If 3D printing mugs or plates for the kitchen, they must be safe for contact with food. Here are 12 vital facts about food-safe 3D printing.
It’s enormous fun to 3D print things that are cool and useful. That feeling never gets old.
But whilst fabricating kitchen utensils or drinking cups in a funky design, you may well have cause to stop and wonder; how safe is 3D printing for daily contact with food and drink? Is PLA food safe, for example? Or is ABS food safe?
These concerns are completely understandable. With both FDM and SLA additive manufacturing techniques, a potent mix of chemicals and heat are used to print and process objects. Which brings to mind another question, is resin food safe?
If there’s a risk of poisoning yourself with toxic substances, or harmful bacteria, then you’re entitled to know about it. Here’s our guide to food safe 3D printing, with a breakdown of the most common concerns and tips for minimizing risks.
Bacteria Buildup
Use a Food Safe Sealant
Sealing a printed object with a food safe epoxy or sealant will plug up the crevices that can collect bacteria. For PLA filament a good option is Polyurethane, which you will find at most home improvement stores. It’s also advisable not to allow your model to come into contact with raw meat or eggs, which are more prone to harmful bacteria growth.
Chemicals in the Filament

ABS filament is generally considered unsafe to use with anything that will come into contact with food. That’s because ABS contains evil toxic chemicals which can contaminate your food and then, by extension… YOU.
Natural PLA is made from corn starch and is generally considered food safe. However, it’s a bit more complicated than that. Some manufacturers will blend in other additives — for color, strength, or other features — that make the filament unsafe to ingest. Some PLA filaments are designated food-safe, but in the first instance you should check with the manufacturer.
Buying a Food Safe Filament
Today there are a number of food-safe filaments on the market, including German RepRap’s PP Plastic and FormFutura’s HDglass (which is an ultra-transparent modified PETG).
How do you know if your filament is food safe? Your filament will come with a material safety data sheet (MSDS) that breaks down the chemical properties and will specify whether it is FDA approved or food safe.
Plus, if a company has gone through the process of being food-grade certified, it will probably say as much on the packaging.
Toxic Particles in the Printing Process

According to a study in 2015 by the Illinois Institute of Technology, desktop FDM printers using ABS and PLA plastic are “high emitters” of ultrafine particles (UFPs). These particles may exist on the surface of your print, and excessive inhalation or ingestion of these UFPs can lead to adverse health effects.
Again, ABS is the worse offender than PLA, but it still pays to operate your 3D printer in a well-ventilated room. And eat your lunch away from the 3D printer. Research in this area is ongoing, but it’s reasonably certain that if you don’t want to breath in UFPs, then you probably don’t want to be swallowing UFP-tainted food either.
Not Dishwasher Safe
Coming back to the problem of bacterial build-up; can’t you just wash the object and everything will be okay? Unfortunately, if you wash a 3D-printed item in hot water or with the dishwasher, they may become deformed and warped with time.
PLA in particular is more sensitive to heat and is definitely not safe to put in the dishwasher. Being a brittle substance, the object can crack into little pieces whilst being washed, so it might cause damage to your dishwasher altogether…
Use Warm Water with Antibacterial Soap

