If the 2D system aims at creating digital images, then the 3D system creates digital sculptures. Depth is a missing puzzle for the 2D system, even though we can feel it through the lights and shadows in the picture. 3D scanning can capture the exact size, color and shape of a physical object simultaneously with 3D scanner’s help and generate a “point cloud” of 3-dimensional data. Indeed the scanned object can also be a person or an environment.
3D scanning technology has become a powerful tool for industries like automotive, aeronautics, dental, jewelry, animation movie, and video game. When it’s combined with 3D printing and used for designing objects, we call this process “reverse engineering”. There are different kinds of 3D scanning which vary in principles, cost, pros, and cons. Let’s see how they work.
Contact 3D Scanners
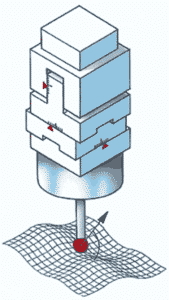
CMM
The full name of CMM is coordinate measuring machine, and it’s the most generally used 3D scanner. CMM measures the geometry of a physical object using a manually or computer-controlled probe.

- Strength: applicable for many kinds of objects; high precision (micrometer level); not restricted by illumination and color of the object;
- Weakness: may damage the surface of the measured object or the probe; relatively slow compared to other methods; suitable for objects without a complex inner structure; affected by the temperature and humidity of the environment; not available if the object is soft.
Non-Contact Scanners
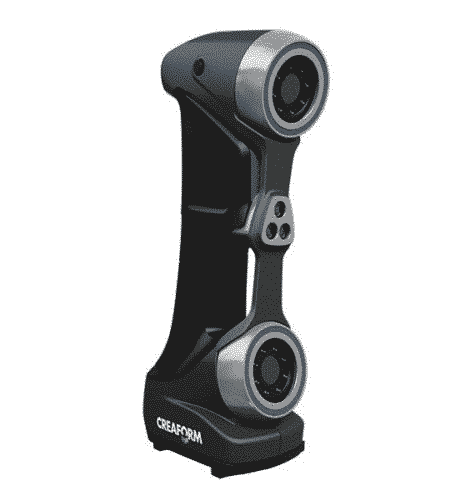

Handheld Laser Scanners – Time-of-flight
The time-of-flight 3D laser scanner emits a pulse of light and the detector will accept the reflected light, then the laser finder calculates the distance by the speed of light and the round-trip time.
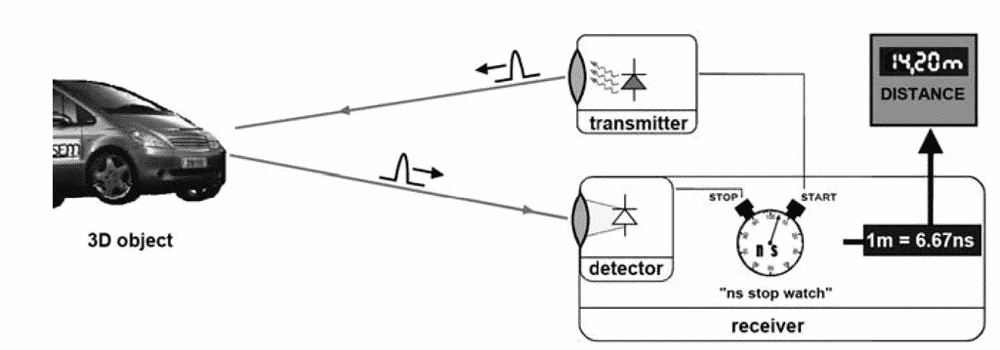
- Strength: can reach a precise of 3.3 picoseconds traveling 1 millimeter; can measure the distance of 10,000-100,000 points every second; capable of operating over a long distance, often used in terrain scanning;
- Weakness: the round-trip time will affect the accuracy, thus it’s not suitable for a close shot; may lose its accuracy when the laser hits the edge of an object.
Handheld Laser Scanners – Triangulation
Triangulation based 3D laser scanners also use laser light but the laser dot, the camera, and the laser emitter form a triangle. Via the geometry knowledge, we can ascertain L≈dtanθ.
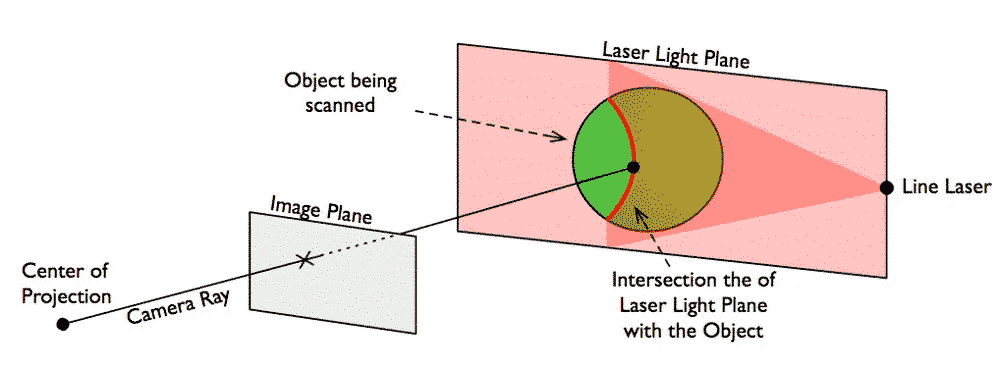
- Strength: the accuracy is relatively high on the distance of tens of micrometers; has a high sampling rate, high resolution, and high precision; can be used cooperatively with camera and GPS system;
- Weakness: will be affected by the temperature, the light intensity & diameter of the laser.
Photometric 3D Scanners

