At FacFox, we are passionate about 3D printing and mathematics. We believe that these two fields have a lot of synergies and applications that can inspire your creativity and innovation. Whether you are a hobbyist, a student, a teacher, or a professional, you can benefit from the interplay of 3D printing and mathematics in different ways.
In this post, we will show you some of the amazing 3D printing and mathematics projects. We hope that these examples will spark your interest and imagination, and encourage you to try your own 3D printing and mathematics projects.
Visualization
One of the main benefits of 3D printing is that it can help you visualize and explore complex mathematical concepts and objects, such as geometry, calculus, topology, fractals, and more. 3D printing can help you create physical models of these concepts and objects, which can enhance your understanding and appreciation of them.

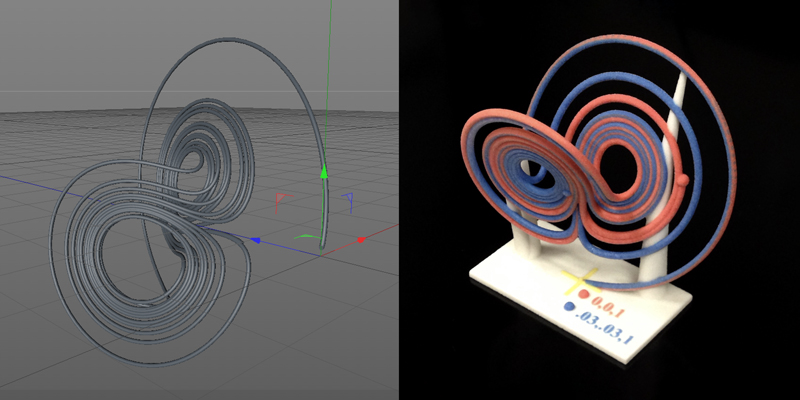
For example, here is a 3D-printed model of the Lorenz Attractor, which is a chaotic system that describes the motion of a fluid under certain conditions. The Lorenz attractor has a beautiful butterfly-like shape, which can be seen as a projection of a three-dimensional curve in the phase space. 3D printing can help you see the intricacy and symmetry of this curve, as well as its sensitivity to initial conditions.
