Draft angles make it easier to remove a rotomolded part from a cavity. These tapers are measured in degrees per side and placed on the surfaces of parts that will be perpendicular to the mold’s parting line. Because different plastics have different mold shrinkage characteristics, draft angles vary by material. The inside draft and outside draft for a rotomolded part differs, too.
For part designers, specifying proper draft angles is an important consideration. Although some parts can be rotomolded straight up-and-down with no draft angle, others require a taper to support mold release. In general, draft angles should be applied to rotationally-molded parts as long as they don’t interference with the part’s functional requirements.
Draft Angles and Mold Release
Molded parts require sufficient cooling to regain their strength and retain their shape. Otherwise, they may not be able to withstand the forces that are applied during mold removal. With rotational molding, draft angles reduce these forces and minimize part stress and warpage. Draft angles also support reduced cooling times for faster cycles and lower manufacturing costs.
The design and manufacture of a donut-shaped part demonstrates the importance of proper draft angles. During cooling, the rotomolded part shrinks. The outer surfaces draw away from the mold cavity, but the surfaces that form the hole in the center shrink tightly onto the mold. By providing sufficient draft angle on these inside surfaces, a part designer can support easier mold removal.
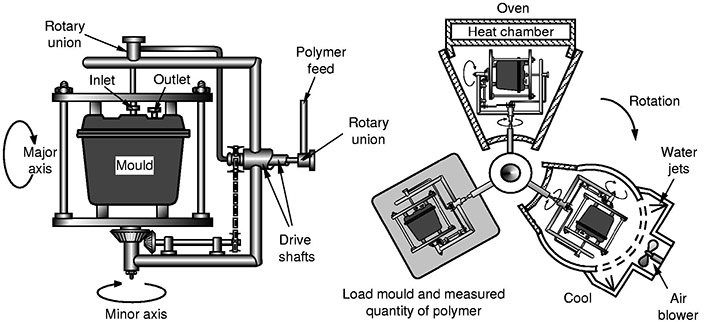
Surface Finishes and Draft Angles
Rotational molding can produce plastic parts with smooth or textured surfaces. With smooth parts, a polished cavity that’s free of tool marks or undercuts will improve mold release. Polishing the inside surfaces of the cavity can improve demolding, but excessive polishing can increase tooling costs significantly.
Rotational molding can also produce parts with textured surfaces. To achieve this effect, the mold cavity contains the reverse details of the plastic part. This rough surface along the cavity walls makes it more difficult to remove the part from the cavity. Therefore, FacFox recommends adding one additional degree per side of draft angle for each .001 textured depth.
Get Rotational Molding Design Assistance from FacFox
For over 15 years, FacFox Manufacturing Group has manufactured rotationally-molded parts that are proudly Made in China. Do you need design assistance for rotomolded parts? For more information, contact us.
Add a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment