Bored of ordinary PLA? Try special blends! Check out our buyer’s guide to find the best PLA filament type for your needs.
PLA filament is by far the most popular material used in desktop FDM 3D printing, and for good reason: It’s easy to use, safe, affordable, and comes in a diverse range of composites, making it ideal for (almost) any application you could possibly think of.
We have gathered the various exotic and unique PLA blends on the market for you to discover and get inspired for your upcoming projects.
If you want to find out more about PLA, how it is made, its pros and cons, the best post-processing methods, and much more, check out our in-depth PLA guide at the end of our list. Feel free to browse or use one of the jump-links below.
SECTIONS
- PLA Filament Blends
- PLA Filament Explained
Press PLA(y) to get started.
PLA FILAMENT: SPECIAL BLENDS
The diversity of blends, colors, and properties of PLA filament is seemingly endless. That’s why we put together a list of the most exciting types you can buy – ordered from most to least popular. We didn’t include color variations because most colors on the spectrum are available.
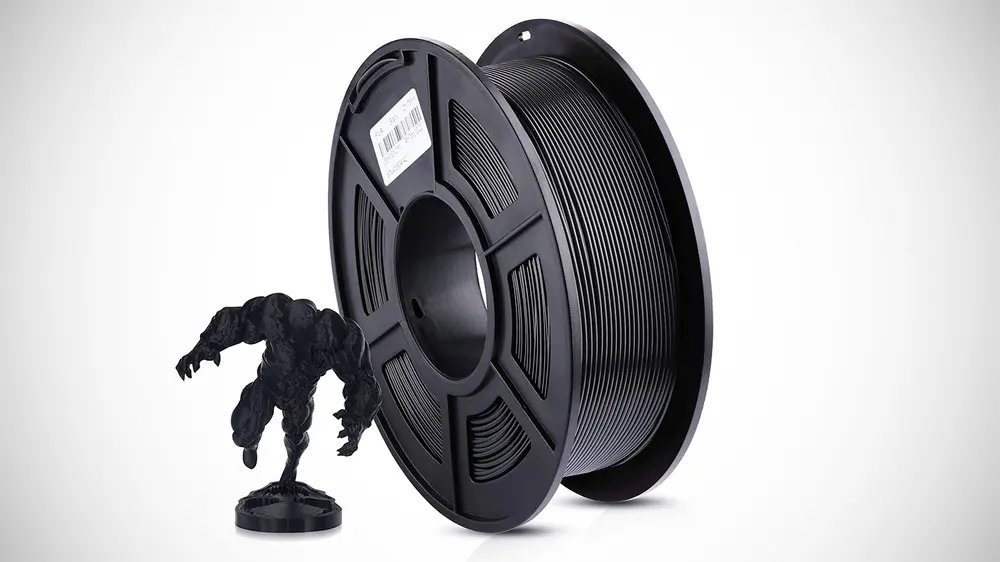
PLA+ / Tough PLA

WHAT IS IT
PLA+ is the enhanced version of PLA. It is mostly the same, with a few slight differences: better surface quality, color, and mechanical properties. Most PLA+ filaments are advertised as being stronger, less brittle, more durable, and better for layer adhesion.
Tough PLA is another term used by some manufacturers. Its properties are generally similar to PLA+, and the boundaries between these two are often fluid and arguably only a marketing approach. There are some tough PLA’s available, though, that promise even better mechanical properties than your regular PLA+s.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Unfortunately, there is no standard formulation for distinguishing between PLA, PLA+, Pro PLA, and whatever-other-branding manufacturers think of. Enhanced PLA is usually a mixture of other plastics, additives, or pigments that help improve on the weaknesses of standard PLA such as moisture absorption, brittleness, and resistance to higher temperatures (although not by much). By and large, enhanced PLAs are not as tricky to print as PETG or ABS, but they are also not quite up there in terms of mechanical properties.
KNOWN MANUFACTURERS
PLA Plus is by far the most commonly used PLA variant. You can find it as PLA+, PLA Plus, or PLA Pro, depending on the brand. For some examples: eSUN’s PLA+ filament is one of the most well known options, Overture’s PLA Professional filament promises enhanced toughness five times that of traditional PLA, and ColorFabb offers a superior blend of PLA branded as PHA.
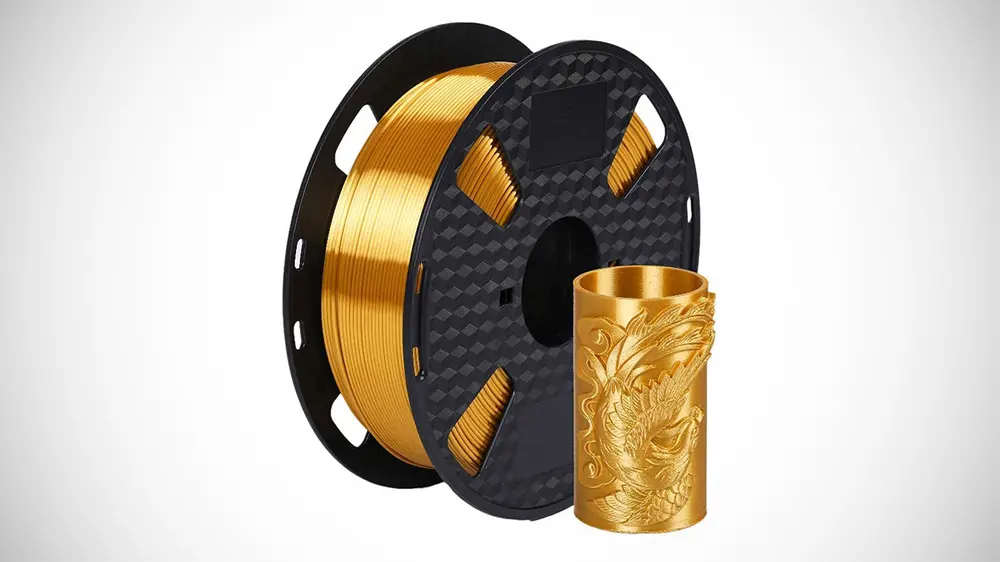
Silk-like PLA

WHAT IS IT
Silk-like PLA is a supremely funky entry and probably one of the prettiest, smoothest, and shiniest PLA filaments going. Silk PLAs produce impressive prints that seem a bit translucent, giving them both a feel and look that they are covered in silk. Forget painting your prints with this filament; its natural appearance is dazzling enough.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
This enhanced PLA owes its glossy look to some elastic additives but shows most of the same pros and cons of regular PLA filament. It is easy to 3D print, but the elastomers can sometimes cause clogging issues and under extrusion. It seems that these filaments work best with slightly elevated printing temperatures compared to regular PLA. The print becomes more durable and less brittle, and the elastomers can melt correctly and give it the signature glossy look.
KNOWN MANUFACTURERS
Many filament makers offer it, but two that have built a reputation for colorful blends are Eryone, offering over ten different colors, or Fiberlogy, which offers silky metallic blends.
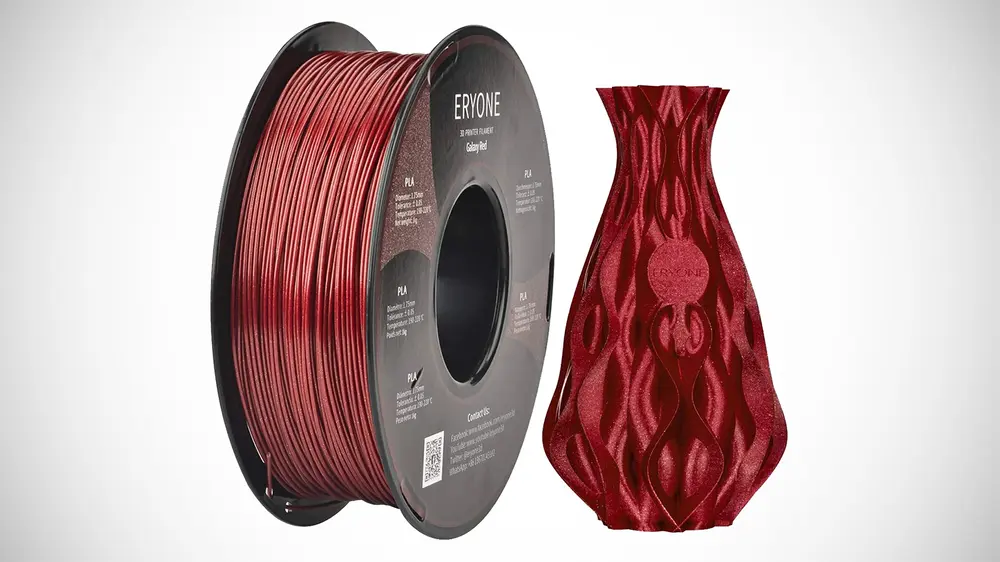
Glitter, Sparkly PLA

WHAT IS IT
Similar to silk-like PLA, sparkly or glittery PLA has that little extra pizzazz that will make your prints gloriously shiny — in this case by adding glitter elements. This not only allows for aesthetic prints, but the added glitter does a great job masking layer lines and generally leaves a smooth-looking print that is optically forgiving where print flaws are present.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
The sparkly effect is achieved by adding ultrafine particles that should easily pass through nozzles without clogging or abrasion. Treat it just like you would standard PLA and have fun.
KNOWN MANUFACTURERS
Glitter PLA is a widely manufactured blend. We reviewed Prusa Research’s Galaxy Black PLA, which works excellent for your everyday prints and covers up any potential print inconsistencies nicely with a smooth surface finish. Eryone also provides glittery PLA in many different colors.
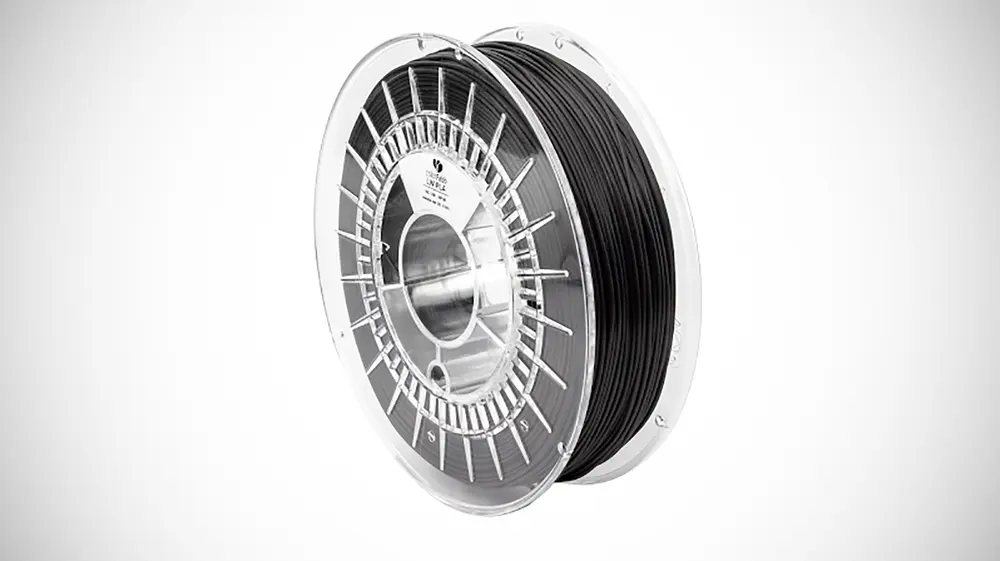
Lightweight PLA

