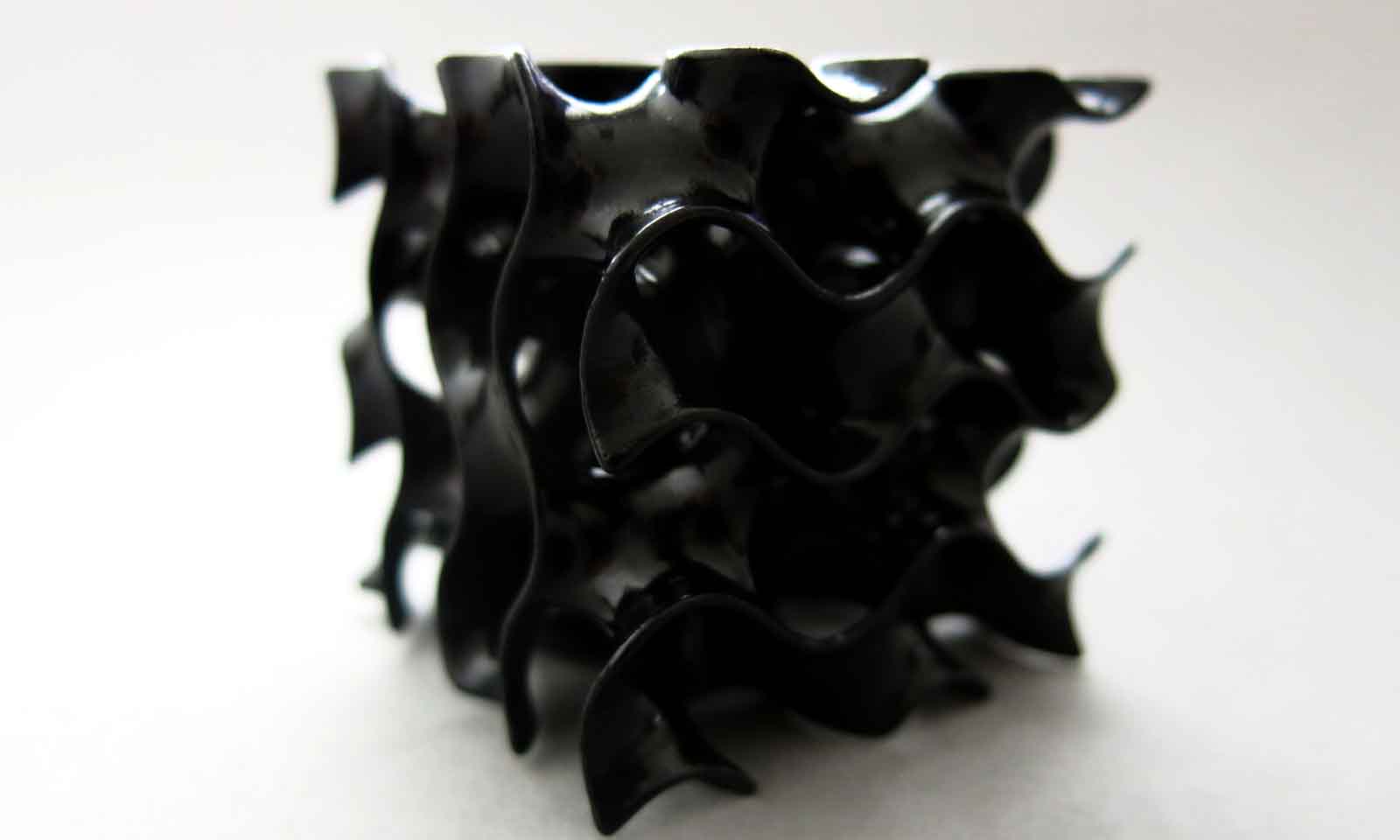
Strengthen your 3D printed objects with specific structures
3D printing materials are so varied that it is easy to find the proper material for your project. When it comes to a mechanical part, the characteristic of the material is the main aspect to consider but do not forget about the design.
