Check out our 3D printing materials guide to learn about all the consumer materials commonly used for home 3D printing today.
The materials used for 3D printing are as diverse as the products that result from the process. To get the most out of your projects, choosing the right materials for your objects is essential.
In the following guide, we will take a look at the most common 3D printing plastics, both for FDM and SLA 3D printers. Whether you are looking for the right filament or the best-suited resin, this concise guide will help you select the best material for your next project or improve the quality of your prints.
This guide focuses solely on desktop 3D printing materials, which means we’ve excluded materials for pros and professional machines – like metals and engineering-grade thermoplastics – as well as materials that you can’t buy off the shelves.
Without further ado, here are the best 3D printer materials for home use.
FILAMENT
The most accessible way to 3D print at home is with a fused deposition modeling (FDM) printer, which has traditionally been the easiest and cheapest way to 3D print.
FDM printers work by fusing together layers of materials to create an object. The material, in this case, is generally a thermoplastic filament, which is melted and then extruded layer by layer onto the print bed.
The most common filaments are made of the thermoplastics PLA, ABS, and PETG, but there are so many more out there that expand what you can create with your FDM printer.
From functional models like tools or prosthetics to fun objects like games or figurines, there’s a filament out there that’s best suited to the task at hand.
PLA

A crowd favorite in our 3D printing materials guide is PLA, which can, under certain commercially attainable conditions, biodegrade. (You’re not going to be able to compost it at home.)
PLA Plastic / Material – The Ultimate Guide
First and foremost, PLA is easy to print with. It has a low printing temperature, doesn’t need a heated bed (although it helps), and doesn’t warp as easily. Another benefit of using PLA is that it doesn’t give off an offputting odor during printing (unlike ABS). Moreover, it is a suitable 3D printing material for single-use food contact. However, PLA is less durable than ABS or PETG and susceptible to heat. So, for any type of engineering part, you’ll be better off with the latter. Avoid using it when making items that might be bent, twisted, or repeatedly dropped, such as phone cases, high-wear toys, or tool handles.
PLA Filament: The Best Special Blends in 2022
PLA is available in a broad range of colors and also comes in a variety of composites from glow-in-the-dark, glittery, or color changing.
ABS

Remember the quality of Lego bricks? Then you can relate to why Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is one of the most popular 3D printing materials to date. Made from petroleum, ABS is commonly used in injection molding and is found in many household items, such as those rock-hard Lego bricks, phone cases, or bicycle helmets – due to its durability, robustness, and temperature resistance.
The Best ABS Filaments of 2022
While it plays a major role in commercial applications such as rapid prototyping, in hobbyist 3D printing, ABS is less popular. This is due to it being slightly more difficult to print – it’s prone to warping without an enclosed and heated build chamber.
Nonetheless, ABS makes a good general-purpose 3D printer filament for DIY projects. Examples include high-wear toys, tool handles, automotive trim components, and electrical enclosures. It is readily affordable, strong, lightweight, allows for easy post-processing, and comes in a broad range of colors. However, ABS releases smelly and toxic chemicals during printing. Adress this by printing in a well-ventilated area and/or with an enclosure.
PETG

PETG is made from Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), the material you know from plastic water bottles, but some ethylene glycol is replaced with CHDM (cyclohexanedimethanol) — hence the letter “G” after PET for “glycol-modified”. The result is a filament that is clearer, less brittle, and easier to use than its base form of PET.
PVA

Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) is soluble in water, and that’s exactly what commercial applications take advantage of. Popular uses include packaging for dishwasher detergent “pods” or bags full of fishing bait. (Throw the bag in water and watch it dissolve, releasing the bait.)
For 3D printing, PVA, like HIPS, is engineered for use as a soluble support material, primarily when paired with another 3D printer filament in a dual extrusion 3D printer. The advantage of using PVA over HIPS is that it can support more materials than just ABS.
The trade-off is a 3D printer filament that is slightly more difficult to handle. One must also be careful when storing it, as the moisture in the atmosphere can damage the filament before printing. Dry boxes and silica pouches are a must if you plan to keep a spool of PVA usable in the long run.
Nylon
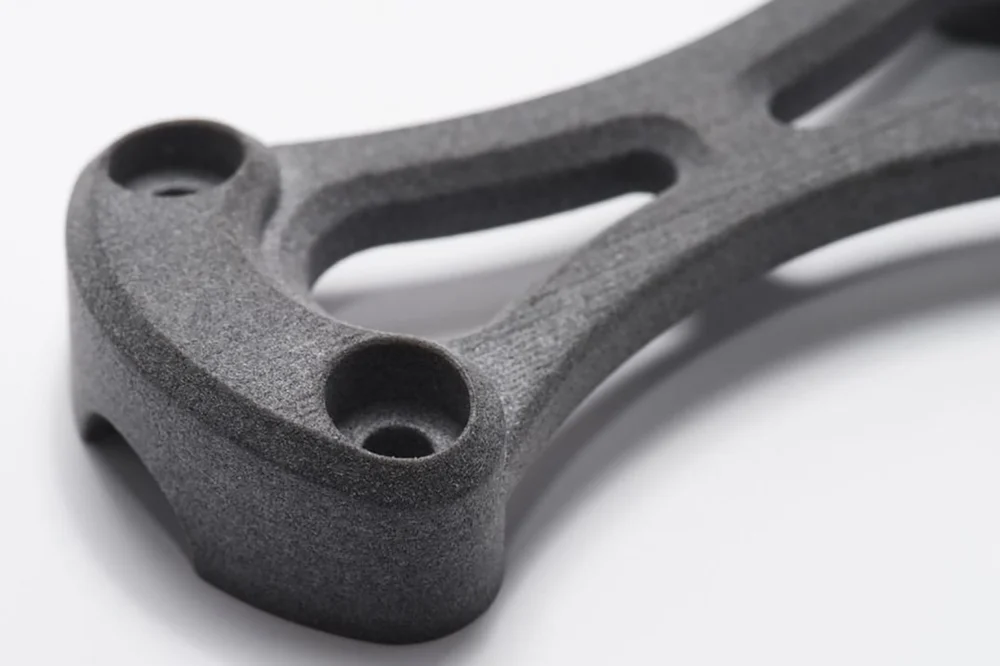

Nylon, a branch of synthetic polymers, is a tough and durable material originally seen in textiles. The technical name for the material is polyamide (PA), while the common name is “nylon” (despite some still associating it with stockings). The material stands out for its toughness and its resistance to high temperatures and impacts. It also has a very low coefficient of friction, making it the ideal 3D printing material for parts that require good tensile and mechanical strength.
The Best Nylon Filaments in 2022
Furthermore, Nylon prints have a rough surface that can be polished smooth. Plus, given its flexibility and strength, nylon is the premier choice for various applications from engineering to the arts.
Nylon 3D Printing: All You Need to Know
While you shouldn’t expect it to print as easily as PLA or PETG, printability shouldn’t be a deal-breaker, but you may need a high-temperature nozzle, as some blends will need up to 300°C to be processed.
Conductive
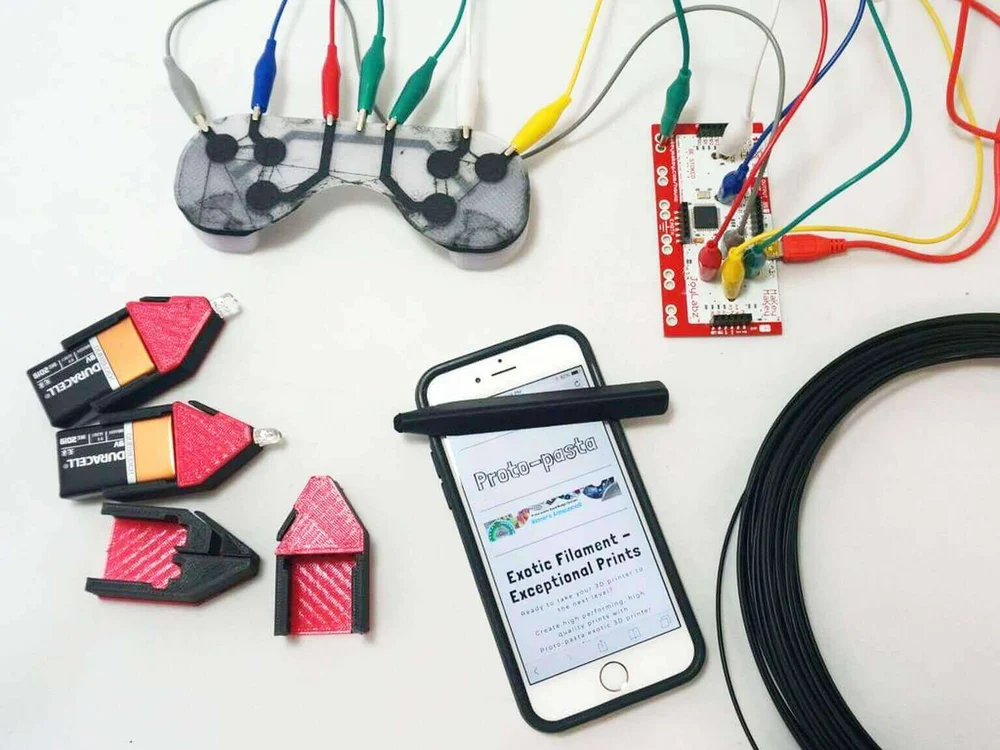
Conductive 3D printer filament does as its name implies: conduct electricity. With the addition of conductive carbon particulates, mostly graphene, to base materials such as PLA or ABS, it’s easy to actualize hobbyist projects by printing low-voltage electronic circuits. Just couple a conductive 3D printer filament with an ordinary PLA or ABS in a dual-extrusion machine.
The Best Conductive Filaments of 2022
This handy material can be used to create touch sensors in applications that require human interface devices like gaming pads and MIDI machines. Other maker projects include conductive traces in wearable electronic devices and creating interfaces between computers, Arduino boards, and other components to build elaborate DIY projects. It’s no substitute for a regular PCB, though.
Although the filament can handle electricity, we recommend having a look at the tech sheet before testing and that you don’t test its limits as burning plastic can release carcinogens.
Wood Composite

