
At present, metal 3D printing technology on a global scale is mainly divided into two camps, direct metal 3D printing (including SLM, EBM, LENS, WAAM, etc.) and indirect metal 3D printing.
Direct metal 3D printing is the direct printing of metal materials into metal Indirect metal 3D printing is to print metal materials through adhesives, etc., and then remove the adhesives to finally obtain metal parts.
Indirect metal 3D printing is aimed at the low-cost mass production market. Indirect metal 3D printing companies represented by Desktop Metal and Markforged are developing rapidly, but their equipment prices are still hundreds of thousands or even millions of yuan.
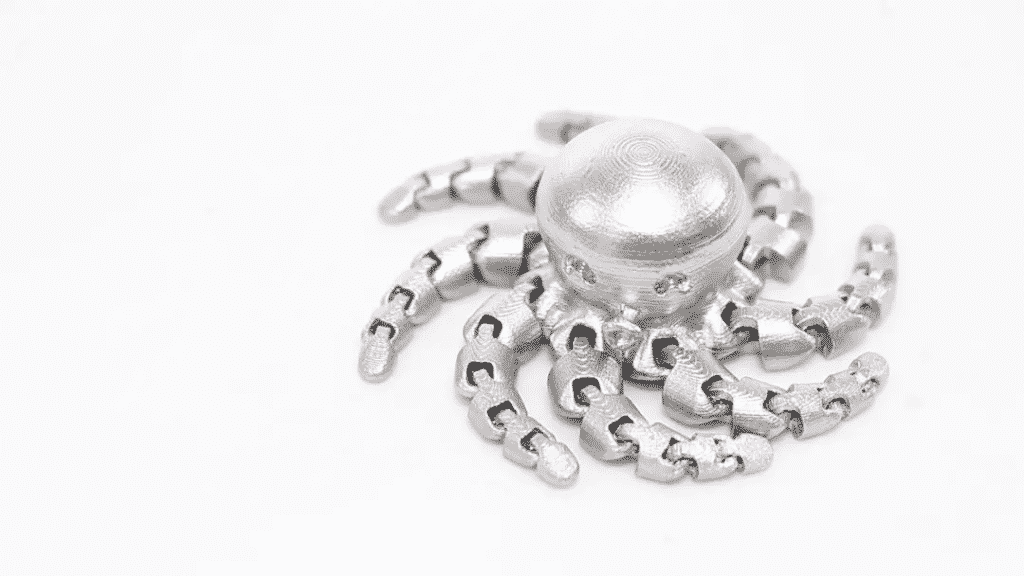
Anycubic just published its 4Max Metal 3D printer and stirred the market. With a build volume of a 270 x 210 x 200 mm, it can print things much larger than the general maximum size of direct metal printers. Also, it’s tuned to print 316L stainless steel filament.
Parameters of 4Max Metal
Printer
- Principle: FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
- Printing volume: 270mm(L)×210(W) ×200mm(H)
- Printing accuracy: 0.05-0.3 mm
- Positioning accuracy: X/Y/Z 0.01/0.0125/0.00125mm
- Number of nozzles: single nozzle
- Nozzle diameter: φ3/0.5mm
- Printing speed: recommended 30mm/s (Max 50mm/s)
Filament
- Consumables: 316L stainless steel
- Diameter: 1.75±0.05mm
- Length: 66m
- Weight: 750g
- Shrinkage rate: 17%-25% (after sintering)
- Certification: ROHS / Reach
How does it work?
4Max Metal works based on an indirect metal printing process. It firstly prints the raw metal parts with the FFF 3D printing technique, then debinds and sinters the parts to get final products.
Below are the illustrations of how it works.
Step 1: Design and Slicing
Considering that the parts will be shrunk during the sintering process, the 3D model should be scaled up a little during the design process.
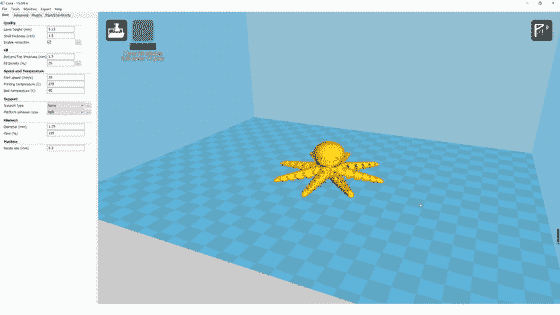
Step 2: Load materials and start printing
316L stainless steel combines high strength, corrosion resistance, and hardness. It’s widely used in manufacturing industrial applications. After input the metal filament into the printer, it will print one layer at one time until it forms the part.

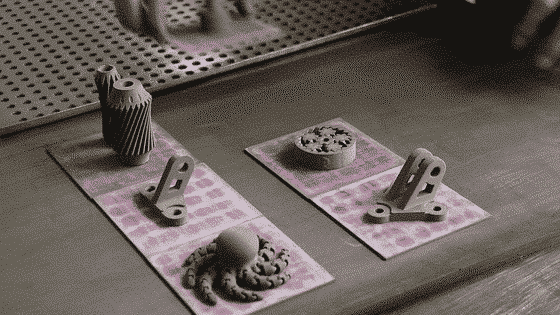
Step 3: Debinding
After printing, the first step in transforming a printed “green” part into fully dense metal is debinding.

Step 4: Sintering
The debonded “brown” parts are placed in a furnace. The remaining binder is burned away and the metal filament is sintered and turns dense.
Benefits and downsides
Compared with the SLM metal 3D printing process, 4max Metal has a better cost advantage. The price is less than 1/200 of an SLM metal 3D printer with the same forming size, and the operation is simple. Based on this calculation, for the price of buying an SLM metal machine, you can purchase 200 pieces of 4max Metal for the production of metal parts, and the production capacity will increase significantly.
Of course, the metal parts printed by FDM technology still have great limitations compared with SLM technology. For example, it’s not so ideal when consider printing accuracy, shrinkage ratio control, density, and strength, etc.