WHAT IS IT
Lightweight PLA, or LW-PLA, is designed so you can print lightweight, low-density PLA parts. It’s especially useful for printing drones, RC planes, cosplay, and other props. Parts are feather-light but retain good strength and are easy to cut, trim and sand. If part weight matters to you, then this is your filament of choice.
WHAT DO YOU NEED TO KNOW
This filament uses an active foaming technology that is triggered by temperature. When the filament is heated to about 230 °C, it begins to foam and increase its volume by up to three times, meaning users can decrease flow by 65% to obtain lightweight parts. Or, users can take advantage of the expanding properties to reduce print time with large layer heights or single extra thick perimeters.
If you want to print lightweight parts which are dimensionally accurate, it’s essential to first determine the possible expansion of the material by looking at the datasheet and printing test cubes at different input variables; namely temperature, speed, and flow rate.
KNOWN MANUFACTURERS
Lightweight PLA is a bit of a unicorn, with not many manufacturers providing the material. Colorfabb is one of the broader-known suppliers with availability in different spool sizes and a handful of colors.
Color Changing PLA
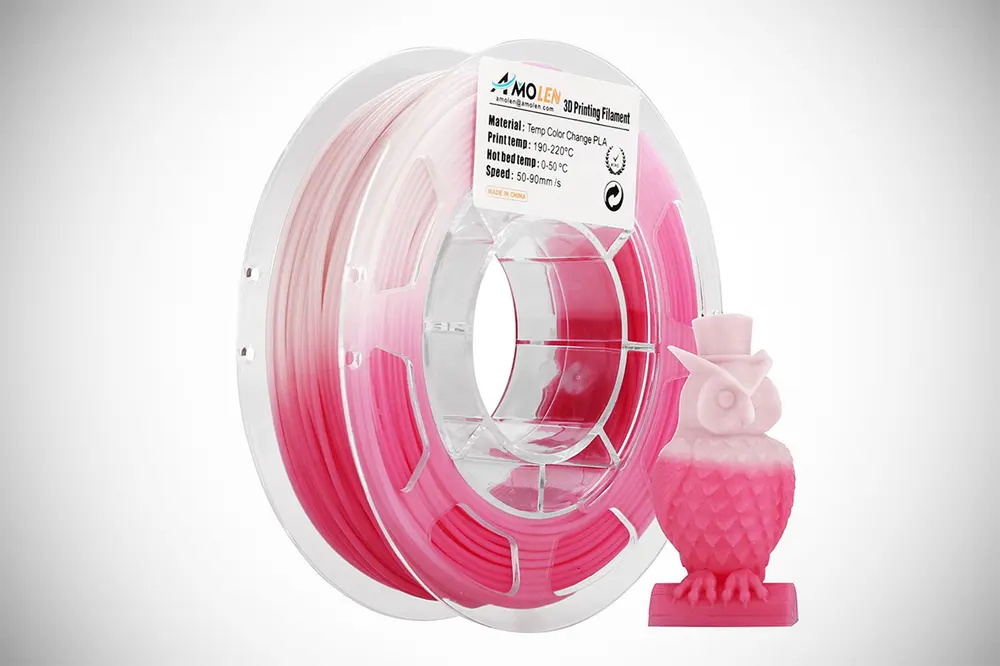

WHAT IS IT
You don’t quite like to get pinned down on just one color for your prints? Enter color-changing PLA filament, changing its color depending on its environment. There are two types of color-changing PLA filament. The first kind is heat sensitive, and the other one is UV sensitive.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Filaments from this category tend to change between a gradient of two colors, for example, from purple to pink, blue to green, or yellow to green. With no special physical, tactile, or functional characteristics, this type of 3D printer filament is purely designed for aesthetic purposes.
KNOWN MANUFACTURERS
Color-changing PLA filament is not the most widely used PLA, yet there are a fair few manufacturers with either temperature or UV-light changing filaments such as Amolen or Sunlu.
Wood PLA
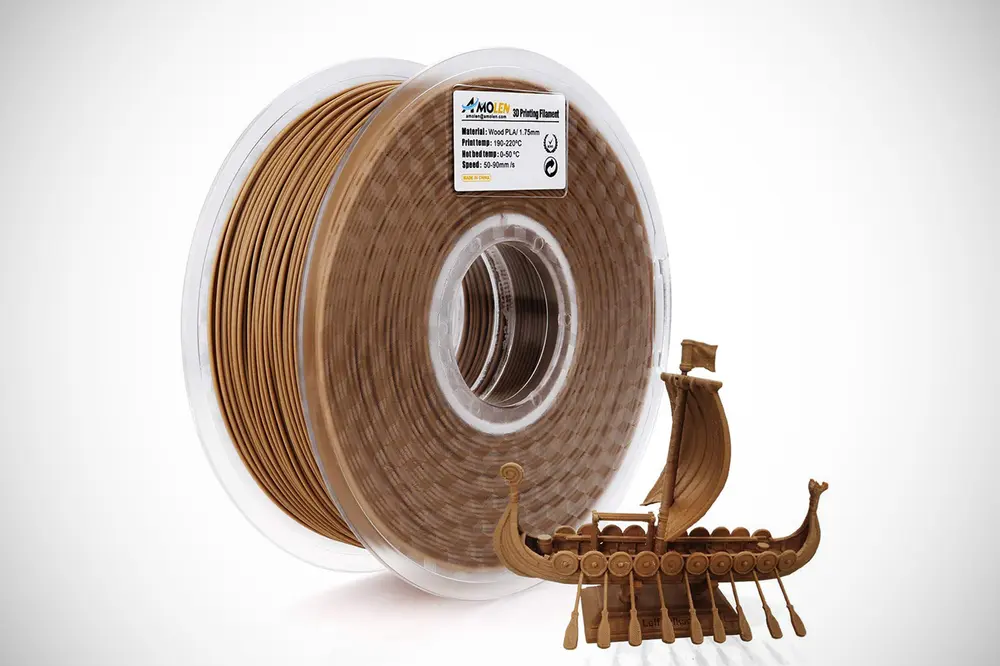

WHAT IS IT
Wood PLA blends will make your prints look like they’re made of, well, wood. By sanding your prints down a bit you’ll be able to give them nice, smooth surfaces with visible grain patterns from the wood fiber.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Wood PLA is made by combining polylactic acid and fibers of different types of wood, such as willow, bamboo, cork, cedar, and more. Typically, wood filaments contain about 70% PLA and 30% wooden fibers, depending on the manufacturer. It is important to note, though, that you should use 0.4 mm or larger nozzles as otherwise, the wood particles might clog up the nozzle.
KNOWN MANUFACTURERS
Wood PLA filament is widely available from manufacturers of all price ranges, ranging from the affordable Hatchbox to Fillamentum, or the extensive range of wood filaments by FormFutura called EasyWood.
Flexible, Soft PLA
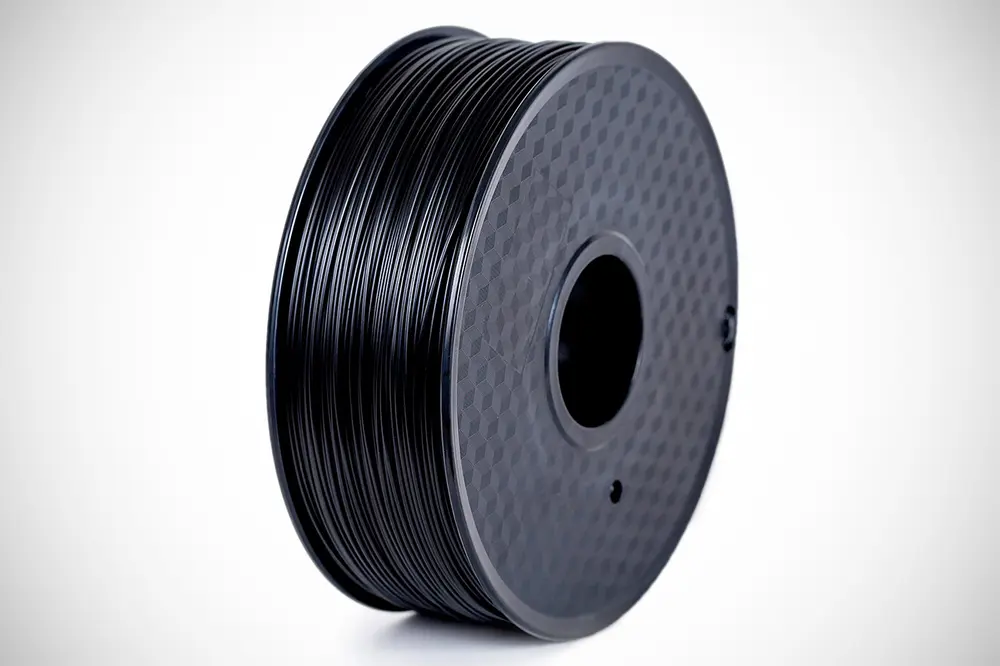