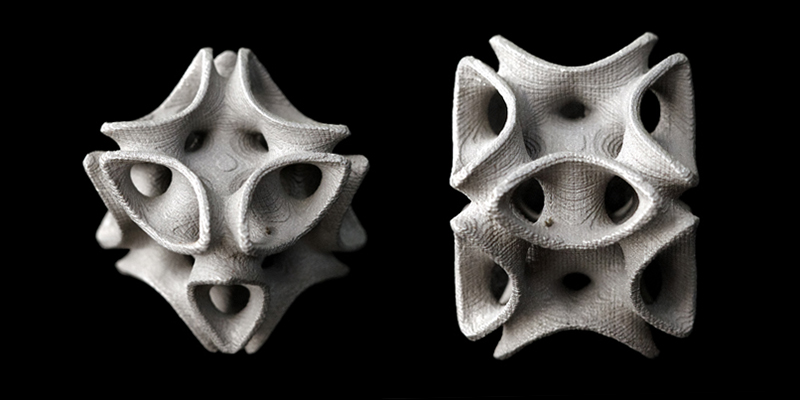
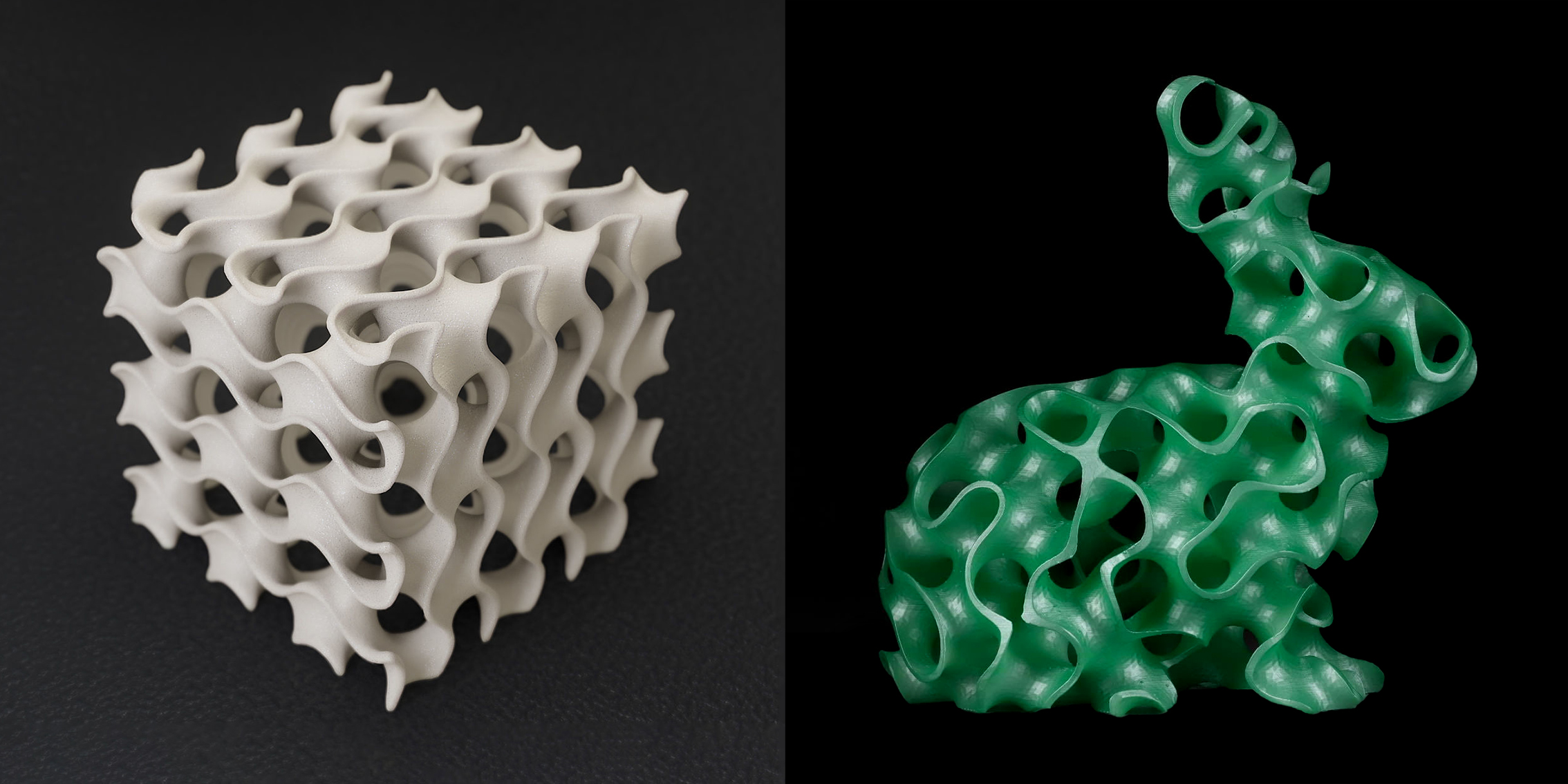
Another example of a mathematical object that can be modeled by 3D printing is a Minimal Surface, which is a surface that has zero mean curvature at every point. Minimal surfaces have fascinating shapes and properties, and can be found in nature, such as soap films and bubbles. 3D printing can help you create realistic and artistic models of minimal surfaces, such as the Costa Surface, the Enneper Surface, and the Gyroid surface.
Education
Another way that 3D printing and mathematics can be combined is by using 3D printing as a tool for teaching and learning mathematics, as well as developing mathematical and design thinking, digital skills, and mindsets. 3D printing can provide you with hands-on, creative, and engaging experiences that can enhance your motivation, curiosity, and problem-solving abilities.
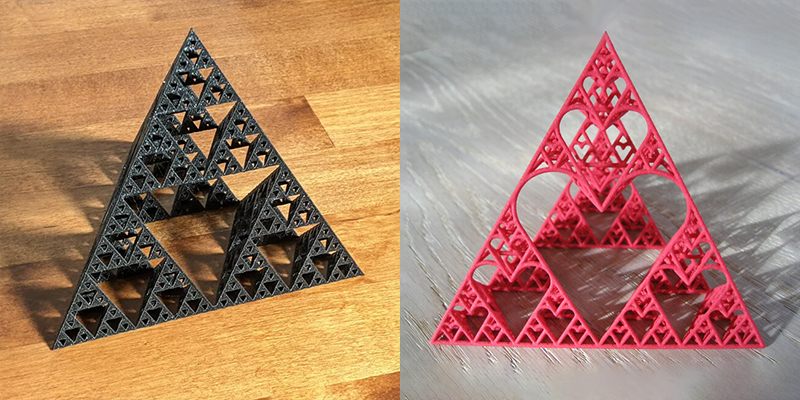
For example, below is a 3D-printed model of the Sierpinski Tetrahedron, which is a fractal that is made by repeatedly subdividing a tetrahedron into four smaller tetrahedras and removing the middle one. The Sierpinski tetrahedron has a self-similar structure, meaning that it looks the same at any scale. 3D printing can help you see and explore the geometric and algebraic properties of this fractal, such as its dimension, area, volume, and number of tetrahedra.
