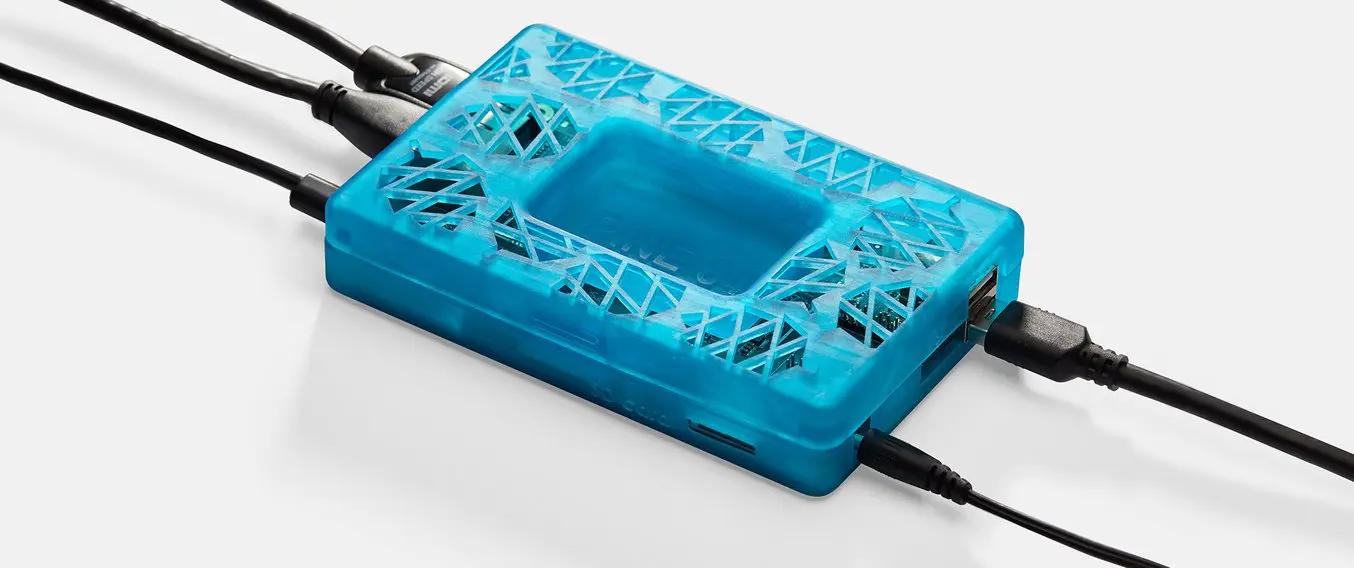
If you’re a product designer or an engineer, chances are you’ll need to make a custom enclosure at some point. This might be a simple container to keep small items organized or a fully functional 3D printed prototype to show stakeholders or test before moving to injection molding.
With CAD software and a desktop 3D printer, you can create a custom 3D printed snap-fit enclosure with interlocking parts in five easy steps.
Step 1: Prepare Your Custom Enclosure Design
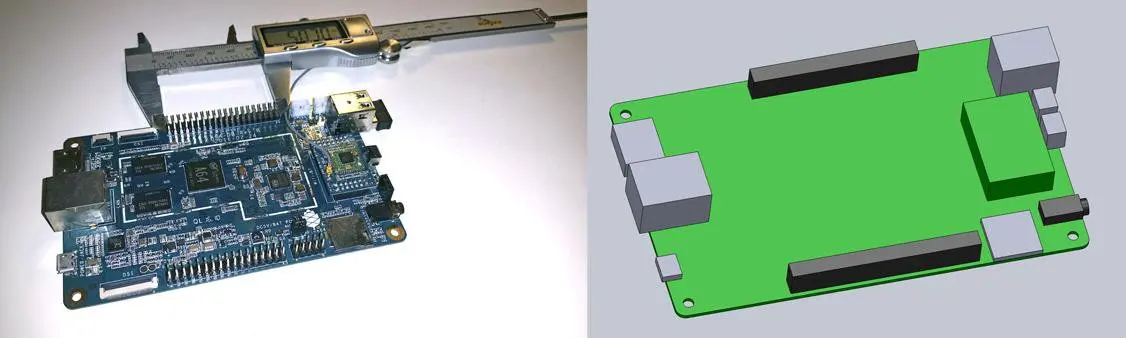
For this project, we’re going to make a case for a Pine 64, a single board computer (download the .STL file on Pinshape to follow along). This tutorial uses Solidworks because of its popularity in product design and engineering, but you can use a similar 3D design software.