Wood 3D printer filament is typically a PLA infused with wood fiber.
Wood 3D filament is another composite, typically PLA infused with wood fiber. There are many wood-PLA 3D printer filaments available today. These include the more standard wood varieties, such as pine, birch, cedar, ebony, and willow, but the range also extends to less common types, like bamboo, cherry, coconut, cork, and olive.
The Best Wood PLA Filaments of 2022
As with other types of 3D printer filament, there is a trade-off with using wood. In this case, the aesthetic and tactile appeal come at the cost of reduced flexibility and strength. Wood-filled filament can also accelerate the degradation of your 3D printer’s nozzle, so keep that in mind before using this material.
Wood 3D Printer: How to 3D Print Wood
Be careful with the temperature at which you print wood, as too much heat can result in an almost burnt or caramelized appearance. On the other hand, the base appearance of your wooden creations can be greatly improved with a little post-print processing! You can cut it, sand it, or paint it.
HIPS
High impact polystyrene (HIPS) is a material blend of polystyrene plastic and polybutadiene rubber. The mixture of these polymers results in a material that’s both tough and flexible.
The Best HIPS Filaments of 2021
HIPS is very similar to ABS, but as the name implies, it can withstand much higher impact forces. It’s easily painted, machinable, and works with a large number of adhesives. Moreover, it’s food-safe, being declared FDA-compliant for food processing applications.
Within the 3D printing world, HIPS is mostly used as support material since it dissolves in limonene solution, eliminating the need for removal via abrasives, cutting tools, or any other such things that leave your print less than perfect. Limonene is a solution made with lemon peels, and it can be easily obtained. This solution, however, can potentially damage 3D printing materials other than ABS.
Metal Composite
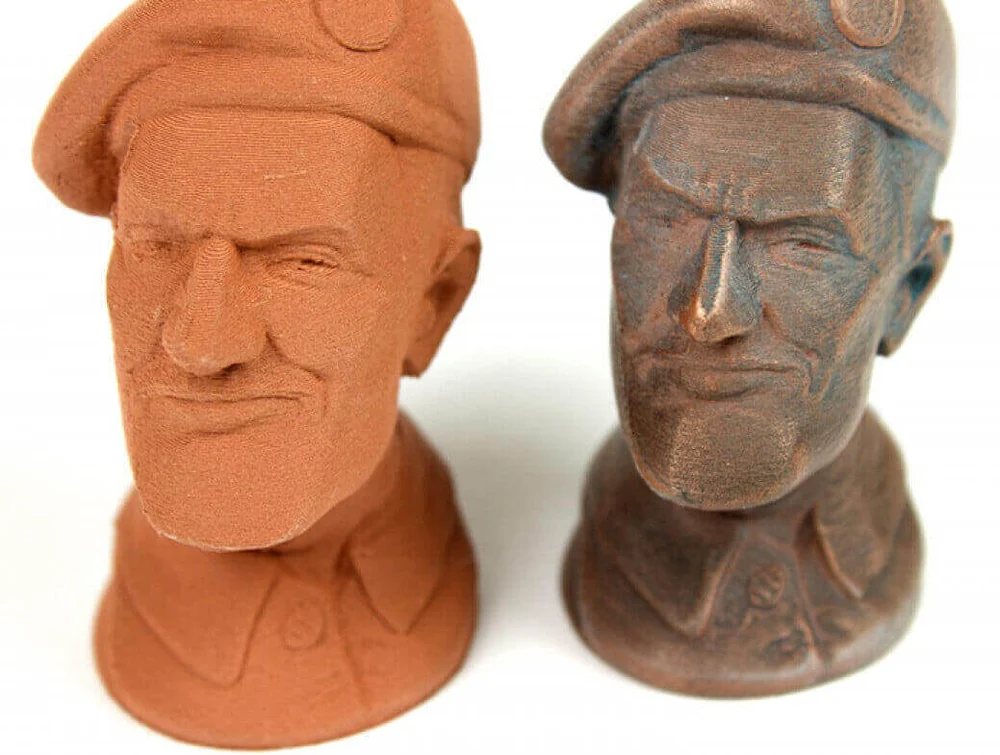