Another example of a 3D printing project that can help you learn mathematics is a 3D printed model of the Pythagorean theorem, which is a famous theorem that states that the square of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. 3D printing can help you visualize and prove this theorem, by creating models of the squares attached to the sides of the triangle, and showing that they can be rearranged to form a square with the same area as the square attached to the hypotenuse.
Innovation
A third way that 3D printing and mathematics can be connected is by using 3D printing as a platform for innovation and discovery in mathematics and related fields. 3D printing can enable you to create new shapes, structures, and patterns that are not possible or practical with traditional methods. 3D printing can also enable you to test and experiment with mathematical hypotheses and models in the real world.
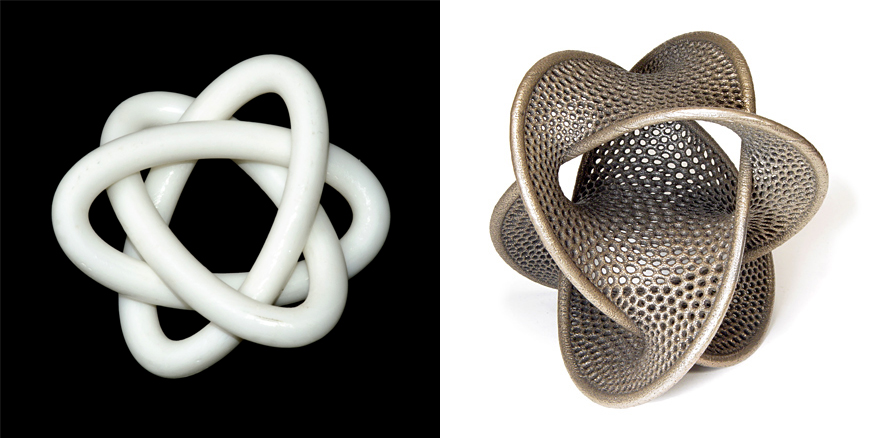
For example, one of our projects is a 3D-printed model of the Borromean rings, which are three interlocking rings that cannot be separated, but none of them are linked to each other. The Borromean rings have a rich history and symbolism, and can be found in art, architecture, religion, and science. 3D printing can help you create and manipulate different versions of the Borromean rings, such as the ones made of circles, ellipses, or knots.

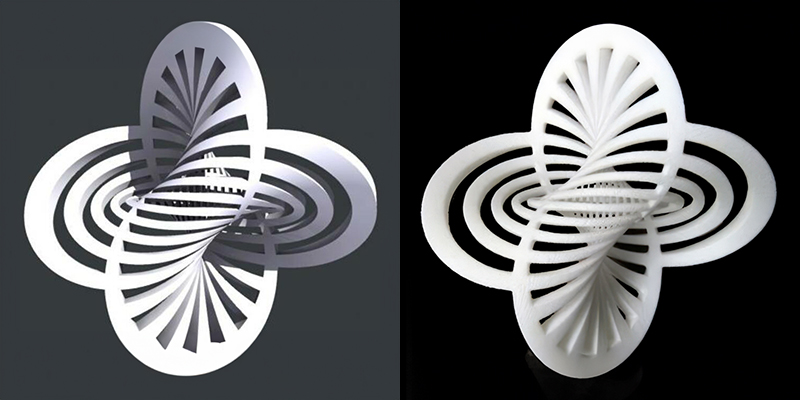
Another example of a 3D printing project that demonstrates the innovation and discovery potential of mathematics is a 3D printed model of the Hopf fibration, which is a way of mapping a four-dimensional sphere onto a three-dimensional sphere, such that every point on the latter corresponds to a circle on the former. The Hopf fibration is a remarkable and beautiful mathematical object, which has applications in physics, chemistry, biology, and computer science. 3D printing can help you create and explore different representations of the Hopf fibration, such as the ones made of tori, spheres, or links.

Conclusion
3D printing and mathematics are two fields that have a lot of potential for collaboration and integration. 3D printing can help you visualize, educate, and innovate with mathematics, and mathematics can help you design, analyze, and optimize 3D prints. 3D printing and mathematics can enrich each other and create new possibilities for creativity and innovation.
For models with overhang structures and complex geometries, we strongly suggest you try SLS 3D printing and MJF 3D printing technologies. The powder itself could serve as supporting structures, so there are no marks leaving on the models.
At FacFox, we are committed to providing you with the best 3D printing and mathematics services and products. Whether you need a 3D printed model of a mathematical concept or object, a 3D printing project for teaching or learning mathematics, or a 3D printing project that showcases the innovation and discovery potential of mathematics, we can help you achieve your goals.
Contact us today via info@facfox.com to get started on your 3D printing and mathematics journey.