First, use digital calipers or a ruler to measure your electronic component. We like to start enclosure designs by accurately reverse-engineering the PCB, measuring the board size, the location of mounting holes, and any ports or plugs that will need to be accessed through the enclosure. You might want to simply measure the overall maximum dimensions as a box, but it’s essential to know exactly where the main features are so that you can accommodate them. In Solidworks, reproduce these measurements as a grouping of basic boxes in a single part file.
Step 2: The Bottom Enclosure
In Solidworks, the enclosure is best designed as an assembly, with each half of the enclosure modeled as a separate part. Starting with the base half of the enclosure as a new part, the first important decision is to determine how much of a tolerance to have between the perimeter of the PCB and the enclosure. This depends on the 3D printing process you’re planning to use to 3D print parts. SLA and SLS 3D printers are highly accurate, so you can tighten the tolerance to 0.5 mm without much risk.
A desktop FDM 3D printer may warp your design and lift it off of the print plate, so you should allow a larger tolerance of 1.5-2 mm to ensure that the PCB will still fit inside even if the walls are somewhat distorted.
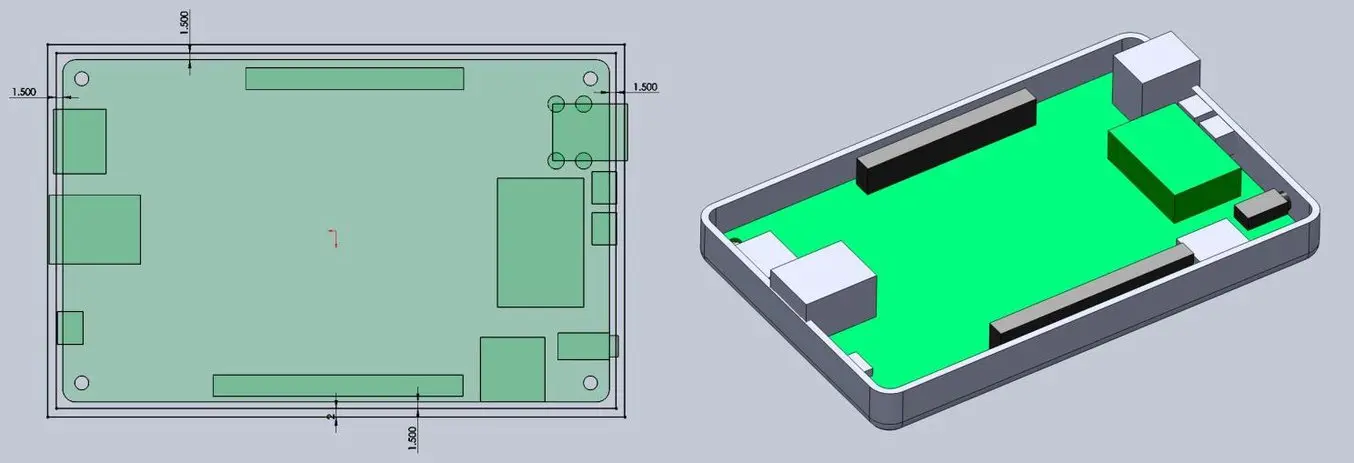
Our next step is to start cutting away the openings for the ports. One common mistake is that you will only cut away just enough material to expose the port connection, be it a USB or HDMI, without taking into account that many cables around the male connector can be quite bulky and need to reach into your enclosure to connect to the port (especially if the port is set in from the edge of the PCB, farther away from the enclosure). So it’s best to be generous with the port openings. An extra 2 mm all the way around is a good starting point.
