
When you’re in need of metal prototypes or parts with superior mechanical properties and specialized aesthetic design, anodizing aluminum is an excellent option. The anodizing process forms a layer of oxide on a metal part, effectively increasing corrosion resistance, and also enhancing visual qualities and keeping the surface from being scratched.
Anodizing aluminum is an extremely durable post-processing method. Not only does it enhance the properties and appearance of a part, it enables better adhesion for paint primers and glues. This technique utilizes anodic films that provide unique aesthetic effects, such as transparent coatings that reflect light or thick coatings that can absorb dies.
Despite having an impact on the mechanical capabilities of metal parts, anodizing aluminum will not take away from the natural appearance of the material. While the anodizing process can also be applied to other metals -such as titanium, zinc and magnesium- aluminum is by far the most widely used of the bunch.
As a part of 3ERP’s extensive offering for premium surface finishes, you can utilize our anodizing aluminum service to enhance the functionality and look of your metal parts and prototypes. To help you make the right decision for post-processing, here’s everything you need to know about anodizing aluminum.

How the Process of Anodizing Aluminum Works
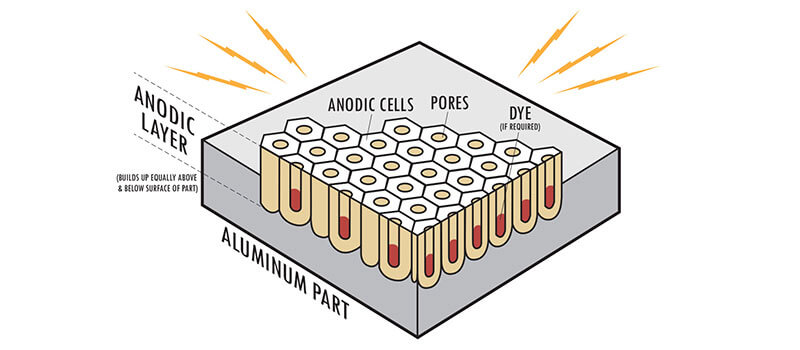
In order to properly anodize aluminum parts, the surface must first be cleaned and rinsed before getting placed into a bath of an electrolytic solution, primarily either sulfuric or chromic acid. This provides an electrically conductive coating that contains a number of positive and negative ions.
So how does this process really work? Well, once the anodizing process is underway, a positive electric charge is sent through the aluminum, while a negative charge is applied to plates in the electrolyte. Basically, the electric current forces the positive ions to attract to the negatively charged plates while the negative ions are attracted to the aluminum part, which the positive anode.
From here, the electrochemical reaction forces pores to open up on the surface of the aluminum so that the positive ions can escape. In a uniformly geometric pattern, these pores dig down into the substrate of the part. The combination of the aluminum surface and negatively charged ions create a barrier layer, which is known in the anodizing aluminum process as the surface layer the makes parts resistant to corrosion.
There are currently four different variations of the anodizing aluminum process, each of which offers distinct advantages over the other:
Anodized Type I: This is the most basic type, using chromic acid to produce a thin and ductile anodized layer on an aluminum part.
Anodized Type II: Instead of using chromic acid, Type II utilizes sulfuric acid in order produce a thicker anodized layer on a part, making it more suitable for coloration.
Anodized Type III: Similarly to Type II, this method also uses sulfuric acid, but produces a thicker anodized layer that is also suitable for coloration. It’s also commonly known as “hard anodizing”.
Chemical Film / Alodine: This method entails coating part with alodine to produce results that are comparable to anodization.
While chromic acid was widely used by manufacturers when the anodizing aluminum process was developed in the early 1900’s, most parts are now anodized with the sulfuric acid (Type II and Type III).
Anodizing aluminum parts also presents an array of options when it comes to adding color. The coloration process works by injecting a pigment into the empty pores of the part. Once the colored pigment reaches the surface, it’s sealed off to preserve the selected color. This creates an visual effect that won’t fade away and can’t be scratched off, keeping the appearance of your parts in premier shape.

The Benefits of Anodizing Aluminum Parts
You might not realize it, but you probably interact with products and parts that have been anodized on a daily basis. The anodizing aluminum process is commonly used for a wide range of applications, producing parts that you’ll regularly find in aircrafts, consumer goods, sporting equipment and electronics, just to name a few.
There are a number of benefit you can leverage when anodizing aluminum parts, both visually and mechanically. For starters, anodized aluminum parts are exceptionally durable and hard. It’s ability to improve resistance to abrasion and corrosion makes this process ideal for parts that will be placed within harsh environments. It also offers terrific thermal insulation to metal parts.
The anodizing aluminum process will help metal parts last longer than raw parts. The coating is much thinner than paints and powders, while still supplying a much harder surface as well.
Another benefit of anodizing aluminum parts is that it offers an environmentally-friendly finish, making it easily recyclable. And, perhaps most importantly, the post-processing technique is affordable compared to painting and powder coating.
Should You Anodize Your Aluminum Parts?
Now that you know more about anodizing aluminum, you can decide whether or not this process is right for your parts. If you need functional aluminum parts that will face corression or wear, such as aircraft parts or consumer goods, this post-processing technique will satisfy your needs. There’s also a visual appeal to anodizing aluminum, particularly because you can add color to your parts while keep the metallic sheen intact.
If you want to learn more about how this technique can help enhance your prototypes and parts, contact FacFox’s expert team to discover how anodizing aluminum can enhance your own production plans.
