Looking for 3D printed rubber or silicone for your product? Unfortunately, these common production materials are now very difficult to produce with 3D printing, often very expensive or with very limited dimensions (and so very expensive). In the future of 3D printing, it will certainly be possible to use these flexible 3D printing materials quite easily to produce or do some rapid prototyping, but it is still complicated. The good news is that you can find good alternatives to other 3D printing flexible materials if you accept to compromise on certain properties. Additive manufacturing allows you to use 3D printing materials with great mechanical performance to print flexible objects. At Sculpteo we offer flexible plastic and flexible resins: PEBA, EPU, and FPU. In this article, we compare their characteristics and how you can use them.
What is a 3D printing flexible material?
A 3D printing flexible material is a material produced thanks to 3D printing and that can be bent or shaped easily. Several 3D printing technologies are offering soft-touch and flexible materials, here are the most common:
- FDM: flexible filament
- Polyjet: Tango resin (photopolymer)
- SLS: PEBA and also PA12 which is slightly flexible
- CLIP: EPU and FPU
- ACEO: silicone
If you would like a complete overview of the 3D printing materials, we have wrapped up every useful information in our 3D Printing Material Bible.
You can also learn more about the 3D printing technologies in our overview article.
How can we compare them?
Durometer, Elongation at break, and tensile strength are the most common measures of flexibility for a material. In this tab, we compare the flexible 3D printing materials that we know the best: Elastomeric Polyurethane (EPU), Flexible Polyurethane(FPU) and PEBA. We also add the value for the 3D printing plastic (PA12) since it is the most used 3D printing material.
| Durometer | Elongation at break | Tensile strength | |
| EPU | 68, Shore A | 310 ± 25% | 6 ± 1 MPa |
| FPU | 71, Shore D | 280 ± 15% | 29 ± 1 MPa |
| PEBA | 87, Shore A | 200 ± 70 | 7-8 MPa |
| PA12 (Plastic) | 75, Shore D | 20 ± 5 | 45 ± 3 N/mm2 |
Which color are available for 3D printing flexible materials?
There’s not a big choice regarding the colors, unless you need black and white parts! CLIP Resins are both blacks when PEBA is white. We don’t offer any dying finishes on PEBA like we do on 3D printed polyamide because it’s difficult to reach the color consistency that you could expect from a professional online 3D printing service. However, you can do it by yourself, but keeping in mind that PEBA can only resist to heat below 60°C without any shape alterations and that the 3D printed parts are porous.
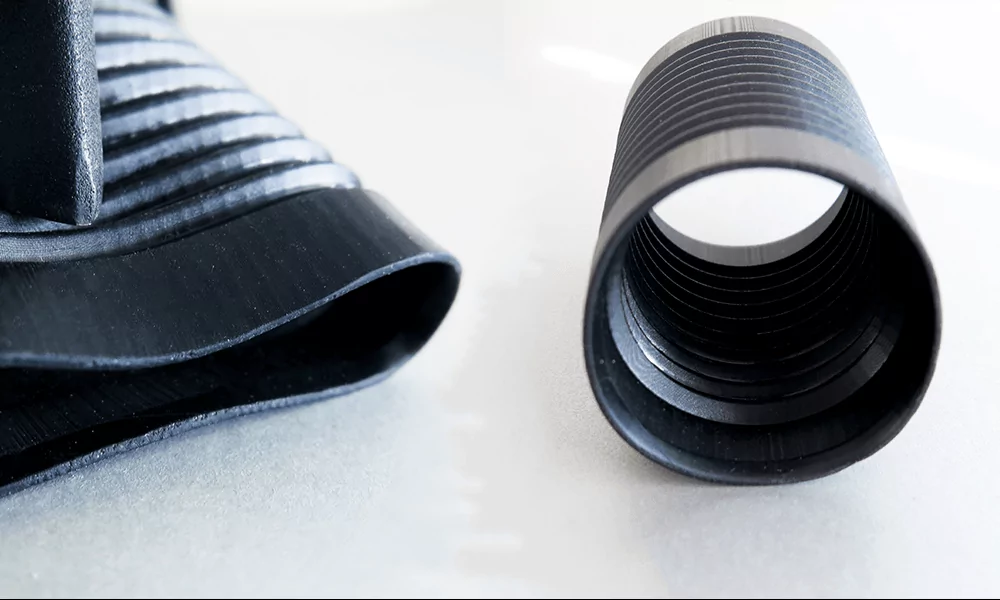
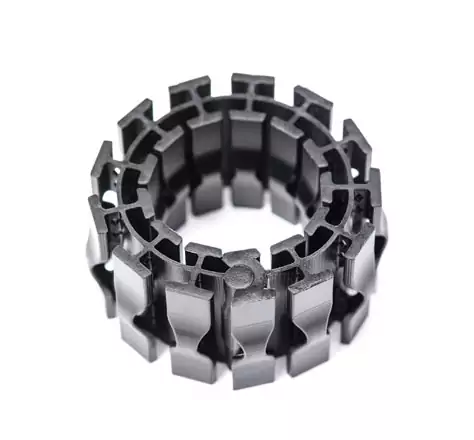


The surface finish of EPU or FPU parts is shiny when the PEBA parts look granular and somewhat porous. One thing you need to take into account when it comes to 3D printing with CLIP Resins (EPU or FPU material) is that your parts will be supported during the 3D printing process. Thus, it will leave some marks on the surface.