The photometric system takes multiple images under varying lighting conditions using a camera. It attempts to invert the image formation model in order to recover the surface orientation at each pixel.
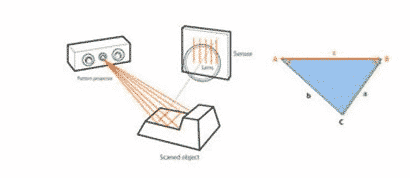
- Strength: can scan multiple points or the entire field of view at once; color and 3D information are available almost at the same time and match at a pixel level; very large depth of field; can calculate 3D data also from a glossy object; available for scanning very large objects;
- Weakness: cannot scan black or transparent objects without the help of the photographic developer.
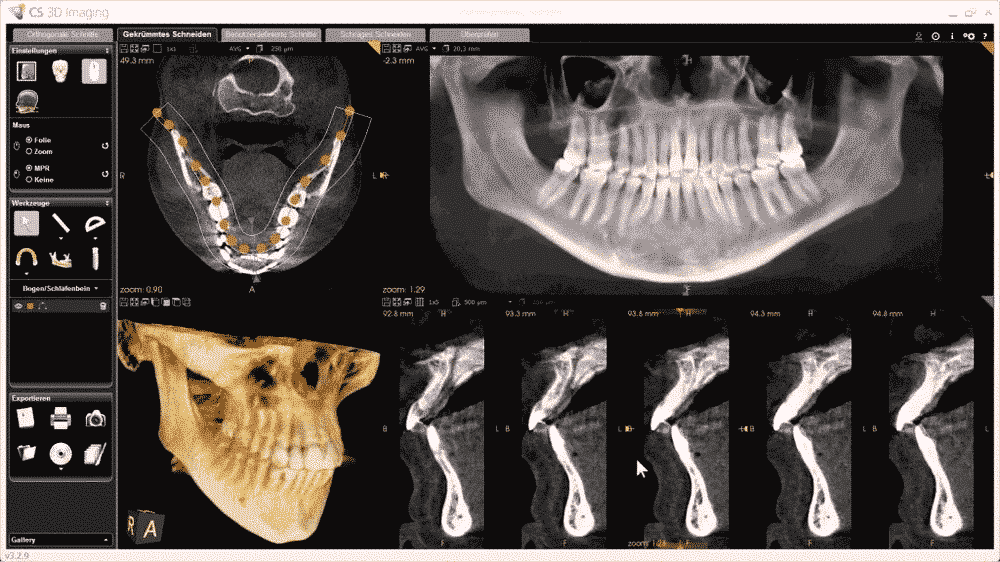
Application:Dental Examination and 3D Scanning
Dentistry consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of the disease and other conditions of the oral cavity. Foresighted clinicians and dental laboratories are harnessing the 3D technology in all the aspects to attain the best outcome for patients. Here we discuss how can 3D printing be involved based on the departments of a dental hospital.
Dental Impression and Teeth Model
A dental impression is a negative imprint of hard and soft tissues in the mouth, from which we can cast a positive teeth model. The teeth model is used for diagnosis and teaching purposes, and it’s important in the treatment planning process for orthodontics and prosthodontics. However, the traditional method of making a dental impression may suffer from a failure such as patients’ emesis, transformation, warped or unclear edges, insufficient space for occlusion, etc.
Dental X-rays
X-rays (radiograph) is another method for the dentists to evaluate the patients’ oral health, which is implemented through all the stages of diagnosis. Although the exposed level of radiation is quite low that dental X-rays is safe enough for both adults and children, most pregnant women are refused to accept any type of radiation exposure considering their developing fetuses. Sometimes the patients have to cross between clinic rooms, wait for X-rays with their mouth open and outflow some saliva and blood, trouble with wearing a lead bib over their chest, abdomen and pelvic region. It’s absolutely not a pleasuring experience.
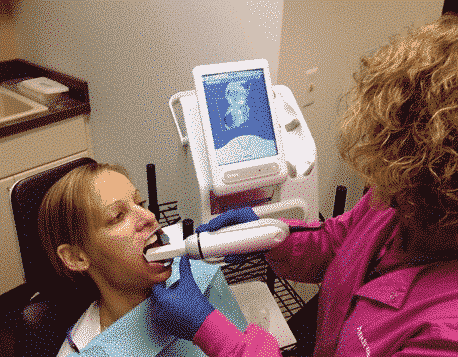
3D Dental Scanning
3D dental scanning effectively avoids the above problems and increases the reliability of the measurement. The dentists can make precise intraoral scanning and generate a 3D model of patients’ teeth. Each scanning device consists of a handheld camera to collect the data inside the mouth region and a computer system to process, analyze and visualize the intraoral structure. No laser is involved but a sensor works without illumination and it’s safe for pregnant women. The scanning process only takes a few minutes and allows a more precise and comparable digital analysis. The 3D printed model made from the scan data, which is unnecessary in some cases as we already have the scan, is also more subtle than the plaster mold.