Connectivity is no longer an option, but a necessity, for AM facilities. It helps to remove the silos between manufacturing equipment and software systems, creating traceable, data-rich workflows.
Connectivity, however, doesn’t exist in a vacuum and requires a specialised platform through which the data can flow.
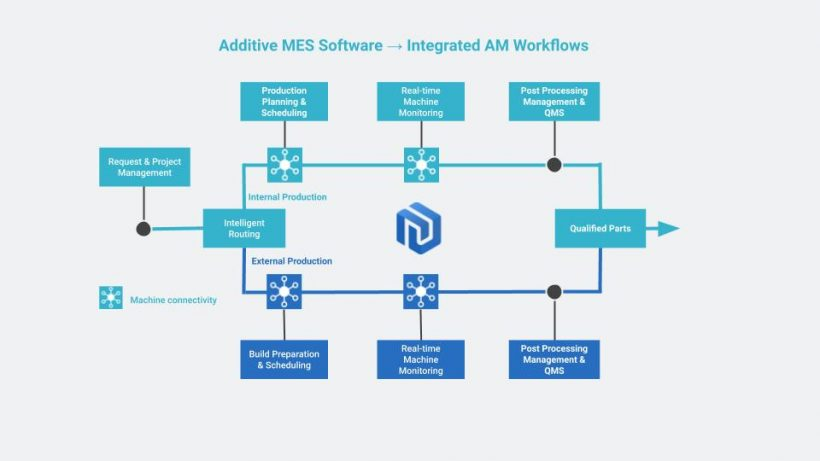
This places the Additive Manufacturing Execution System (MES) – a software that manages and monitors the work in progress on the factory floor – in the spotlight. Additive MES serves as a centralised platform that connects AM processes and harvests data in real time.
This article will explore the role of connectivity-driven Additive MES software in helping your AM facility to achieve greater efficiency across its processes and supply chains.
Why does my AM facility need connectivity?
Data is at the heart of all AM production and is being generated continuously, at every stage of production.
This includes the data from machines and materials, to the data from different software systems (ERP, PLM).
One of the primary challenges to using this data is disconnected systems and manual processes, which don’t allow for real-time access to data.
Let’s take spreadsheets as an example. Many AM facilities are still using spreadsheets to organise projects and schedule AM production.
However, AM production planning, forecasting and reporting are commonly collaborative activities, meaning that they typically require information from different departments. In addition, the final documents are often a result of multiple exchanges of data and files.
Now, if your AM production sites are scattered across different locations, or if certain team members are separated by large distances, the only way to exchange data stored in spreadsheets is through email.
Experience will tell you that such a method of exchange is susceptible to duplicate and even erroneous data. Your team members will tend to find it hard to keep track of similar files going back and forth, and sometimes even end up sending the wrong version.
Furthermore, when it’s time to generate AM production reports, you’ll have to go through a slow consolidation process. In most cases, your employees would have to collect data from different files, summarise them and submit the same to their department heads through emails, portable storage media, or by copying to a commonly shared network folder.
Department heads would have to undergo a similar process before submitting them to their own superiors. Throughout the entire consolidation process, data is subjected to numerous error-prone activities, such as copy-pasting and wrong data entry.
What this tells us is that spreadsheets can’t really support quick decision-making and are unsuitable for establishing workflow transparency and real-time access to data. They just aren’t built for that.
How connectivity helps
On the other hand, when using a connectivity-driven software, instead of spreadsheets, to organise and monitor your AM production, you can link your machines, software systems like ERP, PLM and other systems to ensure a continuous, real-time transfer of data at every stage of production.
Connectivity becomes increasingly crucial when you run AM operations across different locations and need to coordinate suppliers when outsourcing some of your AM activities, like post-processing.
Ultimately, connected AM workflows put the data at your fingertips, enabling you to establish a seamless real-time stream of relevant AM data, that supports full traceability and agile decision-making.
What is the role of Additive MES software in achieving connectivity?
Connectivity is one of the most critical capabilities of Additive MES platforms. It implies the ability of an MES platform to connect production and operation systems so that they can communicate with each other for maximum efficiency.
Connectivity in the AM workflow can be divided across three key areas: machines, operations and supply chains.