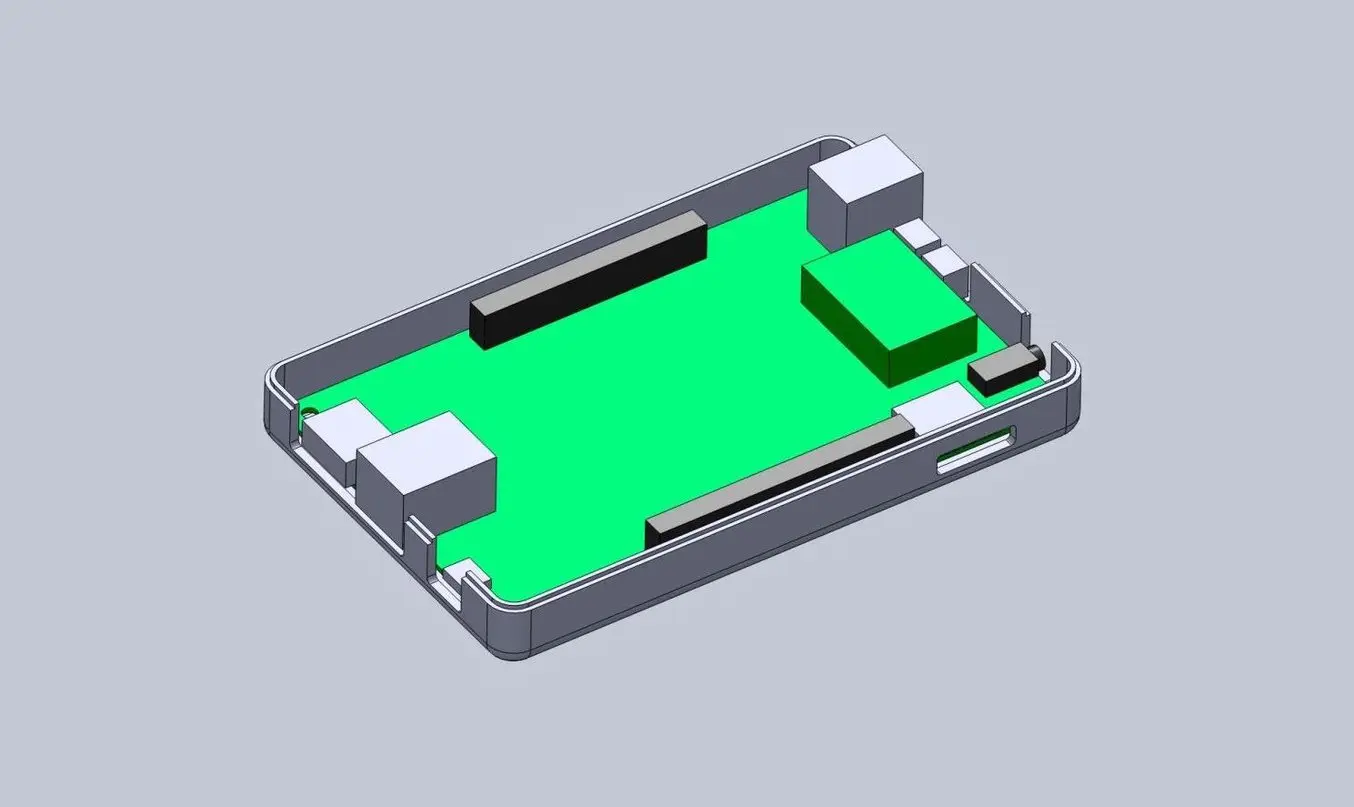
As you can see in the image above, we included extruded cuts, which go all the way from the top, and one cutout for a Micro SD card. The reason that some of the cuts reach the top is that the ports on the board stick out beyond the edge of the PCB, so in order to fit the PCB, we need to allow room for them to slide down. We will close some of these off with our top enclosure part, but you could choose to create a larger bottom enclosure so that the entire PCB and ports fit inside. Just be aware that you will have to push your connecting cables further inside the enclosure.
