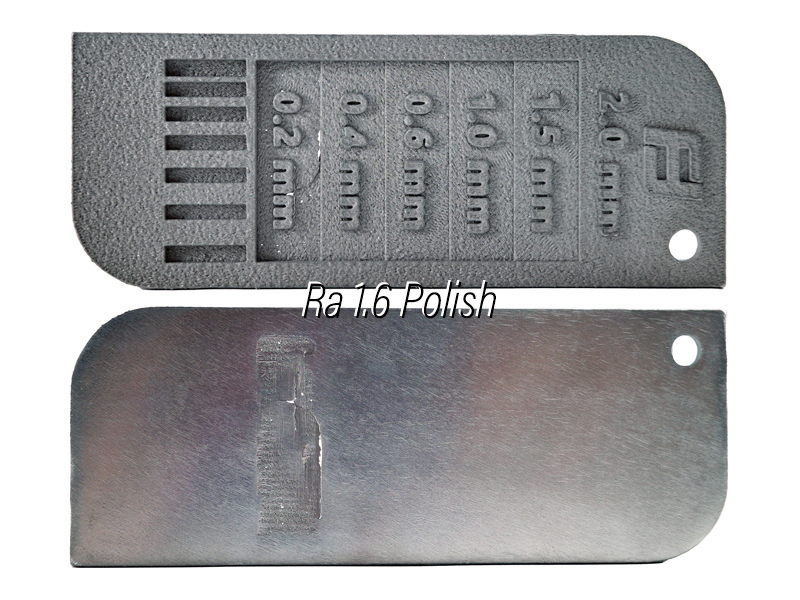
Ra 1.6 polishing
This is the surface finish after polishing the DMLS part with a more intensive polishing wheel and compound. It has a smoother and glossier appearance with almost no layer lines and defects. The thinnest stage (0.2 mm) has broken off due to the polishing force.
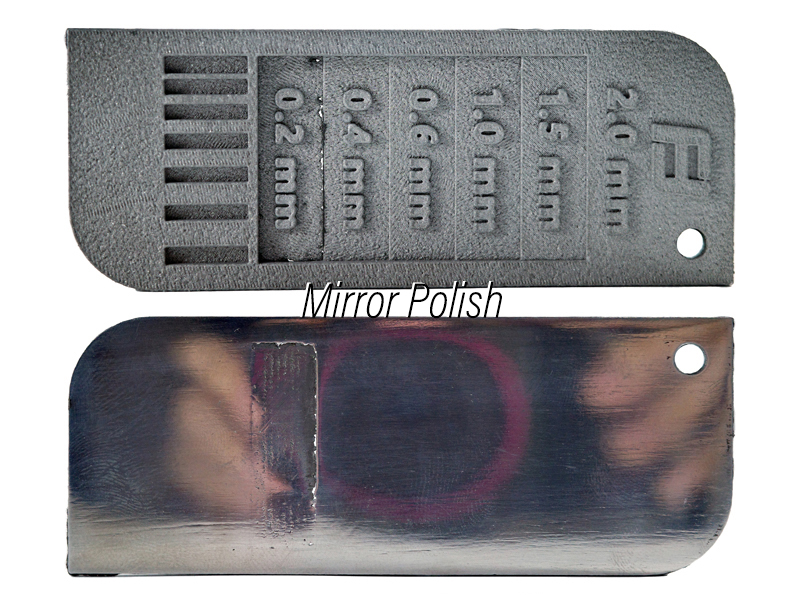
Mirror polishing
This is the surface finish after polishing the DMLS part with the most advanced polishing wheel and compound. It has a mirror-like appearance with no layer lines and defects. The thinnest stage (0.2 mm) has broken off due to the polishing force.
Conclusion
In this article, we have introduced some common surface finishing processes for DMLS 3D printed parts, such as brushing, polishing and coating. We have also shown you some examples of how different surface finishes affect the look and feel of DMLS parts made with aluminum powder that we could offer.
As the sample strips are made with Aluminum alloy, you can take them as a reference when choosing the finishing for your metal prints. Some of the most mature materials for metal printing are titanium alloy (TC4), aluminum alloy (AlSi10Mg), stainless steel (316L), and tool steel (1.2709). The polishing and brushing effects have nearly no differences.
We hope this article has helped you understand more about DMLS 3D printing and its surface finishing options. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to contact us at facfox.com. You can also email us via info@facfox.com. Our engineers are always willing to help!
