A bumpoff is a small undercut in a part design that can be safely removed from a straight-pull mold without the use of side actions. It works like the snaps on the wind flap of a parka or the snaps on a western style shirt—push to close, pull to open. If you look very closely at the two parts of a snap, you will see that there is slight deformation of the material when the snap is opened or closed. The choice of material and design of the snap’s components allows that deformation to take place without damage or significant wear to the mating parts. This is exactly what happens during the ejection of a part with a bumpoff feature.
In the case of a plastic part in an aluminum mold, any deformation that takes place at ejection will be entirely in the plastic part, not in the mold. A number of factors determine the ability of a part to be “bumped-off” without damage. These include the shape of the undercut itself, the resin used to form the part, the geometry of the area surrounding the undercut, and the design of the mold.
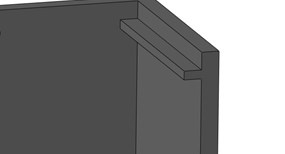
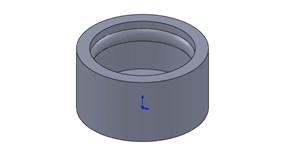
Figures 1 and 2 address the shape of the undercut feature. In order to be successfully bumped-off, the leading edge of an undercut must provide a “ramp” or radius like that in Figure 1 rather than a hook or sharp edge as shown in Figure 2. If other factors are correct, during ejection the ramp-shaped lip inside the cylinder in Figure 1 can ride up over the edge of the groove in the mold that formed it, much as a car rides over a speed bump. Conversely, the hook in Figure 2 will remain lodged in the groove that formed it and either prevent ejection entirely or be torn off when the part is ejected.
Resins such as TPE, unfilled polyethylene, or polypropylene will be flexible enough to bump off, and that’s the material most designers choose for common consumer items such as plastic bottle caps. Brittle materials such as glass-filled nylon or polycarbonate (PC) are quite rigid and not likely to work very well.
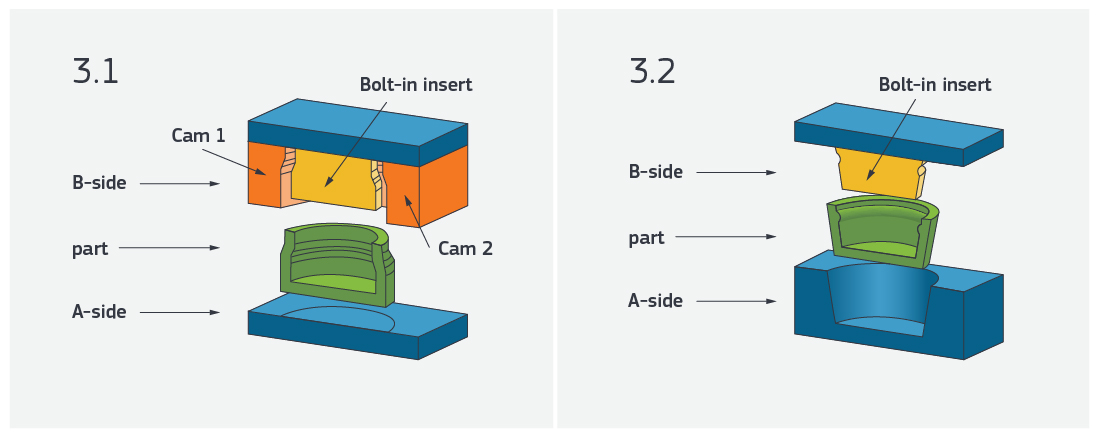
Finally, we consider the shape of the part and the molding technique. At FacFox, we use a bolt-in insert to produce the undercut geometry required, rather than using machining tools such as specialty cutters. FacFox will mill a secondary piece—called a bolt-in insert—that is not part of the mold but is attached to the B side of the mold. Examples can be seen in Figures 3.1 and 3.2.
If you have questions about the feasibility of bumpoffs for small undercuts in your part design, FacFox’ applications engineers are here to help and can be reached at +1 (917) 789-8125.