Step 3: The Top Enclosure
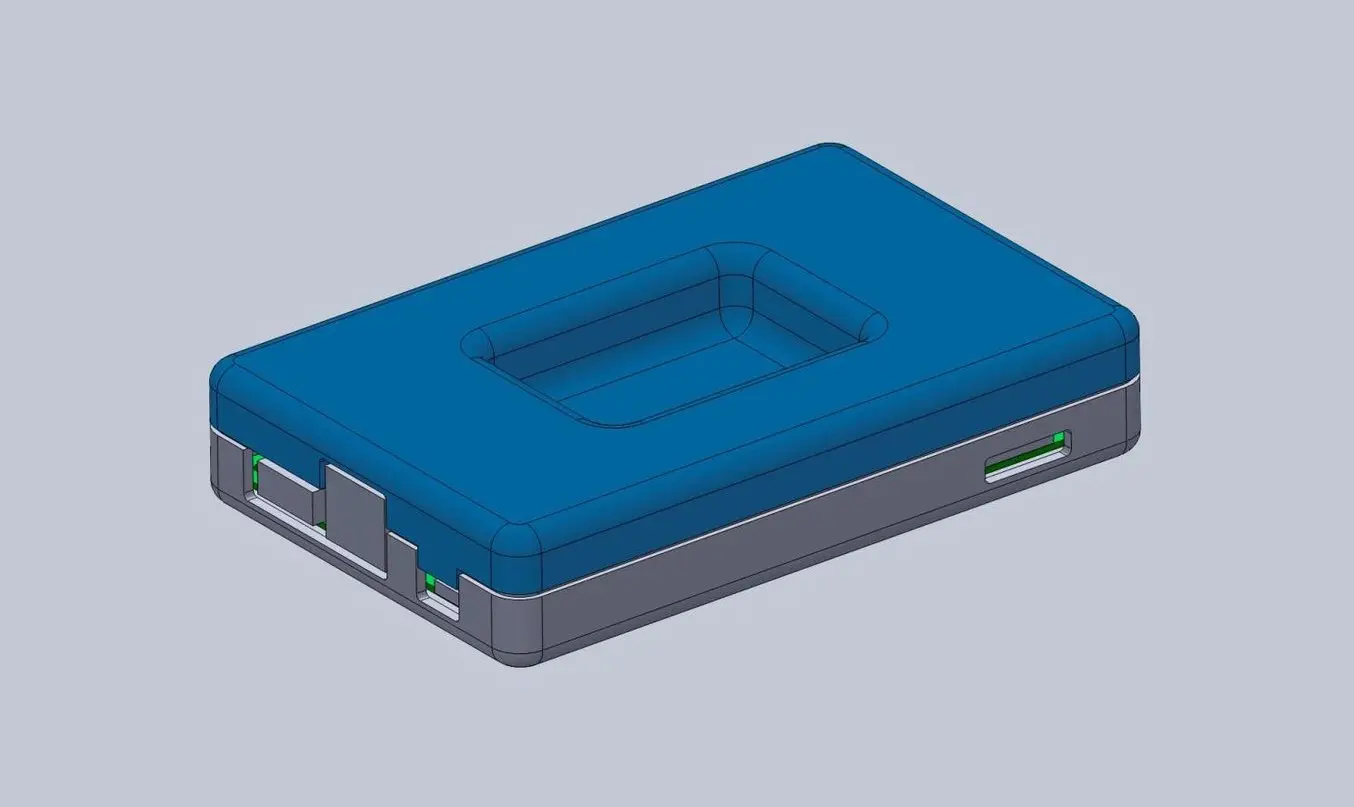
Now that you’ve completed the bottom enclosure, the top section is easy. The above image shows the effect of the parting line running around the perimeter between the two enclosure halves. The top enclosure has had the same treatment of cut details to accommodate some of the taller ports, as well as the addition of material to close off some of the gaps left by the bottom enclosure. We also added an optional sunken middle section.