Brass Nozzles May Contain Lead
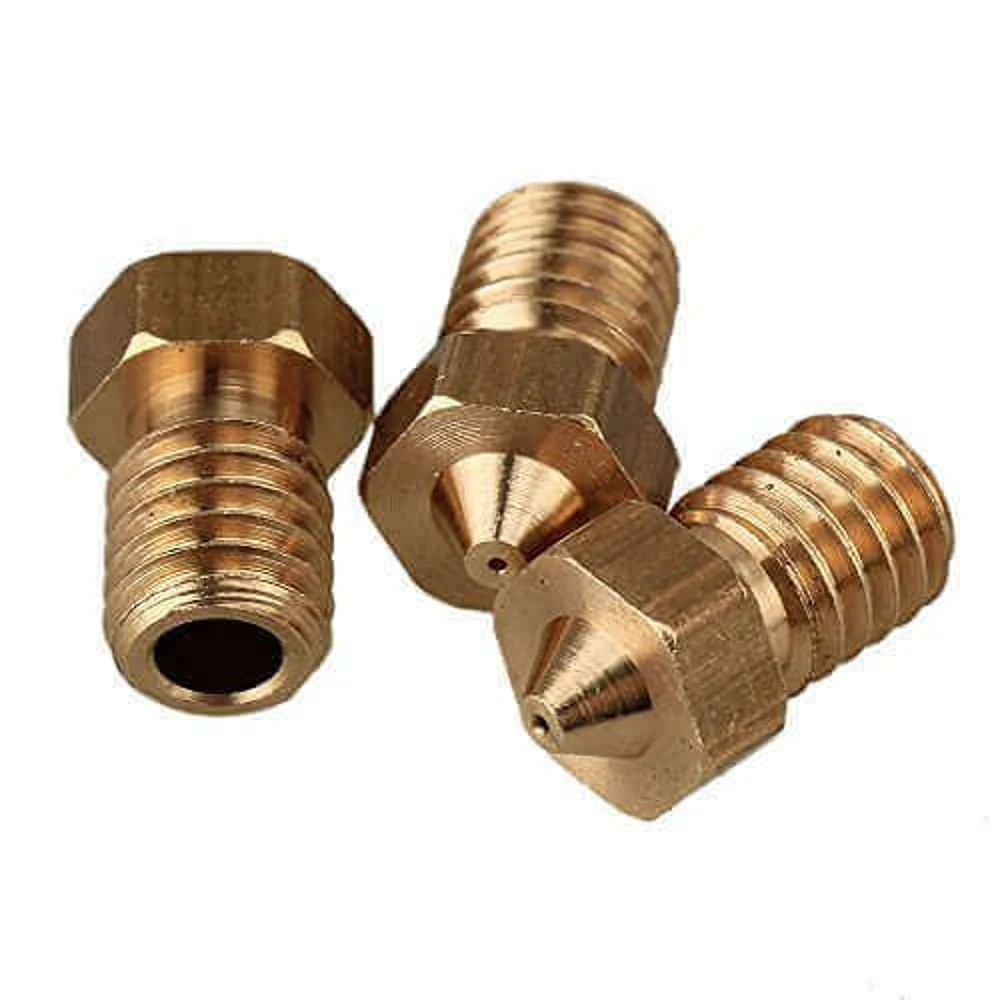

Not all FDM 3D printers have the same type of extruders. Some are made from steel, or aluminum, or brass. In the case of the latter, a brass extruder may contain lead, and lead contamination can cause some nasty health problems. Carefully check your 3D printer to see what type of nozzle you have, and whether it can be easily replaced.
Use a Food Safe Hot End/Extruder
To avoid contamination from your extruder, you should purchase a stainless steel hot end which is considered safe to use with food. This might seem like an excessive precaution if you only plan to fabricate a dinner plate or two. But if you’re very concerned about the risks, or plan to be cranking out a lot of gear for the kitchen, then it’s definitely worth the upgrade.
Limit Food Contact Time
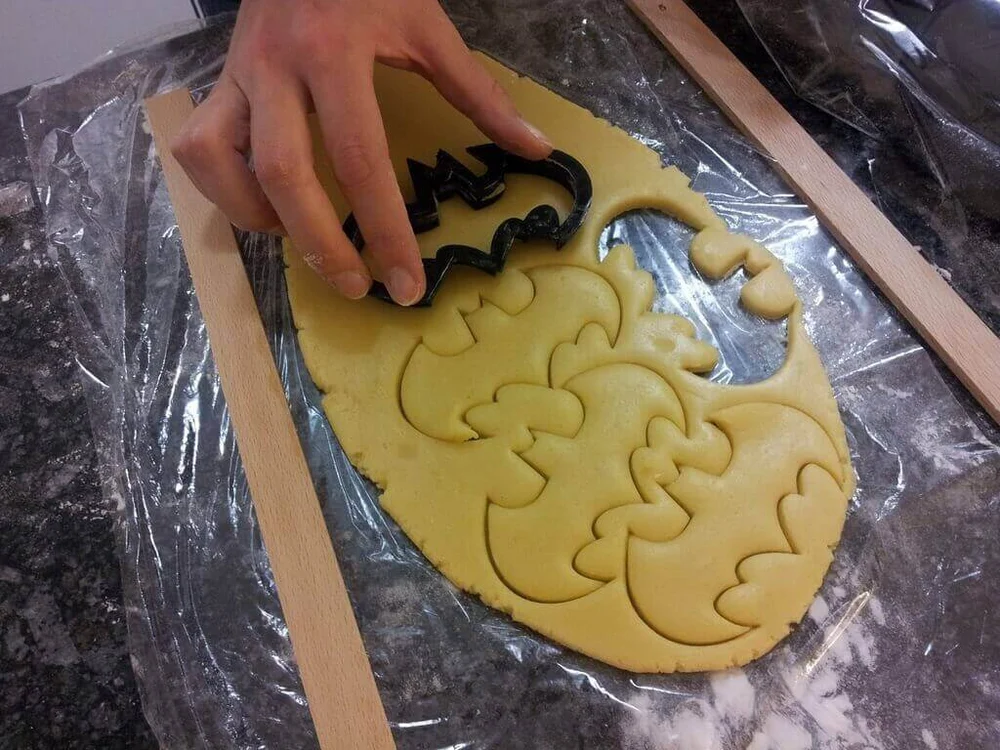

