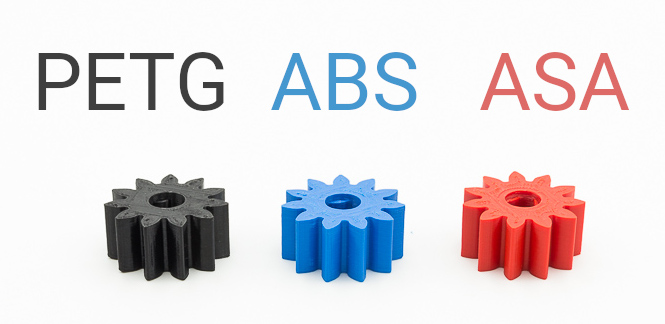
Following the theme of the previous article, where we compared the PETG and the PLA, here are the differences and similarities between the PETG, the ABS and the ASA.
PETG and ABS belong to the group of the most consumed materials in the field of 3D printing FDM / FFF, the first for its balance between strength and ease of printing and the second for its great use in the world of the industry since years. The ASA is attracting more and more consumers, above all those who need a high mechanical and environmental resistance.
ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is the plastic par excellence in the world of the industry at the time of creating housings or external parts of all kinds, normally directed to a constant manipulation. The ABS offers hardness, resistance to certain chemical elements, rigidity and stability at a high temperature (100 ºC). Another advantage of this engineering plastic is that it can be painted or covered with a thin layer of metal. ASA (acrylonitrile styrene acrylate) is known as an advanced ABS very resistant to weathering without the need to be painted or treated superficially.
PETG and the ABS are 3D printing materials with good mechanical properties, with some similarity. Both materials have good shock resistance, but the copolyester has greater resilience, recovery energy after deformation. On the other hand, with ABS parts with greater hardness and rigidity are obtained, since the PETG has a certain elasticity. One advantage that ABS presents is the power to be machined without deformation, something unusual in conventional 3D printing materials. This property is obtained, in large part, thanks to the high glass transition temperature (Tg= 100 °C, see the values of all materials in the following table) and the stability of the material itself. When parts are made for the outside or to be in contact with chemical fluids, the PETG is more resistant to this type of products, to the action of the sun, rain and cold, although there are solutions such as the Plastimperm F10 for waterproofing parts made with ABS. The majority of PETG colors have a high percentage of translucency, something positive in many cases but which makes it difficult to always get the same color code; on the other hand, with the ABS the same RAL and Pantone color code can be obtained without problem. When it comes to printing complex parts, the PETG is less prone to cracking deformations, something that can happen with ABS, especially in large parts and in a 3D printer without a heated cabin, where the concentration of tension due to temperature variation It can be so big that they take off from the base. In case you need to manufacture high volume pieces with supports, it is recommended to use a 3D printer with a heated chamber (3NTR A2) with a soluble support material. For the PETG there are water-soluble support materials (Mowiflex 3D 2000), which greatly simplify the manufacture of complex parts. The ASA maintains, or even increases, the mechanical advantages of the aforementioned ABS and complements them with good resistance to adverse environments, giving an ideal material for automotive exterior parts or power tool housings.
In the field of printing properties, the three materials that are being compared need similar extrusion temperatures (230-260 ºC), with PETG, presenting a certain advantage, which can be printed with a cold base with the help of some type of adhesive (3DLac, DimaFix, Magigoo…) but it is advisable to use hot base for large pieces. In the case of ABS and ASA it is essential to have a hot base (90-110 ºC) and it is even very favorable to make the pieces in a closed 3D printer FDM / FFF cerrada to keep the temperature stable. This stability is also key when cooling a piece, especially with acrylonitriles, as they are prone to contract with abrupt temperature changes. These presents another disadvantage when it comes to printing and is the release of toxic fumes. On the contrary, the PETG does not present this problem, even PETG of certain manufacturers, such as the CPE HG100 of Fillamentum, have the FDA and BPA Free certificates. Due to the higher density of the PETG (1.27 g/cm³) compared to ABS (1.04 g/cm³) and the ASA (1.07 g/cm³), it is advisable to increase the separation between the nozzle and the base of the configuration for ABS. This difference in density (20 %) will increase the weight of the parts manufactured with the copolyester, creating a slight disadvantage.
| ABS | ASA | PETG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waterproof |  |
 |
 |
| Heat resistance |  |
 |
 |
| Cold resistance |  |
 |
 |
| UV resistance |  |
 |
 |
| Chemical resistance |  |
 |
 |
| Machinable |  |
 |
 |
| FDA |  |
 |
 |
Image 2: Comparison table
After all the information cited above, we can say that ABS is a material used in many fields of industry: helmets, power tool housings or even in LEGO blocks. The ASA will increasingly be used to manufacture external parts such as car mirror housings. And PETG will continue to evolve, especially to make prototypes and containers for food.