Step 4: Designing the Snap-fit Joint
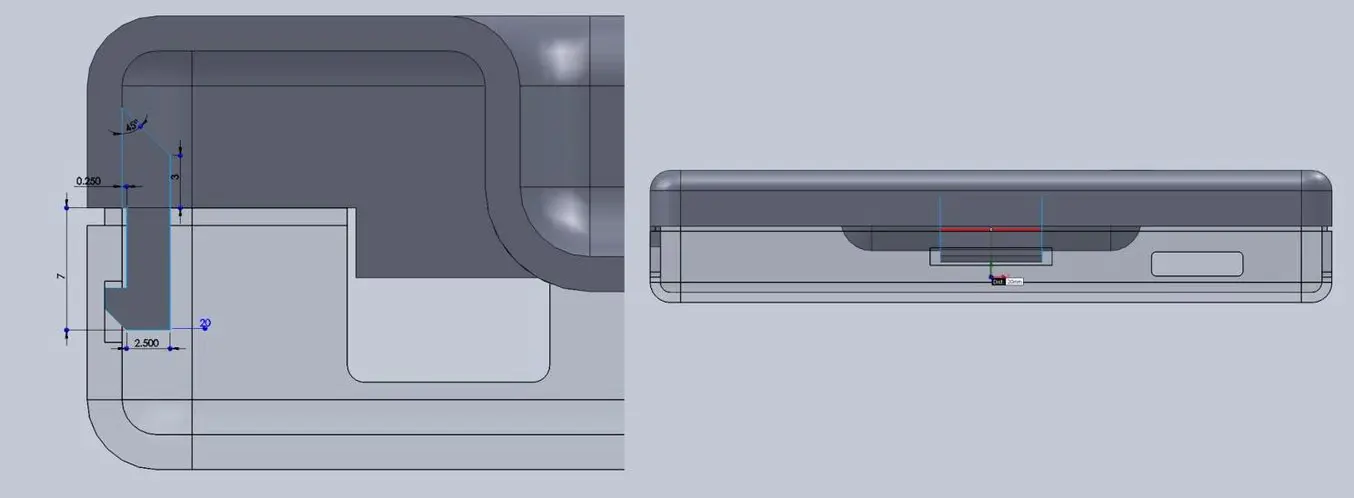
There are many designs for snap-fit components, but we opted for a basic internal cantilever joint. Above you can see the main details for the snap-fit design, which is exactly the same on both sides (male and female parts) of the enclosure. Depending on the space you have to work with, you can lengthen the small protrusion engaging into the snap cavity to create a stronger lock. In our snap-fit assembly, it’s only 1.2 mm, but 2 mm or more would be much more secure. In this particular design, the pins on the PCB take up a lot of room, so the lock is designed to just squeeze in while providing enough force to hold the enclosure together. The cantilever joint is extruded 20 mm long, which adds to the strength.
