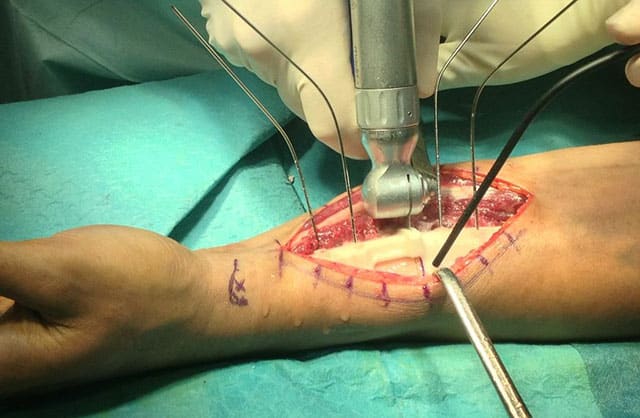
What is a 3D printed orthopedic surgical guide?
The 3D printed orthopedic surgery guide is a personalized surgical instrument prepared using CAD and 3D printing technology according to the needs of the operation.
It is used to accurately locate the position, direction, and depth during the operation. With this tool, surgeons can precisely establish the channels, sections, spatial distances, mutual angle relationships, and other complex spatial structures.
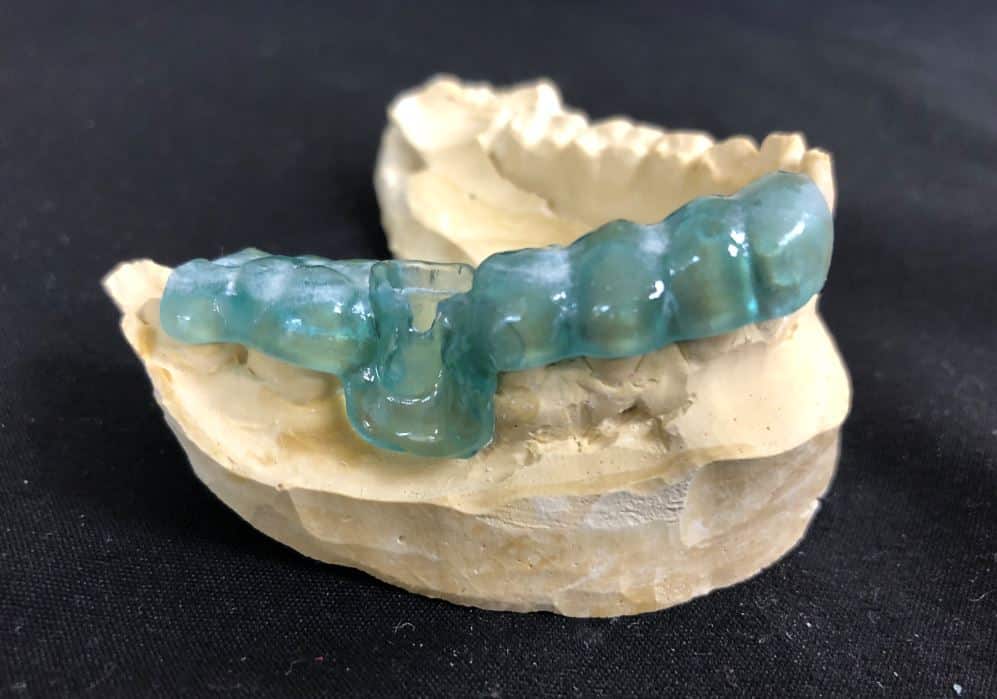
The types of 3D printed orthopedic surgical guide
According to the purpose of 3D printed orthopedic surgical guides, the guides can be divided into 3 categories: Bone Screw Guide, Osteotomy Guide, and other types.
- Bone Screw Guide:
It is mainly used in orthopedic surgery to implement 3D printed guides for positioning, orientation, and depth of nail channels. - Osteotomy Guide:
It mainly refers to the control of the spatial position and angle of the osteotomy site in orthopedic surgery, to improve the anastomosis degree of the prosthesis to the contact area, accurately remove the lesion. - Other types:
These include various 3D printed intraoperative auxiliary positioning devices not included in the other two kinds, such as the combination of bone screw guide and osteotomy guide, installation of positioning guide, personalized orthopedic guide, personalized fracture shaping guide, personalized bone restoration production guide, internal fixation shaping guide, etc.
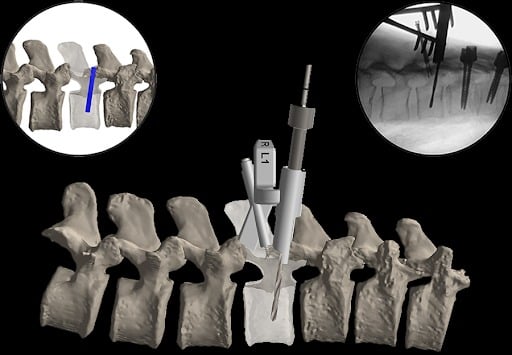
The Precautions of Surgical Guide in Clinical Application
Before the surgical guide is put into clinical application, it is strongly recommended to retain the main technical parameters of the model (such as patient’s information, designer’s information, the model number of equipment, and thorough record of design and production process, etc.) for easy inquiry and supervision, so that the use of surgical guide can be traced.
We also recommend that the surgical guide be used in conjunction with the 3D printed model for preoperative planning and accuracy verification.
The 3D printed orthopedic surgical guide is used directly for temporary navigation and positioning during the operation and is temporarily attached to the bone surface, so it should meet the following requirements:
Appearance and operation requirements
The preparation of 3D printed orthopedic surgical guides should meet the requirements of anatomy and biomechanics, and meet the design needs of clinicians. The guides and the surgical site should be fully matched and attached, and there should be no warping or loosening after installation. The surface should be smooth without residual supporting material or powder debris.
Disinfection and sterilization
In order to effectively prevent pollution and infection, the surgical guide must be disinfected before use. 3D printed orthopedic surgery guides have complex structures and high geometric accuracy requirements. In order to prevent the deformation and distortion of guides caused by sterilization, it is recommended to determine the sterilization method according to clinical needs and classify the sterilization requirements according to different preparation materials of the guides:
- Metals:
Humidity and high-temperature-resistant 3D printed metal guides are strongly recommended for pressure steam sterilization; - Non-metallic:
For 3D printed non-metallic guides that are not resistant to high temperature, humidity and heat, such as ABS, PLA, nylon, and photosensitive resin, low-temperature plasma and ethylene oxide disinfection methods are strongly recommended to sterilize 3D printed guides.
Material biocompatibility
It is strongly recommended that medical grade materials must be used, and the biocompatibility test of the materials must be qualified.