Since this is a consumer materials guide, the “metal” filament you’ll be able to use at home is actually a thermoplastic, typically PLA, that’s been mixed with low amounts of metal particles to give your 3D printed model the optical properties of metal. Even the weight is metal-like, as blends tend to be several times denser than pure plastic filament. It won’t have the actual functionality of metal, though.
3D Printer Metal Filament: The Best Brands of 2021
Metal composite prints can be highly aesthetic, especially for figurines, models, toys, and tokens. It’s great for post-processing, including sanding, polishing, weathering, or tarnishing.
It’s important to note that if you want a filament with actual metal in it, you’ll need to look for the word “composite” or “metal fill.” Beware of filaments with only “metal” in the name, as this might simply indicate a metallic color or shine, which are merely color variants. Also, when printing with metal composites, expect increased nozzle wear. Therefore, it is recommended to switch your brass nozzle to stainless steel or another hardened alloy, as brass nozzles wear out much faster from metal abrasion.
RESIN
Resins (photopolymers) are a range of 3D printable liquids that solidify when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. They’re used in a process broadly known as vat polymerization, which has many variants, including stereolithography (SLA), digital light processing (DLP), and masked stereolithography (MSLA). These essentially all work in the same way: by using the selective application of UV light to trace the shape of an object onto the surface of a photopolymer vat; the resin solidifies to form a layer of the object, which is repeated for every layer of the model until a “green” state model is left.
The Types of 3D Printing Technology in 2022
Resins are an excellent choice for functional and concept models. This material is particularly suited to producing large parts quickly while still maintaining a high degree of detail. Some resins are even strong enough to be machined after curing. Also, high-temperature resins are a cost-effective means to produce injection molds for small-scale production of prototypes.
The popularity of SLA resins stems from their superior speed and accuracy. The downside is that resin is still substantially costlier than other items in this 3D printing materials guide.
Standard Resins

If you’re using an SLA, DLP, or MSLA printer, you’re going to need some resin. Resin can feature all kinds of different properties, but if you’re looking for something straightforward, standard resin’s the way to go.
The Best Resin 3D Printers of 2022
It’s perfect for applications like creating conceptual models, functional models, prototypes, miniatures, and visual arts.
Standard resins come in a range of colors and, like all other resins, can be pretty stinky, so be sure to use them in well-ventilated areas.
Rapid Resin