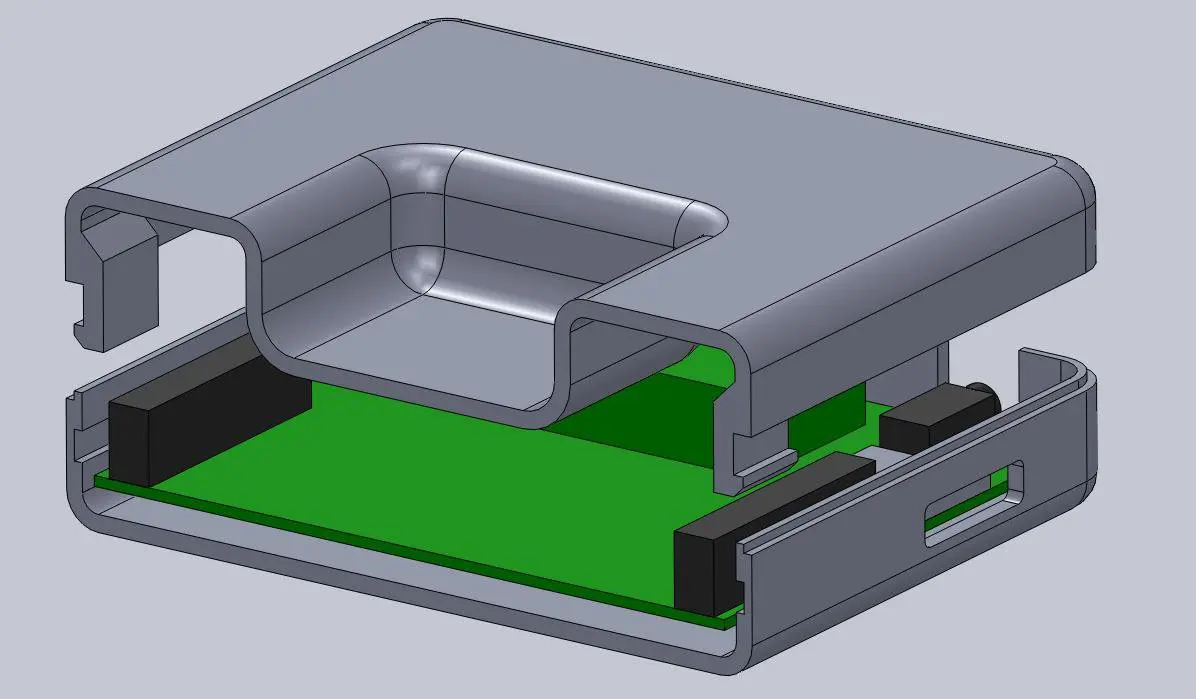
Above you can see a sectioned exploded view of the snap details on the enclosure, along with the PCB showing the location of the pins (in black), which limit the size of the cantilevered joint. Alternatively, instead of the snap cavity hiding inside of the bottom enclosure, you could cut this detail through to the outside, allowing your snap-fit joints to be longer.
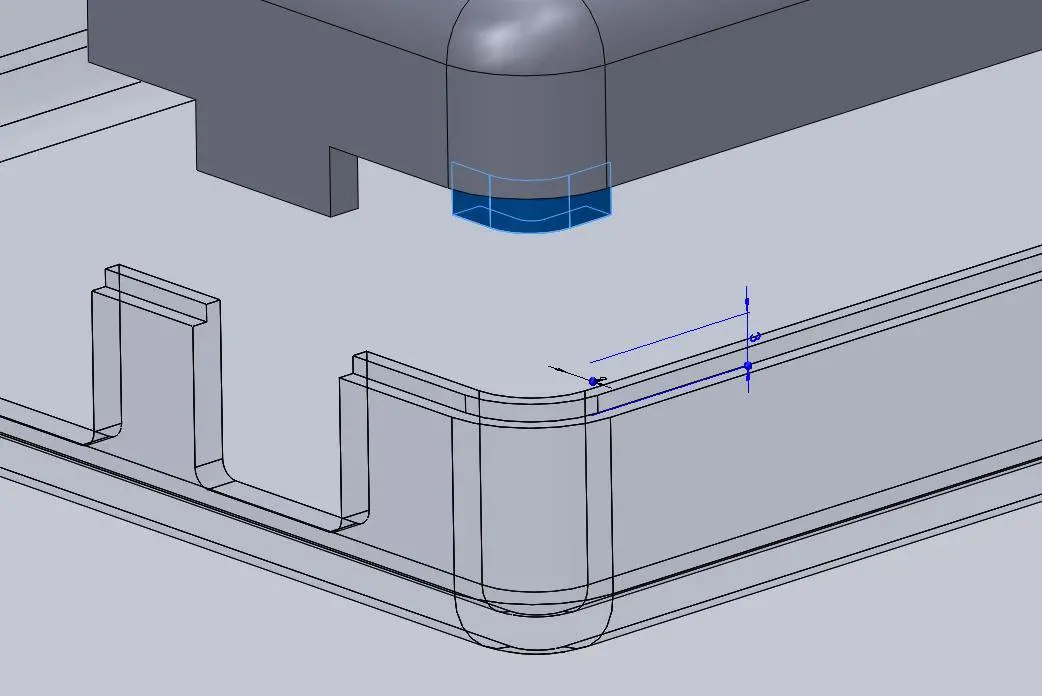
Step 5: Add Final Details To Your Enclosure