WHAT IS IT
This flexible variant, Soft PLA, is a generic term applied to PLA blends that are made to be more flexible. Soft PLA is treated with additional chemicals to take away much of the base material’s natural brittleness, which is why it is sometimes also referred to as “tough rubber”. Similar to TPU and other flexibles, it absorbs vibrations and impacts and is able to withstand bending and stretching, springing back to its original shape once the pressure is taken off.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Compared to other flexible materials, it is known for its strength and durability. Printing it is similar to printing standard PLA, except that one should use a slower print speed and a higher bed temperature. Typically Shore hardness ranges from 90 and 92A and depending on the flexibility you might want to consider a direct drive system as it is less likely to coil up and clog.
KNOWN MANUFACTURERS:
With TPU and other flexible filaments dominating the market, Soft PLA is not the most widely used nor manufactured. Paramount 3D’s Flex PLA is one of the more widely available but there are a handful of smaller manufacturers as well.
Carbon Fiber PLA
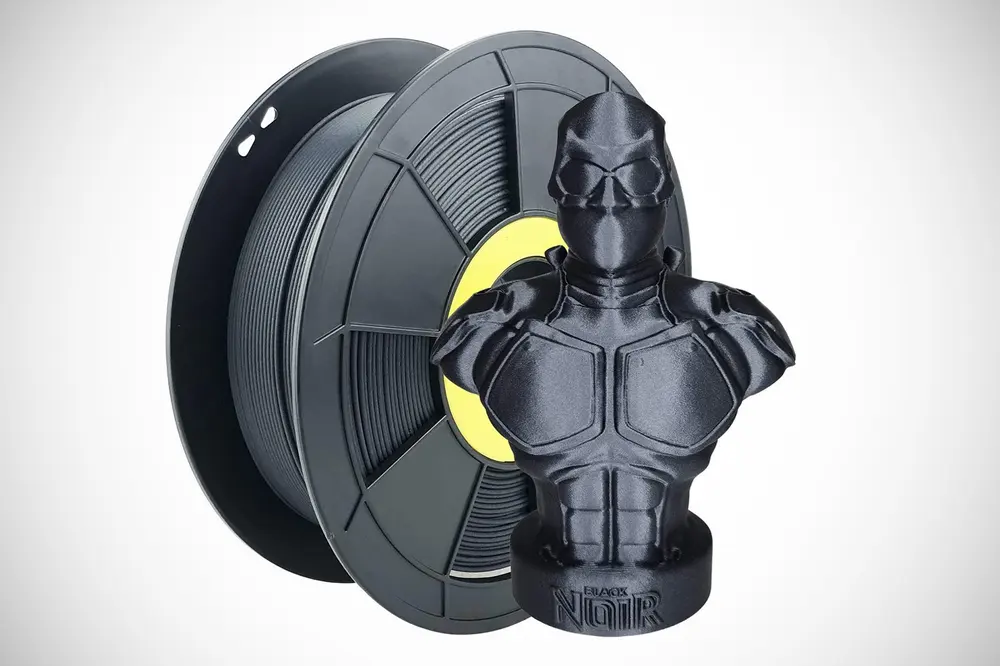

WHAT IS IT
Carbon fiber PLA is a composite material that is more rigid and provides enhanced structural strength due to the added carbon fibers — typically around 10-20%. Increased rigidity, in turn, also means decreased flexibility, making carbon fiber PLA an ideal material for frames, supports, shells, and anything in between that shouldn’t bend.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Carbon fiber PLA typically exhibits the same print properties as “normal” PLA, albeit with an occasional slight temperature increase depending on the composite. However, over time, the carbon fibers will wear out the nozzle. It is recommended that you use a hardened steel nozzle with at least 0.4 mm in diameter as, otherwise, the chopped carbon will destroy weaker nozzles like brass or may lead to clogging smaller diameters. Also, unlike in its processed form, it is more brittle than standard PLA in its filament form, so handle it carefully to prevent breakage.
KNOWN MANUFACTURERS:
Carbon-reinforced materials stem from the professional side of 3D printing but have found their way to the budget sector. The blend is generally only available in black color, but you have a plethora of manufacturers to choose from, such as Ziro or Overture.
Glow-in-the-Dark PLA
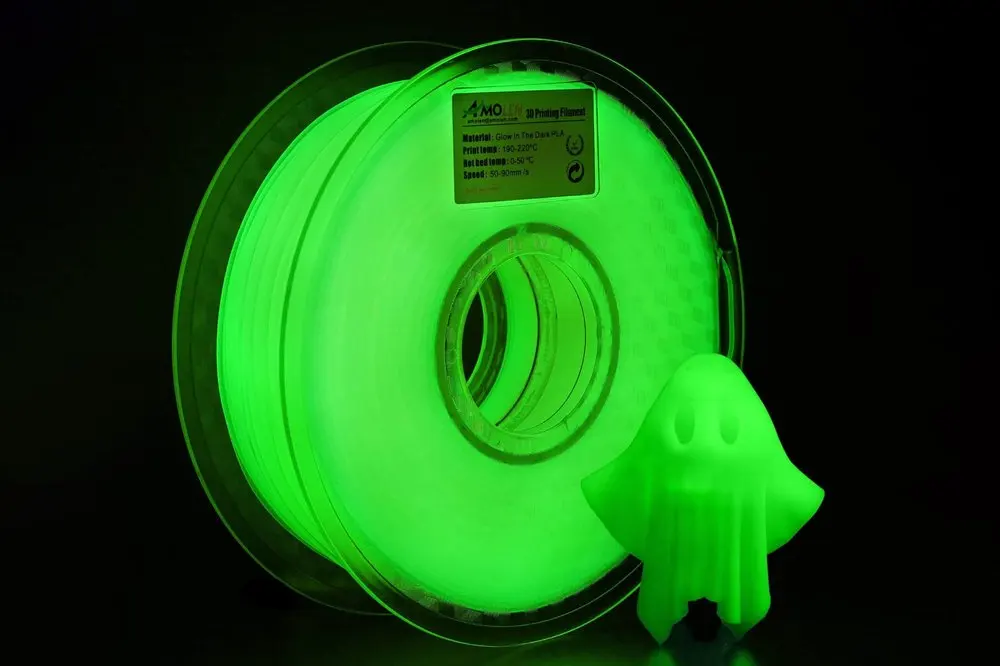

