Welcome to our comprehensive guide on PU molding processes! If you’re looking to explore the world of polyurethane molding and understand the various techniques available, you’ve come to the right place.
In this article, we have compiled a table that outlines six different PU molding processes, providing you with a concise overview of their materials, descriptions, applications, advantages, and limitations.
Whether you’re a manufacturer seeking the ideal technique for your product or an enthusiast eager to expand your knowledge, this resource will help you make an informed decision. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of PU molding processes!
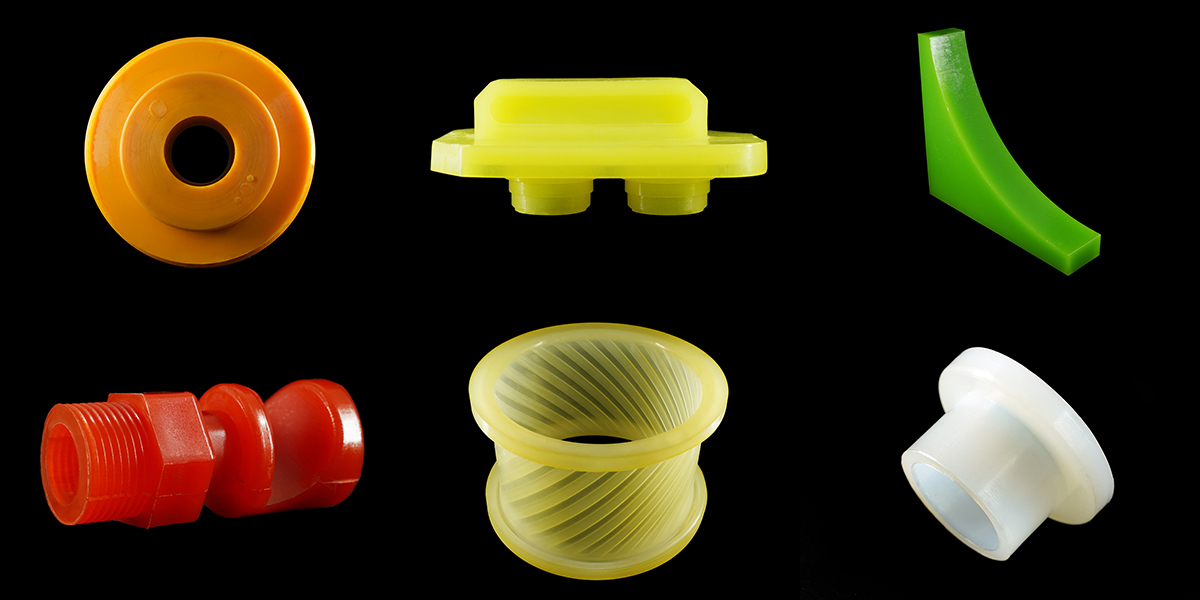

Open Cast Molding: Simplest method for manufacturing polyurethane products with high hardness. Involves pouring heated liquid resin and curative into an open-top mold or from the bottom, allowing it to solidify quickly. Ideal for short runs and offers flexibility in material selection.
Compression Molding: Commonly used for large thermosetting polyurethane products. Involves placing a compounded polyurethane mass in a mold with upper and lower halves, compressing them to force the polymer to flow. Gas is vented, and the product is cured, cooled, and released from the mold.
Spin Casting / Rotational Molding: Used to produce seamless, hollow polyurethane products. Involves rotating a mold filled with powdered polyurethane, which melts and coats the inside surface. Centrifugal force fills molds and removes air bubbles. No high pressure is used, and the product is cooled, rotated for a specific time, and then ejected from the mold.
Injection Molding: Involves heating and melting the polyurethane, followed by injecting it into a mold using high pressures. Curing occurs inside the mold, resulting in solid, semi-solid, or cellular products.
Blow Molding: Creates hollow products by inflating a softened preform inside a mold using thermoplastic polyurethanes. Involves extruding the preform, enclosing it in a mold, and inflating it with compressed air. The product is cooled and ejected from the mold after molding.