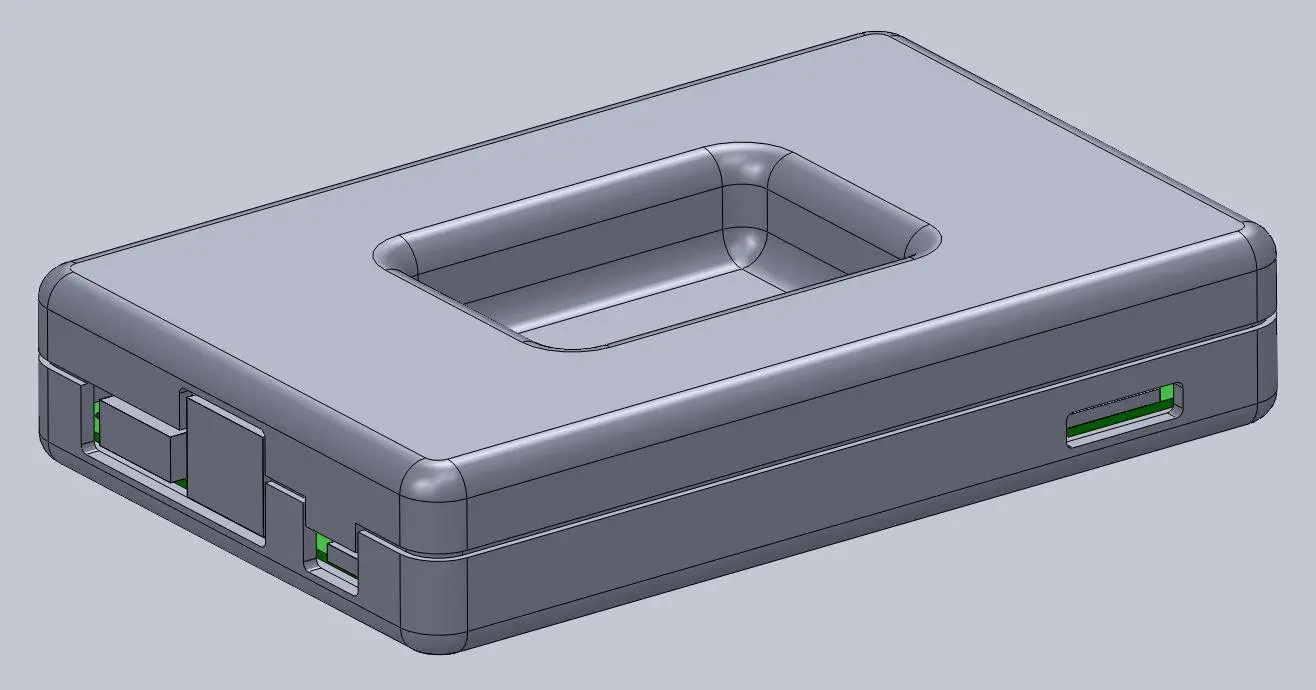
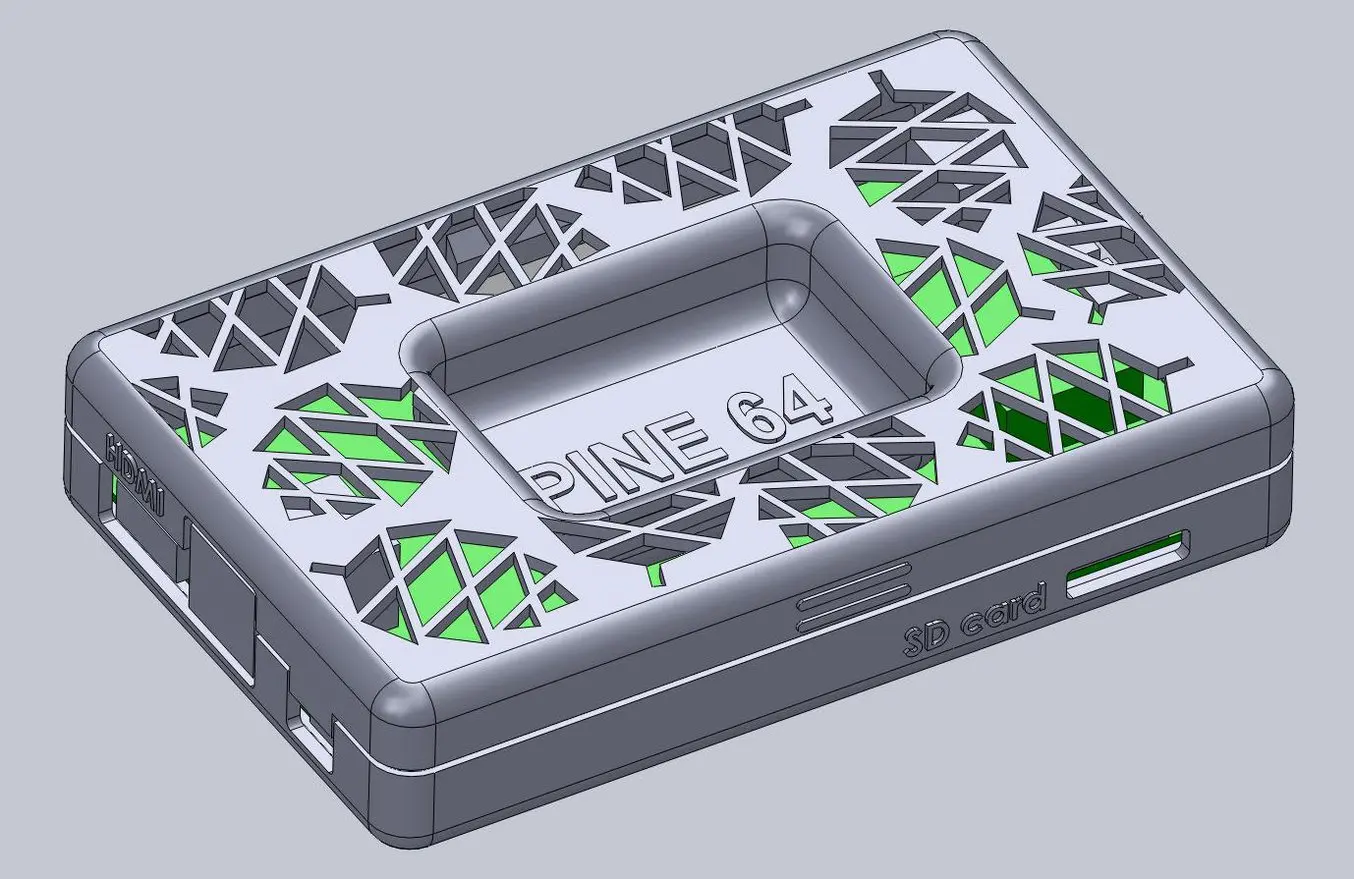
While this might be enough detail for your project, a few added features can bring your 3D printed enclosure to life. For this design, we extruded some text for the Pine 64 name and details like the SD card location. We included the Pine 64 logo as a visual feature, but also to provide ventilation on the top since these boards can heat up. Plus, these details reduce the amount of 3D print material used. Finally, a couple of grip details where the snap-fit joints are located helps indicate where to press your fingers to open the enclosure.
3D Print Your Snap-Fit Enclosure With SLA Printing
SLA 3D printing offers a wide variety of engineering materials for creating accurate 3D printed parts and prototypes and helps you reduce costs, iterate faster, and bring better experiences to market.
Want to see what you can create with SLA 3D printing? We’ll ship a free 3D printed sample part to your office.