WHAT IS IT
Glow in the dark PLA filament is like any standard filament but with one key difference: It glows after being charged with light. This effect is achieved by phosphorescent additives such as strontium aluminate (and sometimes zinc sulfide and calcium sulfide), which absorb UV light and re-emit it as visible light. In other words, they glow magnificently in the dark. Glow-in-the-dark filament comes in many colors including blue, red, pink, yellow, or orange. But green tends to be the most popular and replicates that classic spooky glow.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Keep in mind that you have to “charge” the prints under UV light before they will glow in the dark. Consider printing with thick walls and little infill for best results: the thicker your walls, the stronger the glow. But be aware, these blends tend to also be more abrasive compared to your standard PLA, so better check your 3D printer nozzle.
KNOWN MANUFACTURERS
Glow-in-the-dark PLA filaments can be found far and wide, with a bunch of well-reputed filament manufacturers offering it, mostly in green or blue colors. Try Hatchbox or Gizmo Dorks. If you’re looking for something that has a little more…sparkle, check out the Amolen Shiny Glow special blend.
Conductive PLA
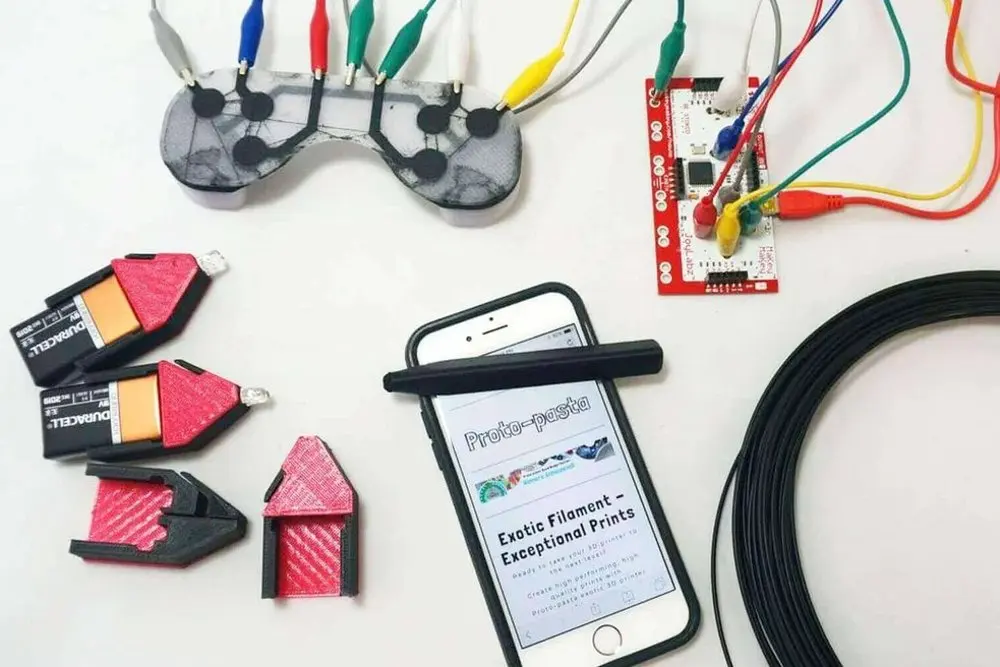

WHAT IS IT
With the addition of conductive carbon particulates to PLA, it’s easy to actualize hobbyist projects by printing low-voltage electronic circuits. If your 3D printing project requires some electrical wiring, you can just print them rather than running wires through your build. This PLA filament is a mixture of polylactic acid and usually some form of carbon – mostly graphene. It’s no substitute for a regular PCB, though.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Even though this 3D printer filament type only supports low-voltage circuitry, the sky’s the limit with customized electronics projects, and even more so when you have a dual extrusion printer with conductive and ordinary filament at hand. Keep in mind, though, conductive PLA needs a power source like a battery to transfer electricity.
Although the filament can handle electricity, we recommend that you don’t test its limits as burning the plastic can release carcinogens. Electrical stress tests have shown that conductive PLA can handle 0 to 60 volts at or under 100 mA, but this varies depending on the brand and should be researched before testing.
KNOWN MANUFACTURERS
Besides conductive PLA, you can also find ABS blends on the market, but overall the choice is pretty sparse. Protopasta’s Conductive PLA is probably the best known here.
High-Temperature PLA
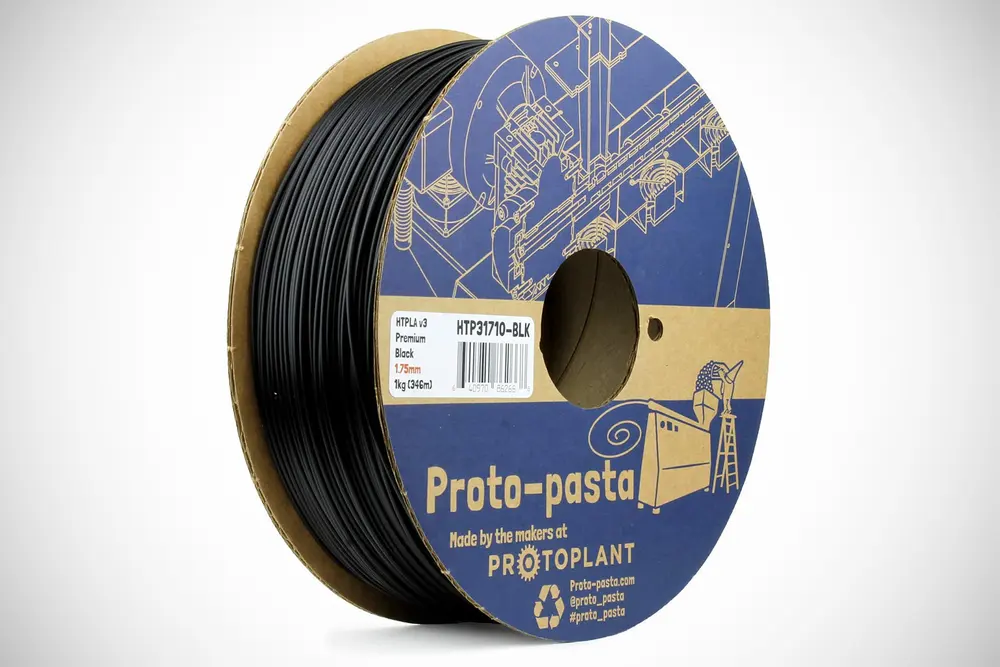