To help to strengthen the material you choose, there are tweaks and design features that give your object strength and solidity.
To quote a few, jigsaw-structures, lattices, Voronoi patterns, topology optimization are some of the most known features to help your object gain strength and resistance.
You can find useful resources on topology optimization on this blog post, or take a look at our previous article on Jigsaw-like structures to improve the solidity of your 3D printed object.
What is a lattice structure?
A lattice structure is an engineering or architectural structure made of a crisscross pattern of strips. This specific design feature forms a network of crosshatch sections that strengthen the whole structure.
Lattice structures are more than an ornamental feature since they give your final object a reinforced and optimized structure.
Its importance in 3D printing
With 3D printing, lattices bring many advantages. They reduce the mass and weight of the object which means less material used and a lower price. Indeed, the plain material structure is replaced by the crosshatch sections which reduces the amount of material used in the 3D printed structure. In the additive manufacturing sector, the less material used to create a part equals to a lower price.
With less material used, the material is as resistant to stress and impact as a plain structure design. However, the overall resistance is driven by the shape of the cells. Learn more about the type of lattices in the last paragraph of the article.
Another main advantage of lattice is its heat-dissipation properties. With a plain structure, the heat is dissipated to the closest wall depending on its thickness. If the heat is poorly dissipated, it can cause shrinkage and damage your object. Thanks to the regularity of a lattice structure and the hollowed crossed-sections, heat can be dissipated faster and more uniformly.
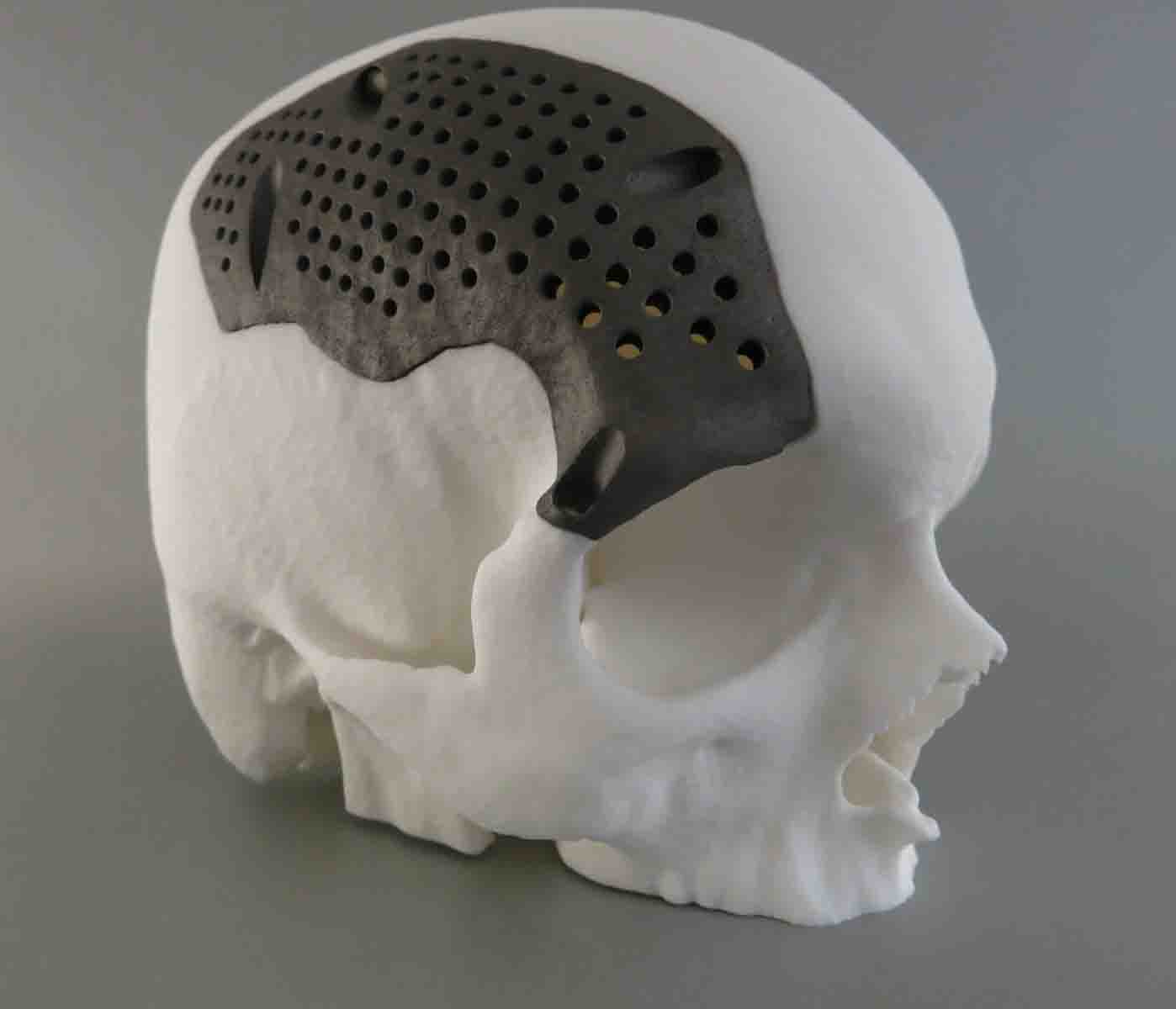
Lattice structures for metal 3D printing
The Automatic Lattice Generator tool allows you to automatically add a lattice structure to your object. It will evaluate the forces and give you a structural evaluation of your model. You will just have to choose which cell structure you want to apply to your design to obtain an optimized and cheaper object.