Another thing to consider is that food safety depends on what the printed object is being used for. Items like knives and cookie cutters don’t come into contact with food or your mouth for very long, so they can be considered safe even without food-grade filament. But if you’re printing a coffee cup or a container which will contact food for longer periods of time, you may want to take extra precautions.
General Food Safety
As you might have gathered, it’s actually pretty difficult to make 3D printing 100% certified “food safe”. That said, there is a difference between something being certified food safe and general food safety. Would you get fatal poisoning from using a 3D-printed glass or bowl once or twice…? Probably not. Like anything in life, just don’t do it to excess.
Choose your Material Wisely
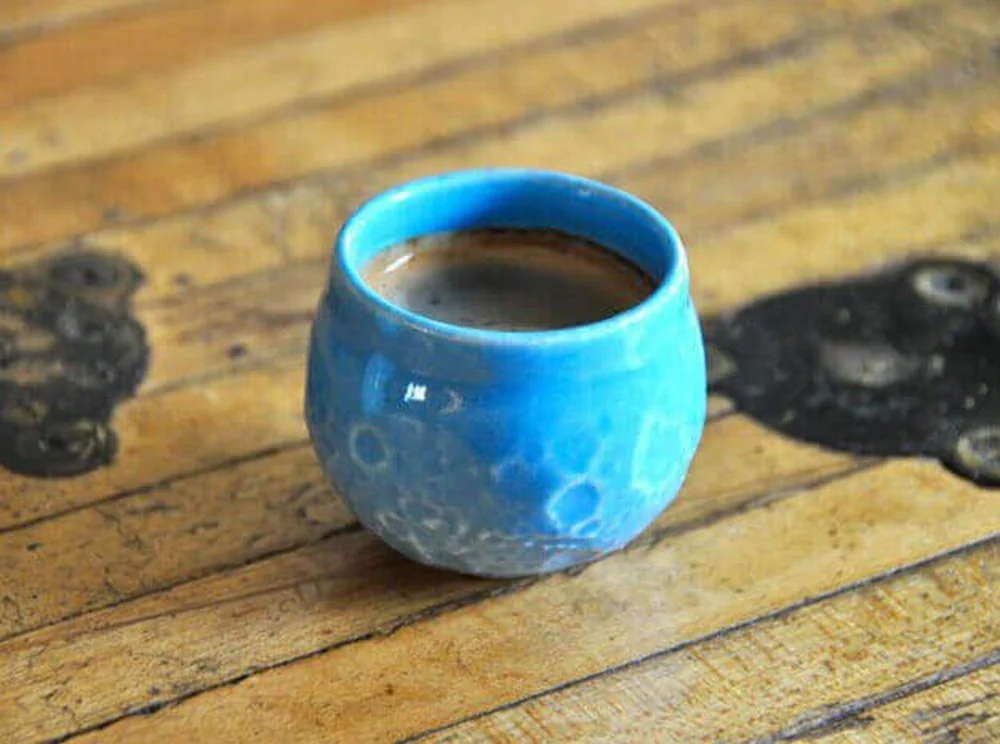

Choose the right material for the object being printed. Using PLA for your coffee cup may be food-safe, but the plastic is too soft for hot drinks and could melt in a dishwasher. ABS might make a stronger choice for the cup, but it’s not certified food safe and has chemicals that are potentially toxic to ingest.
But don’t be disheartened, you’re not just limited to PLA and ABS. Using a professional 3D printing service means you can have that coffee cup printed in ceramic, a proven food-safe material that’s been used for centuries. Problem solved!
Source: https://all3dp.com/2/pla-food-safe-3d-printer-filament-abs/