CNC machining design guidelines: CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing technology that uses computer-controlled cutting tools to create custom parts from a solid block of material. To design parts for CNC machining, some guidelines are:
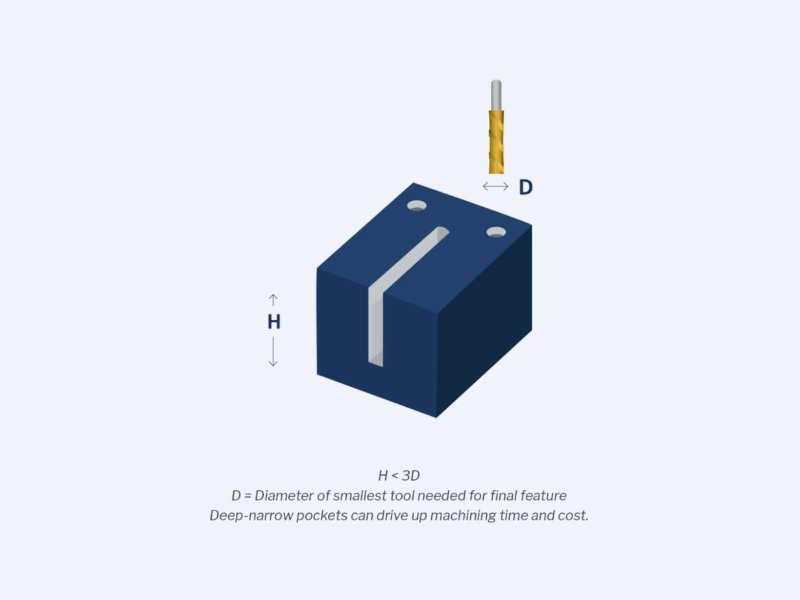
- Avoid deep pockets or slots: These require longer tools that are more prone to breakage and vibration. They also increase the machining time and cost. To avoid them, reduce the depth or increase the cross-section area of the pocket or slot. As a rule of thumb, the depth should not exceed 3 times the diameter of the tool.
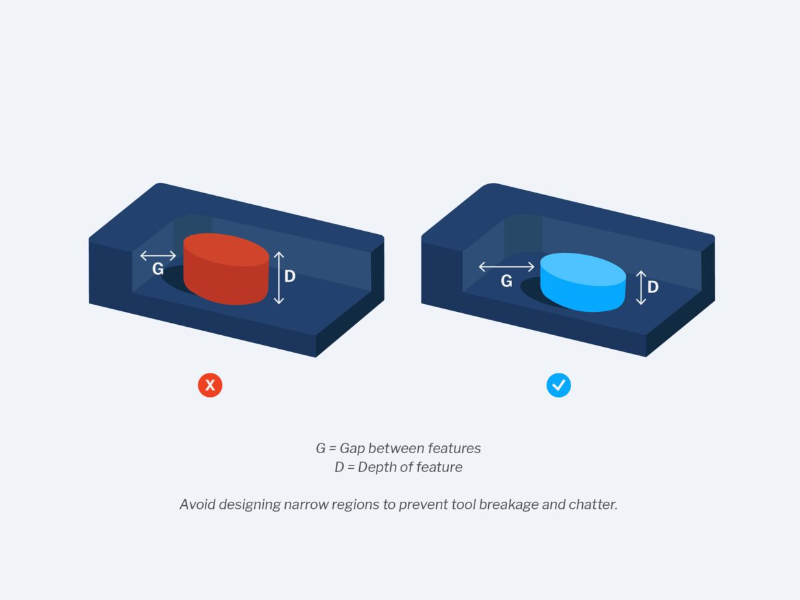
- Avoid narrow regions: These restrict the size of the cutter and limit access to the feature. They also increase the risk of tool breakage and vibration. To avoid them, increase the width or reduce the depth of the feature. As a best practice, wall sections should be greater than 0.01 inches thick.