Lattices are often used with metal 3D printing for prosthesis and implants to create porous surfaces that facilitate osseointegration. This process is particularly important to secure the part in the patient’s body because it allows fusing of the patient’s bone with the 3D printed implant.
How to design them
Lattices can be either visible or inside your object. They can serve as a visual ornament or can be hidden inside the walls of your object to serve only as a structural reinforcement feature.
There is much software only dedicated to the creation of lattice structures:
- Autodesk Within
- Topology
- Netfabb
- Cura
Inside your favorite CAD modeling software, you can also find a tool or a feature to create lattice structures but the software mentioned above is calculating the resistance of your object to create the optimized lattice structure.
3D Printed Lattices: Challenges
The main issue with lattices is to check the final structure. Due to the very complex shape of the object, it is difficult to determine if the part will handle stress and loads in the long term.
There are a few solutions to precisely know if a part with lattices is strong. The most known but time-consuming and expensive is the CT scanning. This method uses X-rays to track the internal structure of the 3D printed part.
Another method consists in evaluating the part’s characteristics during the 3D printing process.
In any case, further research and improvement must be achieved in this domain to generalize the use of lattices in the manufacturing process.
Example of Lattices design
The shape, the size, and the density of the lattice structure are the key element to how your part will handle stress and loads.
For example, the density of lattices defines the resistance and the weight of the part.

On a 3D printed part, the larger is the lattice structure, the heavier and rigid is the object. With a more dense and thinner structure, the object can be very resistant because it can absorb stress thanks to greater flexibility.
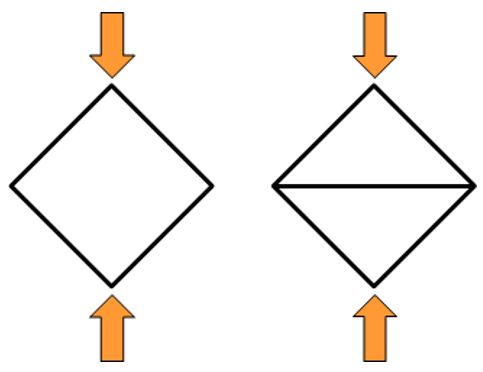
In the diagram above, you can see two different shapes of lattices. The one on the left is more common. The right lattice shape is more resistant thanks to the center support structure.
There are many other shapes of lattices such as Voronoi patterns, hexagonal, specific shaped, or totally random and organic shapes.