Below, we explore the benefits of connectivity-driven Additive MES software, across these three areas, in more detail.
Connecting machines
Machine connectivity facilitates the seamless transfer of data between your hardware and an MES platform, ensuring that machine and production data can be leveraged to enable better decision-making and process optimisation.
One of the key benefits here is that machine connectivity can provide better machine control and greater visibility into real-time operations. It makes it easier to schedule AM jobs and monitor build statuses, material levels, machine uptime and utilisation rates.
What’s also crucial is that you can use the data generated by your 3D printers to identify potential bottlenecks and optimise your processes.
Connecting assets on an Additive MES platform, allows your team to constantly measure the pulse of the equipment and notice any irregularities. This enables a proactive approach to addressing potential issues before they create bottlenecks that impact production.
Excitingly, more systems are now fitted with sensors to continuously monitor the printing process, to ensure quality and prevent print failures.
Ultimately, it will also be possible to feed this data into an MES platform. This will further improve connectivity between machines and your organisation’s IT infrastructure, facilitating greater process reliability and quality control.
Challenges to machine connectivity
Despite the huge benefits of machine connectivity, integration with Additive MES platforms has traditionally been challenging, due to closed systems and other technical hurdles.
Many 3D printer manufacturers still don’t allow integrations with third-party software systems. However, as companies continue to invest in a diverse range of industrial 3D printers, hardware manufacturers are increasingly recognising the value of ensuring their systems are open to integrating with Additive MES software.
One example of this trend is a partnership between EOS and AMFG, whereby our Additive MES software will be integrated with EOS machines, to enable direct data transfer and improved machine control.
Connecting processes
Additive MES software, powered by connectivity, allows your organisation to connect all its internal AM workflows, as well as its production centres, if it’s operating in multiple locations.
This opportunity is largely driven by software integrations. Advanced Additive MES software can easily integrate with your existing software solutions, like ERP and PLM.
This level of integration will help you to establish a streamlined, digital workflow.
Digitising workflow in this way, helps to avoid manual error-prone practices, like re-entry of data from one system to another.
Furthermore, connected processes ensure that you have full visibility across your AM operations. This can be particularly important when operating multiple production sites.
Obviously, managing multiple worksites comes with its own set of challenges, including the risk of inconsistency and miscommunication.
To avoid these risks, connected workflows allow you to track progress from anywhere. Plus, it allows you to keep operations uniform across multiple sites.
‘As manufacturers look to scale their am operations, they will need to manage and execute these operations across their supply chains and, very often, across multiple production centres. This requires integrated processes that can respond to real-time demands — in other words, connectivity,’ says our CEO, Keyvan Karimi, speaking in an interview with 3D Printing Industry
Ultimately, if you’re planning to install additional hardware, or increase the volume of parts produced, connecting and digitising your AM processes will ultimately make it much easier to scale up your operations.
Connecting supply chains
26 per cent of OEMs outsource at least part of their 3D printing production to their suppliers, according to EY.
When outsourcing, you must know what needs to be outsourced, and to whom, to ensure that a product is delivered with the right specifications, at the right time.
Connectivity, enabled by Additive MES software, plays a key role in this, as it provides a centralised platform to facilitate communication with your suppliers and establish traceability across your supply chain.
Finally, integration of data from suppliers allows you to have a holistic view of upstream and downstream supply chain processes, driving greater overall supply network efficiency.
Establishing a connected workflow with Additive MES
Connectivity is becoming an essential requirement for companies running AM operations.
An Additive MES platform, powered by connectivity, helps to introduce greater machine control, to integrate your internal processes and suppliers and, finally, to make the data crucial for decision-making, readily available.
Ultimately, having a connected workflow in place results in an integrated ecosystem, in which your AM facility will thrive.
Learn more about connectivity for additive manufacturing
If you’d like to learn more about connectivity-powered software for your additive manufacturing operations, we recommend reading our new white paper, Additive Manufacturing MES Software: The Essential Guide.
As well as providing more insights into the importance of connectivity for AM workflows, you’ll learn more about how to develop a comprehensive AM strategy and how you can use MES software to help you scale and expand your AM operations.
Source: https://amfg.ai/2020/04/01/3-ways-connectivity-will-enhance-your-additive-manufacturing-operations/