Resin that cures quickly has multiple benefits beyond a quick turnaround. The shortened time frame prevents shrinking and deformation of parts still soft from the bath. Use this resin if precision is needed, such as when making tools or components, and if waiting isn’t your strong suit.
Tough Resins

Marketed under many different names, ABS-like “tough resins” boast a high level of impact resistance.
ABS-Like Resin & Tough Resin: The Best Brands of 2021
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a plastic commonly used in toy manufacturing, personal protective equipment such as hard hats and helmets, and other uses where the object will be put through stress.
Tough resin is ideal for conceptual models, functional parts, and prototypes.
Water-Washable Resins

Water washable resins take away a lot of the mess and stink-factor of standard resins because, well, they’re water washable.
The Best Water-Washable Resins of 2021
That means that instead of using alcohol to clean your parts, you use water. This is a safer, cleaner alternative to use if you’re new to resins, are looking for something that’s easier to work with, hate the smells from printing with resin, or would just like to save some money.
Flexible Resins

Sometimes, you need to be a little flexible. FDM printers use thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), a rubber-like material found on drop-proof mobile phone cases.
But if you’re in the market for a TPU-like resin, it often goes under the line name “Flex” and can be similarly used for items where high elasticity and vibration absorption are needed, such as racecar wheels.
Plant-Based Resin

Using soybeans and similar plants as the setting agents for the resin, rather than traditional sources, plant-based resins make some small steps towards making resin 3D printing less toxic and messy.
Anycubic Resin – A Simple Guide
Be sure to check out the material safety data sheet for any plant-based resin you buy – don’t always assume you can wash it or toss it out in the trash.
Castable Resins
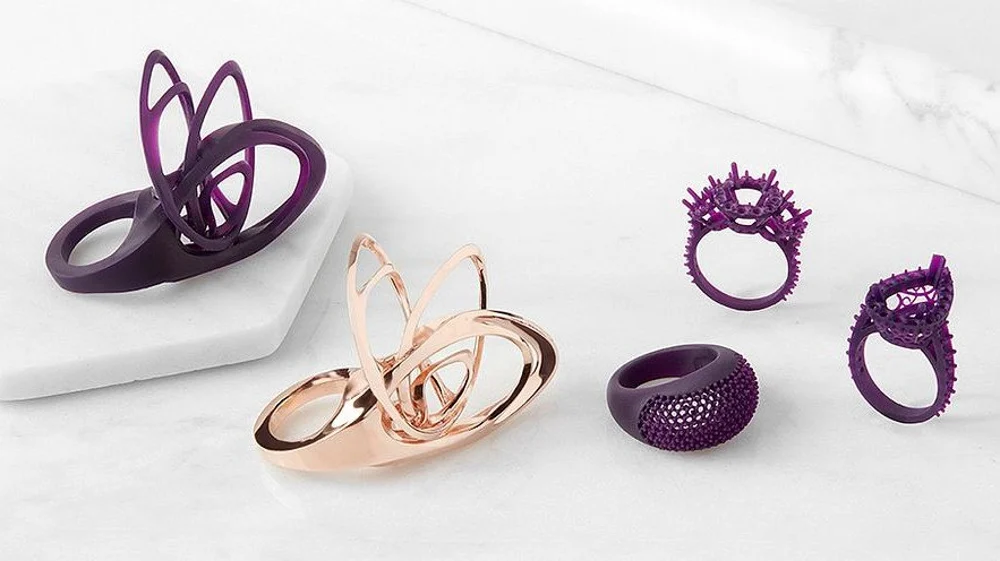

A major advantage of 3D printing is its ease and speed in prototyping, and castable resin and the lost wax method is a prime example of that. A wax model is encased in a plaster-like medium that hardens and is then heated, so the wax model melts away, leaving a mold that’s then filled with liquid precious metal.
The Best 3D Printers for Jewelry of 2021
This way, jewelers can print a model, use it to form a cement mold and burn away the resin in a furnace, allowing the liquid metal to be poured into its place. A single 3D printed ring or brooch in this castable resin can form the mold for dozens in gold, silver, or other metals.
Castable resin 3D makes it possible to create a finely detailed master wax model.
Source: https://all3dp.com/1/3d-printing-materials-guide-3d-printer-material/