WHAT IS IT
High-temperature PLA can be exposed to exactly that: much higher temperatures, up to 150°C depending on the manufacturer, than pure PLA, which typically starts to deform at around 55°C. That’s thanks to the addition of minerals that crystallize when the material has been heat-treated after printing.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
High-temperature PLA prints similar to standard PLA. The heat resistance gets “baked-in” in the post-processing when the printed part is either placed in an oven or a hot water bath. Some filaments even change color during the baking process. Please refer to the manufacturer for precise instructions. The result is a part that maintains strength and form at much higher temperatures than even the likes of ABS or PET (which typically lose structure at around 100°C).
KNOWN MANUFACTURERS
Heat resistant PLA is probably best known from Protopasta which offers a wide selection of different colors.
Translucent PLA
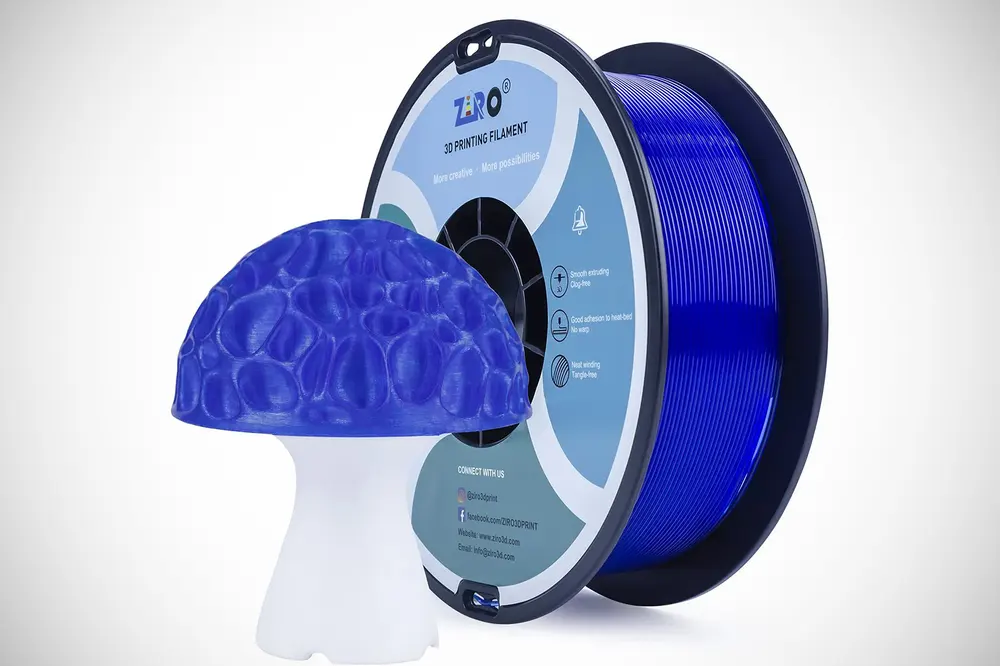

WHAT IS IT
Translucent PLA is permeable to light, making it the go-to PLA for objects you would like to light up with LEDs such as action figures or even lampshades. Even if this PLA filament is sometimes marketed as clear or transparent, it is merely translucent, so don’t expect window pane-like transparency. Its most commonly available color is “clear,” but there are also many color variants available.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Printing in transparent PLA isn’t significantly different from printing with regular PLA. However, if you want the most transparent print, you should use a higher hot end temperature, a larger layer height, and a low infill. This will ensure that the clear material is properly melted, spaced out, and hollow enough for optimal transparency,
KNOWN MANUFACTURERS
Translucent or see-trough PLA is widely available. For example, from Eryone. Manufacturers such as Solutech or Fillamentum even offer a handful of different colors.
Metal PLA
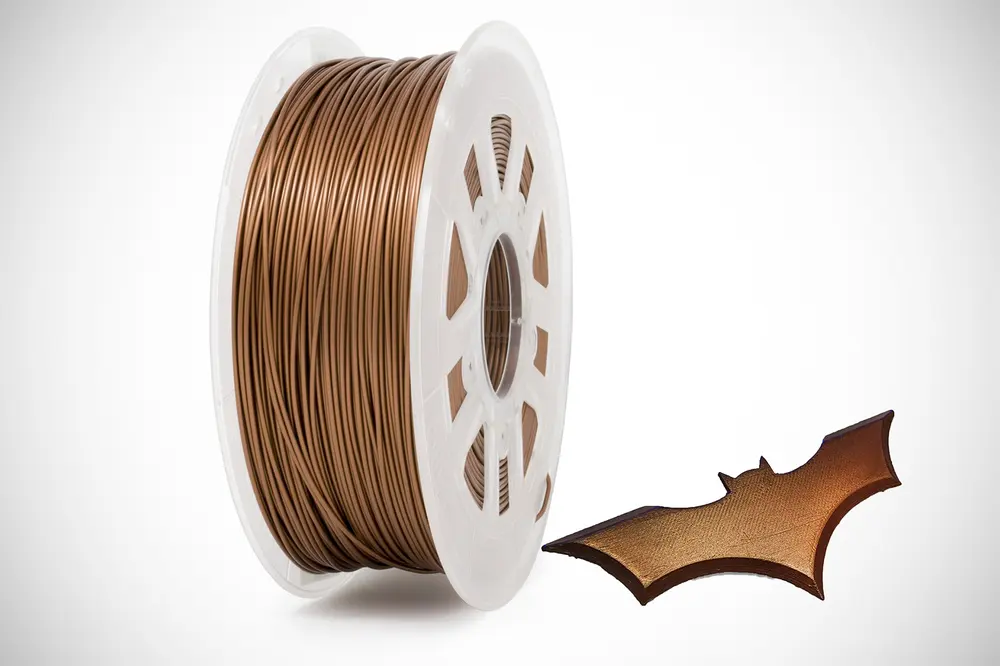