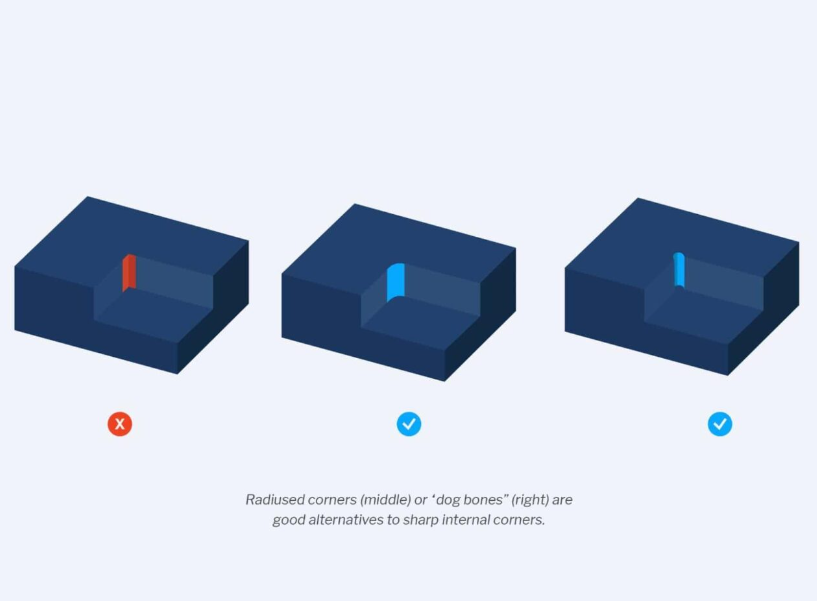
- Avoid sharp internal corners: These are impossible to achieve with circular cutting tools, which leave behind a radius in the corner. To avoid them, use a larger radius than the tool diameter or use alternative methods such as EDM or laser cutting.
- Avoid inaccessible features: These are features that are blocked by another feature and cannot be reached by the cutting tool. To avoid them, ensure that there is enough clearance for the tool to access all features without interference.

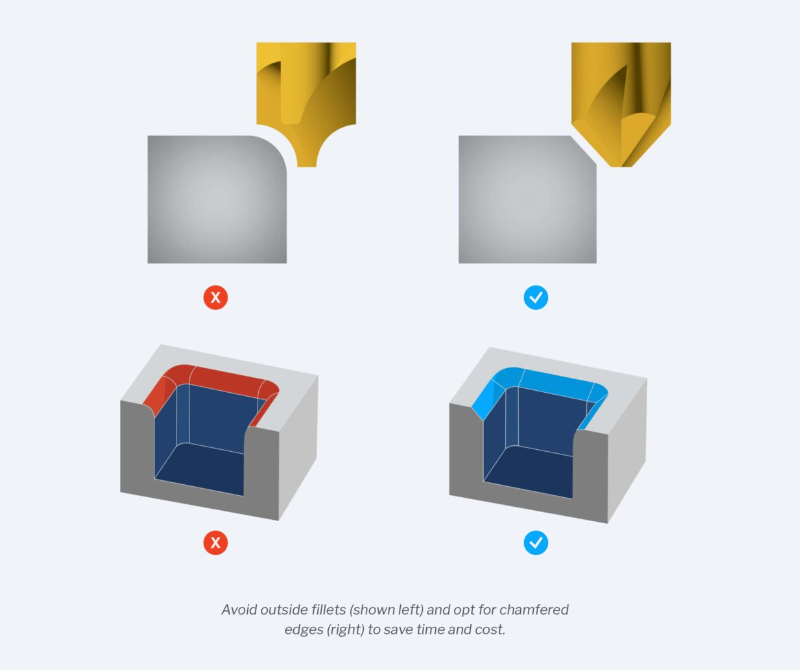
- Avoid outside fillets: These are rounded edges on the top of pockets, bosses, or slots. They require very sharp tools and precise setup, which can be expensive and time-consuming. To avoid them, use chamfers or bevels instead of fillets.