Extrusion: A polyurethane blank is pushed through a shaped die producing a formed urethane part with excellent surface finish, which can be accomplished with hot or cold material.
Polyurethane Casting: Utilizes silicone elastomer molds to inject polyurethane and additive resins. Similar to injection molding with the use of a soft mold, but with more cost-effective and faster mold preparation. Suitable for short runs and low to medium-volume production.
| Molding Process | Material | Suitable Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open Cast Molding | Various Polyurethanes |
|
|
|
| Compression Molding | Thermosetting Polyurethane |
|
|
|
| Spin Casting / Rotational Molding | Polyurethane Powder |
|
|
|
| Injection Molding | Thermoset & Thermoplastic Polyurethanes |
|
|
|
| Blow Molding | Thermoplastic Polyurethanes |
|
|
|
| Extrusion | Thermoset & Thermoplastic Polyurethanes |
|
|
|
| Polyurethane Casting | Polyurethanes and Additive Resins |
|
|
|
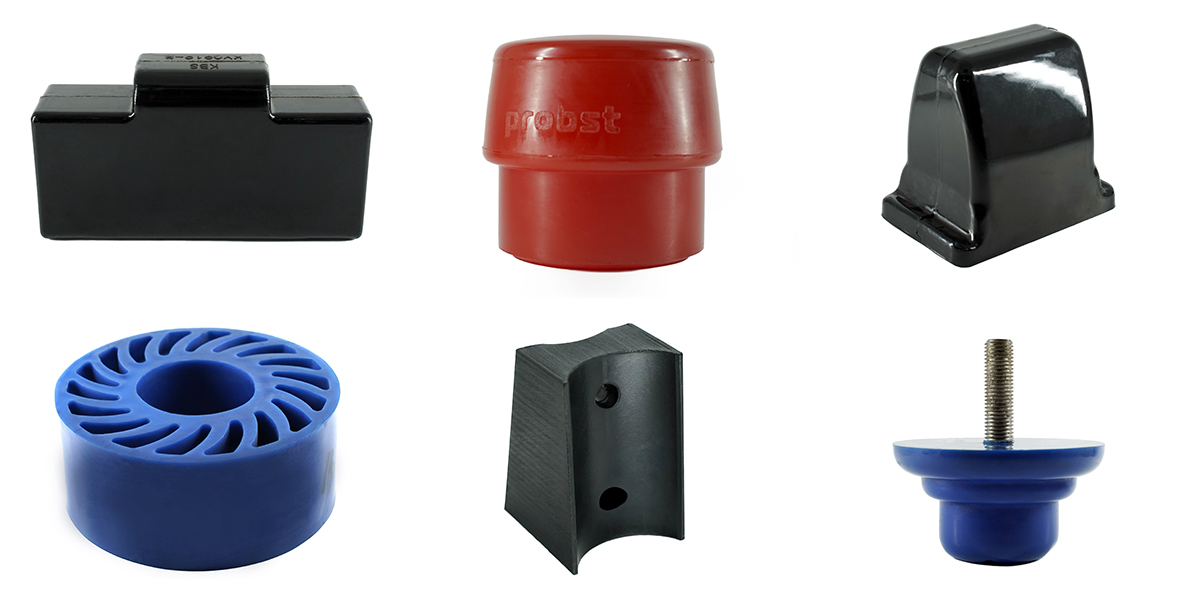

We hope this guide has shed light on the diverse PU molding processes available to you. Each technique offers unique advantages and limitations, making it crucial to assess your specific requirements before making a selection. Whether you’re leaning towards reaction injection molding, extrusion molding, or any other method, understanding the materials, descriptions, applications, advantages, and limitations associated with each process will empower you to make an informed choice. By harnessing the power of polyurethane molding, you can unlock a world of possibilities in manufacturing and material innovation.
When you choose FacFox for your PU molding needs, you benefit from our commitment to excellence. Our stringent quality control measures ensure that each molded part meets the strictest standards, resulting in products with exceptional surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Furthermore, our extensive experience allows us to offer valuable insights and recommendations throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring a seamless and satisfying experience. Contact us today via info@facfox.com for a quote instantly!