

To get the most of additive manufacturing, you want your AM facility to move away from people having to manually enter information about processes and toward machines having the ability to report data to the MES automatically.
The integration between MES and your additive manufacturing equipment can offer the following functionality:
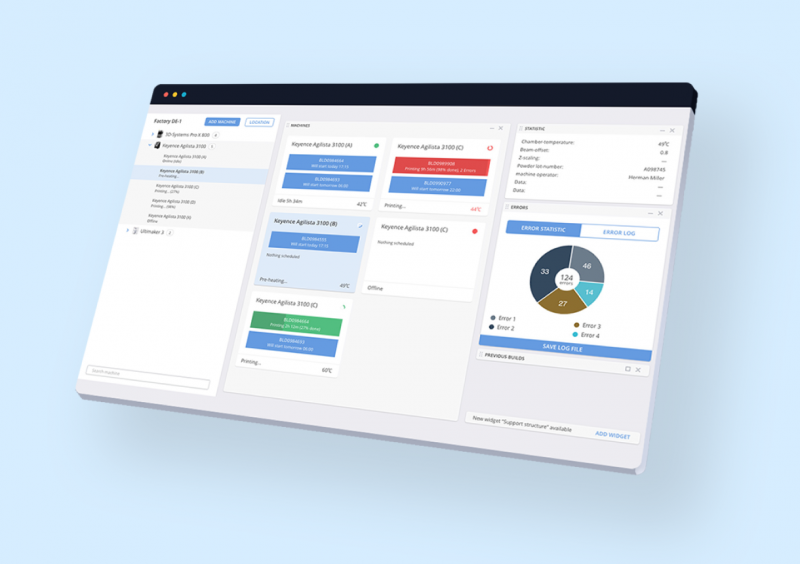
1. Track machine status
Tracking machine status through MES is crucial to the efficient operation of your AM facility.
This method is more accurate than having operators checking status manually. Manual status tracking is time-consuming, error-prone and dependent on the memory of operators.
In a typical situation, when a machine goes offline unexpectedly, your workers’ first reaction would be to get it back up and running. Only after someone has fixed the device do they usually enter the time it went down and for how long.
Machine status detection also collects data on when machines are idle because they are not involved in the current process. Continuous reporting on this data helps you to get a better picture of how your AM facility is functioning and where you can make improvements.
2. Pull processing parameters from machines
Capturing hard measurements from your AM equipment is also possible with machine integration. Data such as the total count of parts coming off of a 3D printer can be communicated to the MES and factored into your OEE.
Tracking the printing time is also an important metric for you to consider to evaluate your overall performance. Machine integration that pulls parametric data allows you to maintain a real-time view of the quality of the products you are producing and the efficiency of your processes.
3. Provide and log error alerts occurring during the printing process
The MES platform, which collects data from your machines, provides you with a dashboard where you can track not only the status of machines but also any errors occurring during the print. This data is logged in the system, which means you can easily access it for further analysis.
Receiving real-time alerts and tracking any process anomalies can go a long way to help you identify and fix the problem faster, potentially preventing unplanned downtime.
The benefits of connecting and monitoring your 3D printers through MES
1. Real-time insight into machine performance
When you have the MES track 3D printers’ status, uptime and errors, it helps you obtain accurate information that factors heavily into calculating the actual Overall Operational Efficiency of your AM equipment.
Without machine monitoring, machine operators and production managers remain largely in the dark on real-time equipment performance. Of course, they can still check on the printer manually, but this can eat up a lot of time and limit productivity, especially if you have several machines running at the same time.
With machine monitoring through MES, this data loop between the machine, production management software and machine operators is seamlessly automated to ensure visibility and connectivity across the production workflow.
Further reading: EOS and AMFG Announce Partnership to Enable Machine Connectivity for Additive Manufacturing
2. Increased productivity
With easy access to real-time machine data through MES, production managers can improve AM production jobs scheduling.
Knowing the machine’s status, print time and throughput helps you predict and plan the capacity of AM machines more accurately. With this knowledge, you can maximise the productivity of your AM facility, ultimately achieving higher ROI on the AM investment.
Further reading: Establishing a Business Case for Manufacturing Execution System in AM
3. Efficient machine maintenance
With real-time alerts enabled by machine monitoring, your maintenance team can easily create notifications to proactively monitor the AM shop floor.
Proactive monitoring can help you forecast maintenance needs based on real-time performance data – rather than rely on the churn of predetermined maintenance schedules, often after the machine’s performance declines.
This immediate awareness of machine issues, data connectivity and equipment health prevents disruptive equipment failures. Instead of waiting for a machine to stop working and producing a faulted part, maintenance can quickly access and analyse their real-time alerts to identify potential root causes, troubleshoot and fix the issue before it turns into downtime.
4. Traceability of relevant quality data
By helping you identify problems and inefficiencies, machine monitoring increases product quality and process innovation.
The capability to store relevant production parameters, such as job print time, as well as print results, gives the production team a clear view of which parameters resulted in the highest-quality printing jobs.
By analysing the collected data, the team can develop proven production strategies, which ensure consistent, high-quality parts each time.
3D printer connectivity and MES: quick wins and long-term results
As we’ve seen, the benefits of integrating machine monitoring with additive MES can go beyond making equipment more efficient.
Machine connectivity and visibility empower machine operators and production managers to innovate the production and maintenance processes.
And as all people, systems, and assets become more efficient, connected and informed, they become better positioned to drive the growth of additive manufacturing, maximising your investment in the technology.