- Avoid thin walls: These can cause chatter in metals and warping or softening in plastics. They also reduce the strength and stiffness of the part. To avoid them, increase the wall thickness as much as possible. The ideal minimum wall thickness is 0.8 mm for metals and 1.5 mm for plastics.

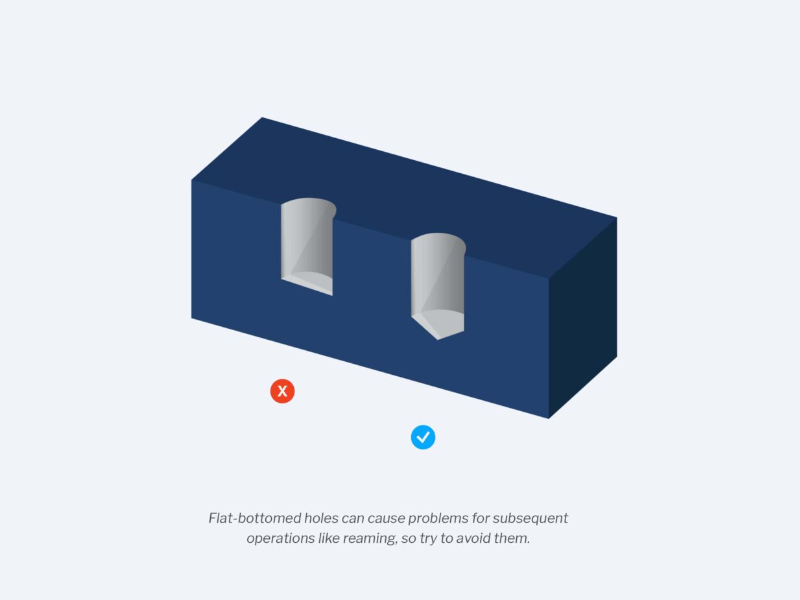
- Avoid flat-bottomed holes: These require special tools and operations that can cause problems for subsequent operations such as reaming. To avoid them, use standard twist drills to create holes with cone-shaped bottoms.
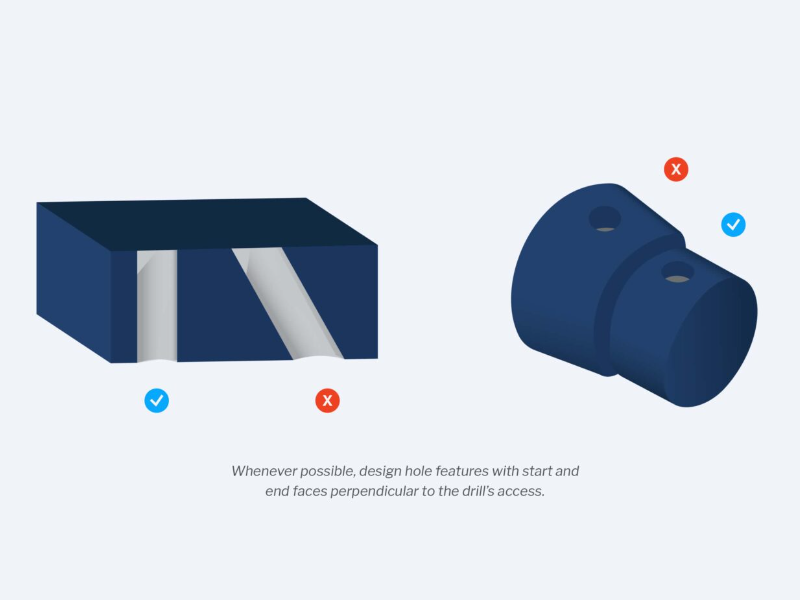
- Avoid non-perpendicular holes: These can cause drill tip wandering and uneven exit burrs that are hard to remove. To avoid them, design hole features with start and end faces perpendicular to the drill axis.