WHAT IS IT
Metal PLA isn’t “real metal” as it is similar to Wood PLA in that it is a mix of metal powder and PLA, but that doesn’t stop the results from having the look and feel of metal (not its mechanical properties, though). Even the weight is metal-like, as blends tend to be several times denser than pure PLA. The most common 3D printer filament blends tend to be up to 50% metal powder and 50% PLA and come in various materials, ranging from copper and bronze to iron and stainless steel. Metal PLA prints can be highly aesthetic, especially for figurines, models, toys, and tokens, as the material is great for post-processing, such as sanding, polishing, weathering, or tarnishing.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
It’s important to note that if you want a filament with actual metal in it, you’ll need to look for the word “composite” or “metal fill.” Beware of filaments with only “metal” in the name, as this might simply indicate a metallic color or shine, which are merely color variants.
When printing with Metal PLA, expect increased nozzle wear. Therefore, it is recommended to switch your brass nozzle to stainless steel or another hardened alloy, as brass nozzles wear out much faster from metal abrasion. Also, the more percentage of metal the filament holds the more brittle it becomes — so it should be appropriately stored and handled with care — and the more you may need to adjust print settings such as temperature, retraction, and layer thickness.
KNOWN MANUFACTURERS
Metal-filled filament comes in many different blends, from stainless steel, aluminum, and copper to bronze and brass. You can even get magnetic iron PLA.
PLA FILAMENT – EXPLAINED
What is PLA Filament?

PLA is short for Polylactic Acid, a thermoplastic polymer derived from renewable resources, specifically corn starch or sugar cane. This sets the material apart from other commonly used plastics procured through the distillation and polymerization of non-renewable petroleum reserves.
PLA is considered biodegradable to a large degree because of its organic origins. This means that, if left undisturbed, it will eventually be broken down by naturally occurring microorganisms like bacteria and fungi. It still takes a long time to decompose, though. Under ideal compost conditions, PLA plastic takes three months to decompose. However, other thermoplastic materials can take up to a thousand years to decompose, making PLA much more environmentally friendly.
PLA material has been thrusted into the spotlight by the rise of FDM 3D printing. As a result, PLA filament is available in various colors and blends, and innovative PLA-based materials seem to be constantly hitting the market.
Outside of 3D printing, PLA is also used to produce medical implants, food packaging, and disposable tableware. But inside the FDM 3D printing sphere, PLA filament is widely thought of as an aesthetic material best used for prototyping.
How PLA is produced
To produce PLA filament, manufacturers start with a raw, granulated resin that is clear in color. The material is put into a blender-type machine, mixing it with the pigments and/or additives that produce a particular color or mechanical properties.
From there, the material is usually dried out at 60 – 80 °C, which reduces the possibility of having the PLA filament pop or clog your 3D printer’s nozzle.
The granulated material goes into a single screw extruder, which is where it’s heated, mixed, and extruded into a solid filament. This filament is then placed into a warm water tank, which cools the material into a round shape. Finally, the round filament is run through a cold water tank and wound onto a spool.
PLA filament comes in two sizes for FDM 3D printing; 1.75 mm and 2.85 mm. This diameter size is determined by how fast or slow the material producer pulls the filament through the die.
What are the Benefits of PLA Filament?
There are a number of benefits to 3D printing with PLA filament, especially if you’re a beginner or looking for a frustration-free experience.
- Easy to print: PLA is super easy to print with; virtually all 3D printers can print this material as it doesn’t even require a heated bed. PLA requires relatively low temperatures compared to other printing materials, doesn’t require an enclosure, and can be printed somewhat fast (around 60 mm/s). Post-processing is also easier when it comes to PLA, enabling users to improve surface quality with a bit of sanding and trimming.
- Inexpensive: PLA is pretty cheap to buy compared to other, more specialized printing materials such as nylon or polycarbonate (PC), making it a great option for rapid prototyping and, generally, makers on a budget.
- Wide range of colors and options: PLA filament comes in so many different colors because the material itself is easily pigmented. Manufacturers have made this filament in almost any color you can think of. Additionally, we’ve listed the composite and special blends above.
- Biodegradeable and eco-friendly: As PLA is sourced from plants, it makes sense that it’s biodegradable — unlike other plastics (e.g. ABS) that are made from refining crude oil, which harms the environment.
- Non-toxic: PLA is non-toxic when it can be kept uncontaminated, expanding its applications to areas like the medical and food industries.
- No fumes: Fumes are unavoidably released when thermoplastics are melted, and these fumes, especially from toxic materials like ABS, can contain harmful inhalants and even carcinogens. While PLA can release some fumes, there is almost no odor and far less risk.
What are the Drawbacks of PLA Filament?
Although there are numerous advantages to using PLA filament over other options, the material has a few drawbacks.
For instance, PLA filament tends to deform or melt when heat is applied, making it impractical for parts that require heat resistance. It’s also less sturdy than ABS or PETG, making it better for aesthetic uses rather than mechanical.
Additionally, PLA is not food-safe and is quite brittle in nature, making it more prone to breaking under stress.
- Brittle and relatively weak: The most obvious disadvantage of PLA is its low flexural strength. 3D printed PLA parts are significantly weaker than injection-molded parts and even parts 3D printed in other materials like PETG and ABS. PLA parts also don’t usually bend; they snap very quickly after enough force is applied, meaning the material is very brittle.
- Low temperature and chemical resistances: On top of not being the strongest material out there, PLA isn’t very heat resistant either. PLA has a low glass transition temperature, so parts printed in this material tend to deform under hot conditions, making PLA a less ideal material for outdoor use. Additionally, certain chemicals cause PLA to release its raw chemicals, namely lactic acid, which can be harmful in high quantities.
- Slow decomposition: Even though PLA is biodegradable, as you might expect from plastic, it still takes a long time to decompose. Under ideal composition conditions, PLA plastic takes three months to decompose, which is a long time compared to other decomposable materials.
As with most 3D printing materials, whether or not PLA filament is the right choice is wholly dependent on what you’re planning to 3D print.
When Should You Use PLA Filament?