Which 3D Printing flexible material is the most rubber-like?
Elastomeric polyurethane (EPU) is the 3D printing flexible material that is closer to what you could expect from 3D printing with rubber since its shore A is 68. The material is highly elastic, tear resistant and resilient. This dark elastomer is perfect to design caps, gaskets or seals for instance.
EPU is comparable to TPO Elastomer and it has excellent mechanical behavior: it elongates over 310% before breaking and exhibits elastic behavior over a wide temperature range.
Nevertheless, EPU is a great flexible rubberlike material, but it is not food-safe or biocompatible; so you cannot use it for any 3D printing food-related applications.
Which flexible 3D Printing material is good for prototyping?
When it comes to prototyping, the most important is to choose a solution that simulates the most critical properties of the final material: is it elongation? flexibility? chemical resistance? surface quality? The duration of the part is also less critical than for production parts. We added the 3D printed plastic (PA12) in this section because we know that many of our clients use it for its flexibility.
Based on our production experience, we put down this list of parts and an evaluation of each 3D printing flexible material. This list is not exhaustive and is general. Feel free to contact us if you want an advice on your personal design.
| Type of parts | EPU | FPU | PEBA | PA12 |
| Hinges | + | +++ | – | + |
| Sealing gasket | +++ | – | ++ | – |
| Vibration absorber part | +++ | + | ++ | + |
| soles | +++ | – | +++ | – |
| Bellows | +++ | – | ++ | – |
| Watch rubber strap | ++ | – | + | – |
Which 3D flexible material is good for production parts?
CLIP engineering resins (EPU or FPU) have been designed by Carbon for production uses. They are consistent and resistant to many elongations, they stand up to repeated bending and flexing. So if you’re considering using 3D printing for producing hundreds or thousands of parts, you should focus on theses materials.
But it’s really dependant on how much you are ready to review your 3D file and the timing of your project. To take the most benefit of EPU or FPU resins, it is important to deeply study the CLIP technology and to design your parts to make the most of it. We have done it successfully with some of our clients such as Oracle. But it was not a one-step process and it took several iterations and several weeks.
If EPU and FPU are first choice materials when it comes to production; you still need to consider PEBA. Even if PEBA is less durable than CLIP resins, we see production parts that don’t need to last forever: it is commonly used in the medical industry, for orthotics for instance.
They use flexible 3D printing materials!
Have you ever thought about 3D printing clothes? Indeed, 3D printers and haute couture could be more and more linked in the future. The fashion designer Iris Van Herpen is known to use 3D printing to create some parts of her collections.
Flexible plastic material is perfect for this application, as clothes have to be quite flexible to follow the movement of a body. Moreover, it has a great visual quality. The “Virus Collection”, designed by Anastasia Ruiz is the perfect example. It has been 3D printed with TPU, though our online 3D printed service.
Futurecraft 3D is a pair of running shoes created by Adidas, using additive manufacturing. The midsole of these shoes has been 3D printed. The shoe has to be wearable, so you inevitably need to use a flexible material to build a midsole. That’s why they used TPU.
If you want to learn more about shoes and 3D printing, check out our blogpost about 3D printed shoes.
You can find more informations about design guidelines or printing process for flexible plastic material on our material page.
In this article, we compared 3D printing flexible materials based on their characteristics and their common applications. But we don’t forget that there is another key factor for decision: BUDGET! With our instant quoting tool, this question can be easily answered: you just need to upload your 3D file to our platform, then select the material you’re looking for and you will get price and delivery time instantly. Let us know which 3D printing flexible material you prefer!