PLA filament is a great material for numerous applications. Although it lacks the mechanical properties found in other filament types, PLA is easy to print and comes in many colors and styles.
Therefore, most PLA filament types are great for visual prints and rapid prototyping, particularly in cases where the 3D printed part won’t encounter too much stress or strain and so, won’t be dependent on mechanical properties, durability, or degradability.
You’ll also probably want to avoid using PLA filament for 3D printed items that will be bent or twisted, such as tool handles or phone cases. This material is usually not very heat resistant, so it’s better to use a filament with better mechanical properties.
Other than that, PLA filament is a great option for nearly any other application. Some of the most popular uses for PLA include visual models, figures and characters, low-wear toys, non-functional prototype parts, and containers.
What are the Optimal Print Settings for PLA Filament?
Depending on the type or blend of PLA you’re using, the optimal print settings will be a bit different. The average PLA filament has a melting point somewhere between 180 to 200 degrees C.
The best temperature for a PLA filament that has a 1.75 mm diameter will be lower than a material with a 2.85 mm diameter. Another deciding factor in what print temperature you should input is the blend of PLA you’re using.
Although a heated bed may help with the adhesion of PLA filament, it’s not necessary. This is why PLA is an especially appealing option for really frugally minded 3D printer users, as a glue stick or painter’s tape can be used to get that first layer to stick.
You should also keep in mind that PLA has a glass transition temperature between 60-65 °C, which is the point where the plastic starts to become viscous or rubbery.
When working with PLA filament, be sure to consult with the manufacturer to figure out the optimal print settings. Since PLA comes in many shades and blends, there is no precise temperature that works for them all.
Post-Processing with PLA Filament
There are numerous ways to post-process PLA filament, and these methods sometimes depend on which type of PLA you’re using.
After sanding your model, you could use a primer or filler to cover any other crevices that will impact the way your paint settles on the print. Acrylic paint is the best option for PLA filament, and is generally affordable and comes in many colors.
Another option is polishing, which works especially well with special metal PLA filaments. Using some latex gloves and a polishing cloth, you can hand polish your 3D model with Tetrahydrofuran.
Is PLA Filament Toxic?

Compared to the toxic fumes that are emitted from ABS, PLA filament is a much safer alternative. However, that doesn’t mean that this material is completely safe.
While ABS is known to emit styrene, which is a toxic and carcinogenic chemical, PLA filament emits a benign and less hazardous chemical named lactide. Some have argued that the chemical emitted from PLA is essentially harmless.
Either way, there’s no denying that PLA is a much safer material to print with than ABS. As long as you have some decent ventilation and a sizable workspace, you shouldn’t be overly concerned about the toxicity of PLA filament.
Is PLA Filament Food Safe?

In its most natural state, PLA filament is made from corn starch, which is generally considered food safe. But once the material is injected with additives for color or strength, this can all quickly change.
There are a few filaments out there that are marketed as being food-safe. You can also check the material safety data sheet (MSDS) on your PLA filament, which will tell you about the chemical properties and whether it is FDA approved or food safe.
However, no matter how food-safe your PLA filament might be, you still run the risk of having bacteria building up between the layers. To avoid this, you can seal the surface of a 3D print with a food-safe epoxy or sealant, which covers the crevices that may otherwise end up collecting these nasty germs.
Another tip is to keep your 3D printed object away from the dishwasher. Instead, you should wash with warm water and a mild anti-bacterial detergent, which will reduce the risk of bacteria and also keep your print from melting.
Lastly, you should probably get your hands on a stainless steel nozzle that is considered to be food-safe. This might be a major investment for someone who’s only planning to print a couple of kitchen utensils, but the cleanliness of the nozzle is important.
How Do I Store PLA Filament?
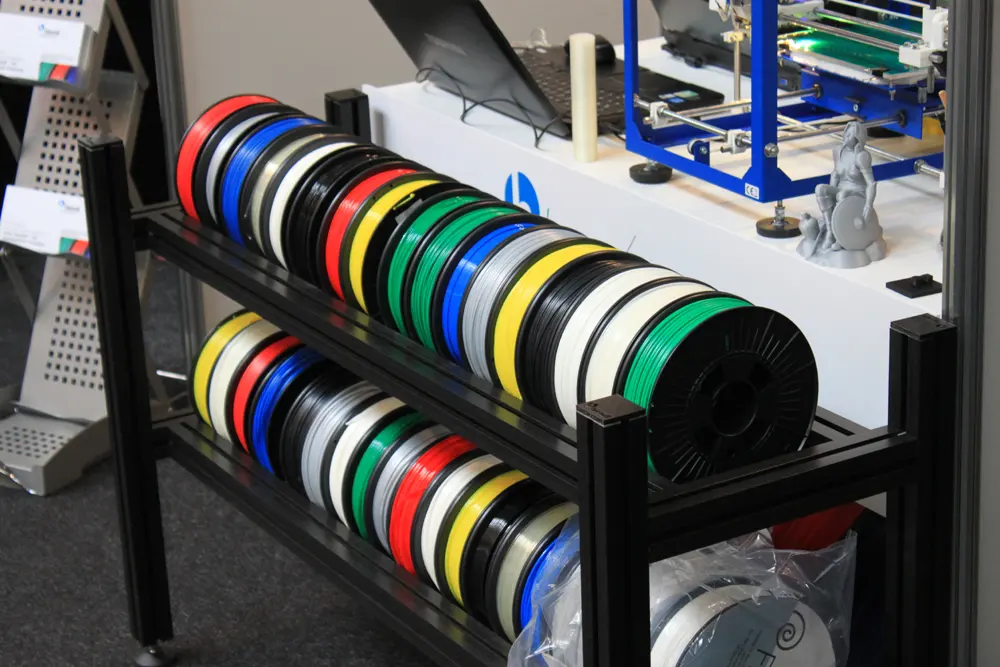

If you’re anything like us, you’ll probably want way more than just one spool of filament to feed your 3D printer. As we’ve stated, there are endless types of PLA filament to purchase, and all of them should be properly stored to ensure quality.
3D printing filament storage is extremely important no matter what material type you have on the spool. When left out in the open, these plastics tend to absorb water from the air, and this humidity can cause some massive problems in your 3D printing experience.
This phenomenon is called hygroscopy, which is a characteristic that makes 3D printing filament attract water molecules. For specialty filaments like Nylon and PVA, the problem can occur in just a matter of hours. Therefore both should be stored in an airtight container right away.
Although PLA filament has a longer shelf life, humidity can also creep into the material eventually, which in turn will negatively impact your prints.
Once water absorption takes place, you can face increased brittleness, diameter augmentation, filament bubbling, filament degradation, or easily breakable filament. To prevent this, you should store your PLA filament inside an airtight container or a specialty box.
There are a number of storage solutions that have been developed, and you can even build your own pretty easily.